|
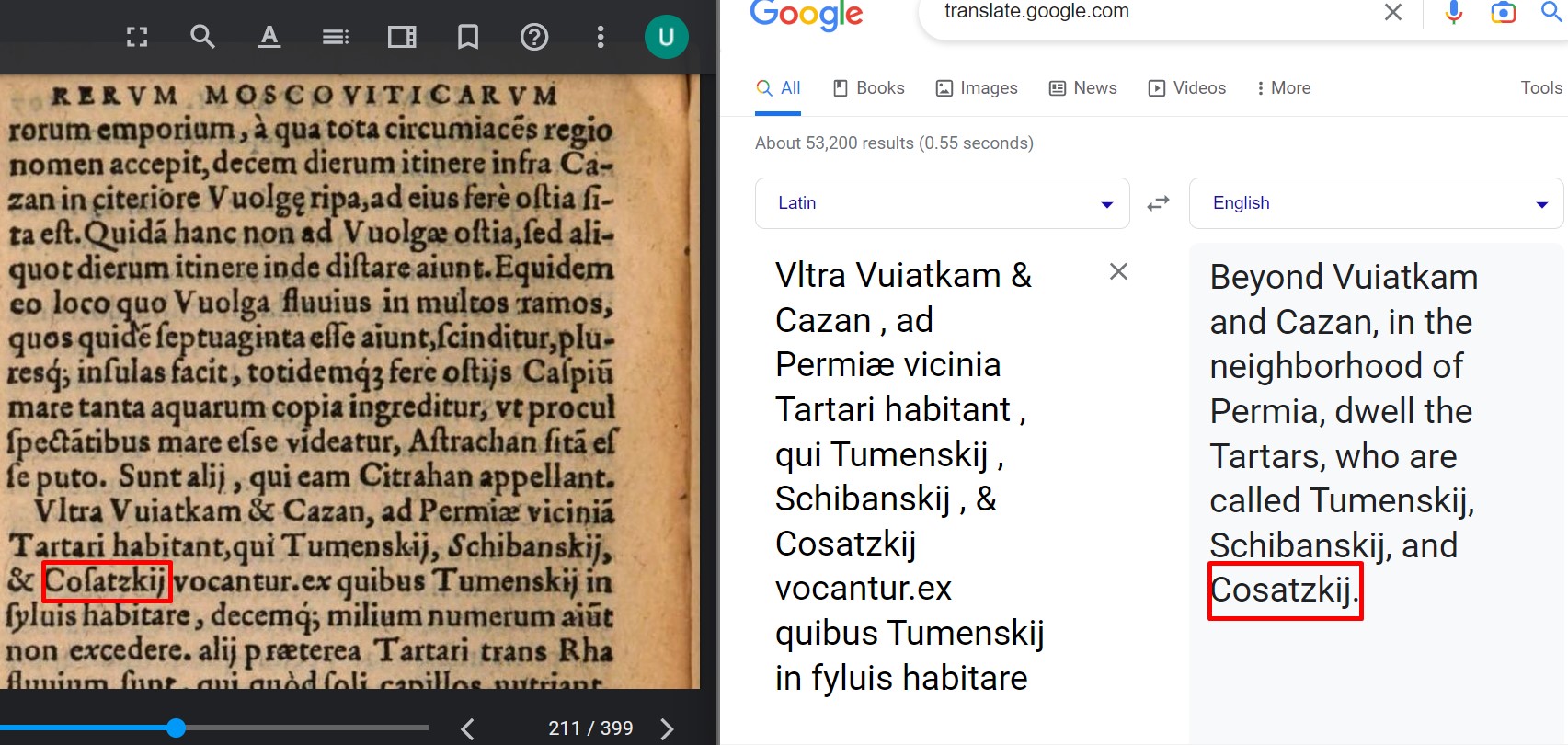
Mongolian Kazakhs
The Kazakhs (also spelled Qazaqs; Kazakh: , , , , , ; the English name is transliterated from Russian; russian: казахи) are a Turkic-speaking ethnic group native to northern parts of Central Asia, chiefly Kazakhstan, but also parts of northern Uzbekistan and the border regions of Russia, as well as Northwestern China (specifically Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture) and Mongolia (Bayan-Ölgii Province). The Kazakhs are descendants of the ancient Turkic Kipchak tribes and the medieval Mongolic tribes, and generally classified as Turco-Mongol cultural group. Kazakh identity is of medieval origin and was strongly shaped by the foundation of the Kazakh Khanate between 1456 and 1465, when following disintegration of the Golden Horde, several tribes under the rule of the sultans Janibek and Kerei departed from the Khanate of Abu'l-Khayr Khan in hopes of forming a powerful khanate of their own. ''Kazakh'' is used to refer to ethnic Kazakhs, while the term ''Kazakhstani'' u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Costume
A folk costume (also regional costume, national costume, traditional garment, or traditional regalia) expresses an identity through costume, which is usually associated with a geographic area or a period of time in history. It can also indicate social, marital or religious status. If the costume is used to represent the culture or identity of a specific ethnic group, it is usually known as ethnic costume (also ethnic dress, ethnic wear, ethnic clothing, traditional ethnic wear or traditional ethnic garment). Such costumes often come in two forms: one for everyday occasions, the other for traditional festivals and formal wear. Following the rise of romantic nationalism, the pre-industrial peasantry of Europe came to serve as models for all that appeared genuine and desirable. Their dresses are crystallized into so-called "typical" forms, and enthusiasts adopted that attire as part of their symbolism. In areas where Western dress codes have become usual, traditional garments ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture
Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture ( kk, Іле Қазақ автономиялық облысы) (also as Yili) is an autonomous prefecture for Kazakh people in Northern Xinjiang, China, one of five autonomous prefectures in Xinjiang. Yining City is its capital. It is bordered by Mongolia, Russian Federation and Republic of Kazakhstan on the northeast to southwest, with a boundary line of 2,019 kilometers. Including Khorgas, Bakhty and Jeminay, there are 9 ports of entry at the national level. With the unique location advantage, Ili has been an important commercial hub and international channel of opening up to the west. The autonomous prefecture covers an area of 268,591 square kilometers, accounting for 16.18% of Xinjiang. Direct-administered regions () within the prefecture cover 56,622 square kilometers (21.08% of total area) and have a population of 4,930,600 (or 63.95% of registered population). There are about 3.6 million Kazakhs in Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture. The Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Turkic Language
Proto-Turkic is the linguistic reconstruction of the common ancestor of the Turkic languages that was spoken by the Proto-Turks before their divergence into the various Turkic peoples. Proto-Turkic separated into Oghur (western) and Common Turkic (eastern) branches. One estimate postulates Proto-Turkic to have been spoken 2,500 years ago in East Asia. The oldest records of a Turkic language, the Old Turkic Orkhon inscriptions of the 7th century Göktürk khaganate, already shows characteristics of Eastern Common Turkic and reconstruction of Proto-Turkic must rely on comparisons of Old Turkic with early sources of the Western Common Turkic branches, such as Oghuz and Kypchak, as well as the Western Oghur proper (Bulgar, Chuvash, Khazar). Because early attestation of these non-easternmost languages is much more sparse, reconstruction of Proto-Turkic still rests fundamentally on the easternmost Old Turkic of the Göktürks. Phonology Consonants The consonant system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the Turkic family. There is a high degree of mutual intelligibility, upon mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brill Publishers
Brill Academic Publishers (known as E. J. Brill, Koninklijke Brill, Brill ()) is a Dutch international academic publisher founded in 1683 in Leiden, Netherlands. With offices in Leiden, Boston, Paderborn and Singapore, Brill today publishes 275 journals and around 1200 new books and reference works each year all of which are "subject to external, single or double-blind peer review." In addition, Brill provides of primary source materials online and on microform for researchers in the humanities and social sciences. Areas of publication Brill publishes in the following subject areas: * Humanities: :* African Studies :* American Studies :* Ancient Near East and Egypt Studies :* Archaeology, Art & Architecture :* Asian Studies (Hotei Publishing and Global Oriental imprints) :* Classical Studies :* Education :* Jewish Studies :* Literature and Cultural Studies (under the Brill-Rodopi imprint) :* Media Studies :* Middle East and Islamic Studies :* Philosophy :* Religious Studies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu'l-Khayr Khan
Abu'l-Khayr Khan ( uz, Abulxayirxon) (1412–1468) was a Khan of the Uzbek Khanate which united the nomadic Central Asian tribes.DeWeese, Devin A. (1994) ''Islamization and native religion in the Golden Horde: Baba Tükles and conversion to Islam in historical and epic tradition'' Pennsylvania State University Press, University Park, Pa., p. 345 He created one of the largest and most powerful Turkic states during the period of 15th century. The Uzbek Khanate weakened in the decades following his death in 1468. He was succeeded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerei Khan
Kerei Khan (, ) ( 1424, White Horde - 1473/ 4, Kazakh Khanate) was a co-founder and the first Khan of the Kazakh Khanate from c. 1465 to 1473. History There are currently two versions how the first dynasty of the Kazakh khans originated. According to one of them is that they were from the House of Orda-Jedzhena. On the other, they were descendants of the thirteenth son of Jochi-Khan-Toucas-Timur. In the late 1450s, part of the nomadic population, headed by Janibek and Kerei, separated themselves from the rule of Uzbek Khan Abu'l-Khayr. They migrated to Moghulistan and settled in the valleys of the Chu and Talas rivers. Khan of Moghulistan united with them, offering them support against their opponents. Around 200,000 nomads joined Janibek Khan and Kerei Khan's movement, which had had a huge power and influence that it sparked fear in Abu'l-Khayr. As a response he undertook a military campaign in Moghulistan in 1468, but died suddenly on his way. After the death of Abu'l-Khayr, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janibek Khan
Abū Saʿīd Janibek Bahadur Khan bin Barak Sultan (, , ), otherwise known by his shortened regal name Janibek Khan, was a co-founder and second Khan of the Kazakh Khanate from 1473 to 1480. He was a son of Barak, Khan of the Golden Horde from 1422 to 1427. Barak Khan's father was Koirichak, grandson of Urus Khan, a direct descendant of Genghis Khan. Genghis Khan is Jochi Khan's father, Jochi Khan's son Tukai-Timur, Tukai-Timur's son Uz-Timur, Uz-Timur's son Khodja, Khodja's son Badakun-Uglan, Badakun-Uglan's son Urus Khan, Urus Khan's son Koirchak-khan, Koirchak-khan's son Barak Khan, and Barak Khan is Zhanibek/Janibek's father. From his wife Jahan Begum Khanum, Janibek had nine sons: Qasim (who became his successor), Mahmud, Iranji, Ithik, Janysh, Qanabar, Tenish, Usuk, and Juak. She also bore him two daughters, Suyimbike and Amanbike. Janibek Khan was a co-leader of a new Kazakh Khanate, following a successful rebellion against the Uzbek Khan Abu'l-Khayr Khan in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmentation of the Mongol Empire after 1259 it became a functionally separate khanate. It is also known as the Kipchak Khanate or as the Ulus of Jochi, and replaced the earlier less organized Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the death of Batu Khan (the founder of the Golden Horde) in 1255, his dynasty flourished for a full century, until 1359, though the intrigues of Nogai Khan, Nogai instigated a partial civil war in the late 1290s. The Horde's military power peaked during the reign of Uzbeg Khan (1312–1341), who adopted Islam. The territory of the Golden Horde at its peak extended from Siberia and Central Asia to parts of Eastern Europe from the Ural Mountains, Urals to the Danube in the west, and from the Black Sea to the Caspian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakh Khanate
The Kazakh Khanate ( kk, Қазақ Хандығы, , ), in eastern sources known as Ulus of the Kazakhs, Ulus of Jochi, Yurt of Urus, was a Kazakh state in Central Asia, successor of the Golden Horde existing from the 15th to 19th century, centered on the eastern parts of the '' Desht-i Qipchaq''. The khanate was established by Janibek Khan and Kerei Khan in 1465. Both khans came from Turco-Mongol clan of Tore which traces its lineage to Genghis Khan through dynasty of Jochids. The Tore clan continued to rule the khanate until its fall to the Russian Empire. From 16th to 17th century, the Kazakh Khanate ruled and expanded its territories to eastern Cumania (modern-day West Kazakhstan), to most of Uzbekistan, Karakalpakstan and the Syr Darya river with military confrontation as far as Astrakhan and Khorasan Province, which are now in Russia and Iran, respectively. The Khanate was later weakened by a series of Oirat and Dzungar invasions. These resulted in a decline and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turco-Mongol Tradition
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century, among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these Khanates eventually assimilated into the Turkic populations that they conquered and ruled over, thus becoming known as Turco-Mongols. These elites gradually adopted Islam (from previous religions such as Tengrism) as well as Turkic languages, while retaining Mongol political and legal institutions. The Turco-Mongols founded many Islamic successor states after the collapse of the Mongol Khanates, such as the Kazakh Khanate and Tatar Khanates that succeeded the Golden Horde (e.g., Khanate of Crimea, Astrakhan Khanate, Kazan Khanate) and the Timurid Empire, which succeeded the Chagatai Khanate in Central Asia. Babur (1483–1530), a Turco-Mongol prince and a great-great-great-grandson of Timur, founded the Mughal Empire, which ruled almost all of the Indian sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |