|
Monin–Obukhov Similarity Theory
Monin–Obukhov (M–O) similarity theory describes the non-dimensionalized mean flow and mean temperature in the surface layer under non-neutral conditions as a function of the dimensionless height parameter, named after Russian scientists A. S. Monin and A. M. Obukhov. Similarity theory is an empirical method that describes universal relationships between non-dimensionalized variables of fluids based on the Buckingham π theorem. Similarity theory is extensively used in boundary layer meteorology since relations in turbulent processes are not always resolvable from first principles. An idealized vertical profile of the mean flow for a neutral boundary layer is the logarithmic wind profile derived from Prandtl's mixing length theory, which states that the horizontal component of mean flow is proportional to the logarithm of height. M–O similarity theory further generalizes the mixing length theory in non-neutral conditions by using so-called "universal functions" of dimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Layer
The surface layer is the layer of a turbulent fluid most affected by interaction with a solid surface or the surface separating a gas and a liquid where the characteristics of the turbulence depend on distance from the interface. Surface layers are characterized by large normal gradients of tangential velocity and large concentration gradients of any substances (temperature, moisture, sediments et cetera) transported to or from the interface. The term boundary layer is used in meteorology and in physical oceanography. The atmospheric surface layer is the lowest part of the atmospheric boundary layer (typically the bottom 10% where the log wind profile is valid). The ocean has two surface layers: the benthic, found immediately above the sea floor and the marine surface layer, at the air-sea interface. Mathematical formulation A simple model of the surface layer can be derived by first examining the turbulent momentum flux through a surface. Using Reynolds decomposition to express ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
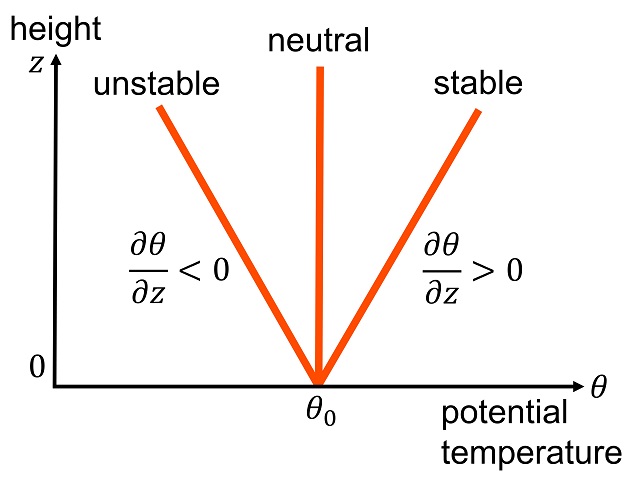
Potential Temperature
The potential temperature of a parcel of fluid at pressure P is the temperature that the parcel would attain if adiabatically brought to a standard reference pressure P_, usually . The potential temperature is denoted \theta and, for a gas well-approximated as ideal, is given by : \theta = T \left(\frac\right)^, where T is the current absolute temperature (in K) of the parcel, R is the gas constant of air, and c_p is the specific heat capacity at a constant pressure. R/c_p = 0.286 for air (meteorology). The reference point for potential temperature in the ocean is usually at the ocean's surface which has a water pressure of 0 dbar. The potential temperature in the ocean doesn't account for the varying heat capacities of seawater, therefore it is not a conservative measure of heat content. Graphical representation of potential temperature will always be less than the actual temperature line in a temperature vs depth graph. Contexts The concept of potential temperature applies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Log Wind Profile
The log wind profile is a semi-empirical relationship commonly used to describe the vertical distribution of horizontal mean wind speeds within the lowest portion of the planetary boundary layer. The relationship is well described in the literature. The logarithmic profile of wind speeds is generally limited to the lowest 100 m of the atmosphere (i.e., the surface layer of the atmospheric boundary layer). The rest of the atmosphere is composed of the remaining part of the planetary boundary layer (up to around 1000 m) and the troposphere or free atmosphere. In the free atmosphere, geostrophic wind relationships should be used. Definition The equation to estimate the mean wind speed (u_z) at height z (meters) above the ground is: where u_* is the friction velocity (m s−1), \kappa is the Von Kármán constant (~0.41), d is the zero plane displacement (in metres), z_0 is the surface roughness (in meters), and \psi is a stability term where L is the Obukhov length from Monin- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Layer
The surface layer is the layer of a turbulent fluid most affected by interaction with a solid surface or the surface separating a gas and a liquid where the characteristics of the turbulence depend on distance from the interface. Surface layers are characterized by large normal gradients of tangential velocity and large concentration gradients of any substances (temperature, moisture, sediments et cetera) transported to or from the interface. The term boundary layer is used in meteorology and in physical oceanography. The atmospheric surface layer is the lowest part of the atmospheric boundary layer (typically the bottom 10% where the log wind profile is valid). The ocean has two surface layers: the benthic, found immediately above the sea floor and the marine surface layer, at the air-sea interface. Mathematical formulation A simple model of the surface layer can be derived by first examining the turbulent momentum flux through a surface. Using Reynolds decomposition to express ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissipation
In thermodynamics, dissipation is the result of an irreversible process that takes place in homogeneous thermodynamic systems. In a dissipative process, energy (internal, bulk flow kinetic, or system potential) transforms from an initial form to a final form, where the capacity of the final form to do thermodynamic work is less than that of the initial form. For example, heat transfer is dissipative because it is a transfer of internal energy from a hotter body to a colder one. Following the second law of thermodynamics, the entropy varies with temperature (reduces the capacity of the combination of the two bodies to do work), but never decreases in an isolated system. These processes produce entropy at a certain rate. The entropy production rate times ambient temperature gives the dissipated power. Important examples of irreversible processes are: heat flow through a thermal resistance, fluid flow through a flow resistance, diffusion (mixing), chemical reactions, and electric cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Eddy Simulation
Large eddy simulation (LES) is a mathematical model for turbulence used in computational fluid dynamics. It was initially proposed in 1963 by Joseph Smagorinsky to simulate atmospheric air currents, and first explored by Deardorff (1970). LES is currently applied in a wide variety of engineering applications, including combustion, acoustics, and simulations of the atmospheric boundary layer. The simulation of turbulent flows by numerically solving the Navier–Stokes equations requires resolving a very wide range of time and length scales, all of which affect the flow field. Such a resolution can be achieved with direct numerical simulation (DNS), but DNS is computationally expensive, and its cost prohibits simulation of practical engineering systems with complex geometry or flow configurations, such as turbulent jets, pumps, vehicles, and landing gear. The principal idea behind LES is to reduce the computational cost by ignoring the smallest length scales, which are the most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice County P5310407
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly '' Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and ''Porteresia'', both wild and domesticated, although the term may also be used for primitive or uncultivated varieties of '' Oryza''. As a cereal grain, domesticated rice is the most widely consumed staple food for over half of the world's human population,Abstract, "Rice feeds more than half the world's population." especially in Asia and Africa. It is the agricultural commodity with the third-highest worldwide production, after sugarcane and maize. Since sizable portions of sugarcane and maize crops are used for purposes other than human consumption, rice is the most important food crop with regard to human nutrition and caloric intake, providing more than one-fifth of the calories consumed worldwide by humans. There are many varieties of rice and culinary preferences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |