|
Monica Lam
Monica Sin-Ling Lam is an American computer scientist. She is a professor in the Computer Science Department at Stanford University. Professional biography Monica Lam received a B.Sc. from University of British Columbia in 1980 and a Ph.D. in Computer Science from Carnegie Mellon University in 1987. Lam joined the faculty of Computer Science at Stanford University in 1988. She has contributed to the research of a wide range of computer systems topics including compilers, program analysis, operating systems, security, computer architecture, and high-performance computing. More recently, she is working in natural language processing, and Virtual assistant, virtual assistants with an emphasis on privacy protection. She is the faculty director of the Open Virtual Assistant Lab, which organized the first workshop for the World Wide Voice Web. The lab developed the open-source Almond voice assistant, which is sponsored by the National Science Foundation. Almond received Popular Scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popular Science
''Popular Science'' (also known as ''PopSci'') is an American digital magazine carrying popular science content, which refers to articles for the general reader on science and technology subjects. ''Popular Science'' has won over 58 awards, including the American Society of Magazine Editors awards for its journalistic excellence in 2003 (for General Excellence), 2004 (for Best Magazine Section), and 2019 (for Single-Topic Issue). With roots beginning in 1872, ''Popular Science'' has been translated into over 30 languages and is distributed to at least 45 countries. Early history ''The Popular Science Monthly'', as the publication was originally called, was founded in May 1872 by Edward L. Youmans to disseminate scientific knowledge to the educated layman. Youmans had previously worked as an editor for the weekly ''Appleton's Journal'' and persuaded them to publish his new journal. Early issues were mostly reprints of English periodicals. The journal became an outlet for writings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Engineering
The National Academy of Engineering (NAE) is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Engineering is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), the National Academy of Medicine, and the National Research Council (now the program units of NASEM). The NAE operates engineering programs aimed at meeting national needs, encourages education and research, and recognizes the superior achievements of engineers. New members are annually elected by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. The NAE is autonomous in its administration and in the selection of its members, sharing with the rest of the National Academies the role of advising the federal government. History The National Academy of Sciences was created by an Act of Incorporation dated March 3, 1863, which was signed by then President of the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association For Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membership group, claiming nearly 110,000 student and professional members . Its headquarters are in New York City. The ACM is an umbrella organization for academic and scholarly interests in computer science ( informatics). Its motto is "Advancing Computing as a Science & Profession". History In 1947, a notice was sent to various people: On January 10, 1947, at the Symposium on Large-Scale Digital Calculating Machinery at the Harvard computation Laboratory, Professor Samuel H. Caldwell of Massachusetts Institute of Technology spoke of the need for an association of those interested in computing machinery, and of the need for communication between them. ..After making some inquiries during May and June, we believe there is ample interest to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asus Zen UI
ASUS ZenUI is a front-end touch interface developed by ASUS with partners, featuring a full touch user interface. ZenUI is used by Asus for their Android phones and tablets, and is not available for licensing by external parties. ZenUI also comes with Asus-made apps preloaded like ZenLink (PC Link, Share Link, Party Link & Remote Link). History Before ZenUI, Asus made a front-end interface for Android phones and tablets called ASUS WaveShare UI. The ZenUI made its debut in Asus Zenfone Series, Asus MemoPad 7 (ME176C) and Asus Padfone Mini (2014). WaveShare UI ASUS WaveShare UI was a front-end touch interface developed by ASUS & partners. WaveShare UI was used by Asus for Android smartphones and tablet computers and was not available for licensing by external parties. WaveShare UI was originally released on the Asus PadFone hybrid smartphone/tablet, and was later used on other Asus products. The last gadget to use the WaveShare UI was the ASUS MeMO Pad HD 7. Gadgets that used A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moka5
Moka5 (also called MokaFive) was a desktop virtualization company founded in 2005. It ceased operation in 2015 after an apparent bankruptcy. The company's software began as a lab experiment at Stanford University and founders include professor Monica S. Lam and John Whaley. It was based out of Redwood City, California and its final CEO was Dave Robbins. Moka5 provided end-to-end desktop management solutions including client virtualization, central management, and layering solutions. Using the Moka5 Suite, users can run a virtual desktop from consumer devices including tablet computers smartphones. Moka5 offered secure cloud storage for virtual desktops and lets users access multiple computing platforms and operating systems across devices. See also *desktop virtualization *virtual desktop *enterprise software Enterprise software, also known as enterprise application software (EAS), is computer software used to satisfy the needs of an organization rather than individual users ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SQL Injection
In computing, SQL injection is a code injection technique used to attack data-driven applications, in which malicious SQL statements are inserted into an entry field for execution (e.g. to dump the database contents to the attacker). SQL injection must exploit a security vulnerability in an application's software, for example, when user input is either incorrectly filtered for string literal escape characters embedded in SQL statements or user input is not strongly typed and unexpectedly executed. SQL injection is mostly known as an attack vector for websites but can be used to attack any type of SQL database. SQL injection attacks allow attackers to spoof identity, tamper with existing data, cause repudiation issues such as voiding transactions or changing balances, allow the complete disclosure of all data on the system, destroy the data or make it otherwise unavailable, and become administrators of the database server. In a 2012 study, it was observed that the average w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datalog
Datalog is a declarative logic programming language. While it is syntactically a subset of Prolog, Datalog generally uses a bottom-up rather than top-down evaluation model. This difference yields significantly different behavior and properties from Prolog. It is often used as a query language for deductive databases. In recent years, Datalog has found new application in data integration, information extraction, networking, program analysis, security, cloud computing and machine learning. Its origins date back to the beginning of logic programming, but it became prominent as a separate area around 1977 when Hervé Gallaire and Jack Minker organized a workshop on logic and databases. David Maier is credited with coining the term Datalog. Features, limitations and extensions Unlike in Prolog, statements of a Datalog program can be stated in any order. Furthermore, Datalog queries on finite sets are guaranteed to terminate, so Datalog does not have Prolog's cut operator. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Security
Application security (short AppSec) includes all tasks that introduce a secure software development life cycle to development teams. Its final goal is to improve security practices and, through that, to find, fix and preferably prevent security issues within applications. It encompasses the whole application life cycle from requirements analysis, design, implementation, verification as well as maintenance. Approaches Different approaches will find different subsets of the security vulnerabilities lurking in an application and are most effective at different times in the software lifecycle. They each represent different tradeoffs of time, effort, cost and vulnerabilities found. * Design review. Before code is written the application's architecture and design can be reviewed for security problems. A common technique in this phase is the creation of a threat model. * Whitebox security review, or code review. This is a security engineer deeply understanding the application through ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensilica
Tensilica was a company based in Silicon Valley in the semiconductor intellectual property core business. It is now a part of Cadence Design Systems. Tensilica is known for its customizable Xtensa microprocessor core. Other products include: HiFi audio/voice DSPs (digital signal processors) with a software library of over 225 codecs from Cadence and over 100 software partners; Vision DSPs that handle complex algorithms in imaging, video, computer vision, and neural networks; and the ConnX family of baseband DSPs ranging from the dual- MAC ConnX D2 to the 64-MAC ConnX BBE64EP. Tensilica was founded in 1997 by Chris Rowen (one of the founders of MIPS Technologies). It employed Earl Killian, who contributed to the MIPS architecture, as director of architecture. On March 11, 2013, Cadence Design Systems announced its intent to buy Tensilica for approximately $380 million in cash. Cadence completed the acquisition in April 2013, with a cash outlay at closing of approximately $326 mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
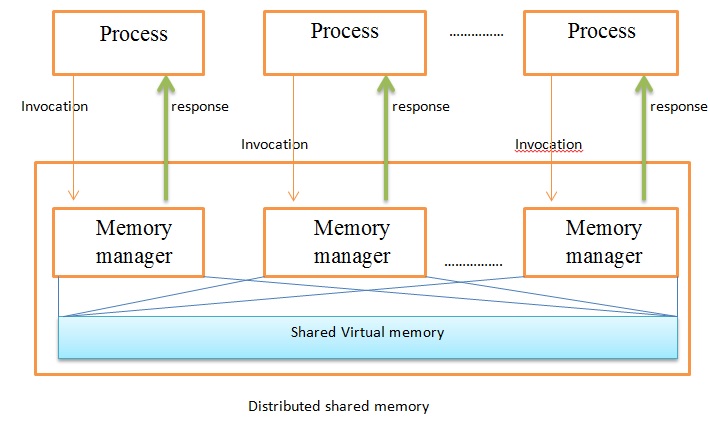
Distributed Shared Memory
In computer science, distributed shared memory (DSM) is a form of memory architecture where physically separated memories can be addressed as a single shared address space. The term "shared" does not mean that there is a single centralized memory, but that the address space is shared—i.e., the same physical address on two processors refers to the same location in memory. Distributed global address space (DGAS), is a similar term for a wide class of software and hardware implementations, in which each node of a cluster has access to shared memory in addition to each node's private (i.e., not shared) memory. Overview A distributed-memory system, often called a multicomputer, consists of multiple independent processing nodes with local memory modules which is connected by a general interconnection network. Software DSM systems can be implemented in an operating system, or as a programming library and can be thought of as extensions of the underlying virtual memory architecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford DASH
Stanford DASH was a cache coherent multiprocessor developed in the late 1980s by a group led by Anoop Gupta, John L. Hennessy, Mark Horowitz, and Monica S. Lam at Stanford University. It was based on adding a pair of directory boards designed at Stanford to up to 16 SGI IRIS 4D Power Series machines and then cabling the systems in a mesh topology using a Stanford-modified version of the Torus Routing Chip. The boards designed at Stanford implemented a directory-based cache coherence protocol allowing Stanford DASH to support distributed shared memory for up to 64 processors. Stanford DASH was also notable for both supporting and helping to formalize weak memory consistency models, including release consistency. Because Stanford DASH was the first operational machine to include scalable cache coherence, it influenced subsequent computer science research as well as the commercially available SGI Origin 2000. Stanford DASH is included in the 25th anniversary retrospective of selected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |