|
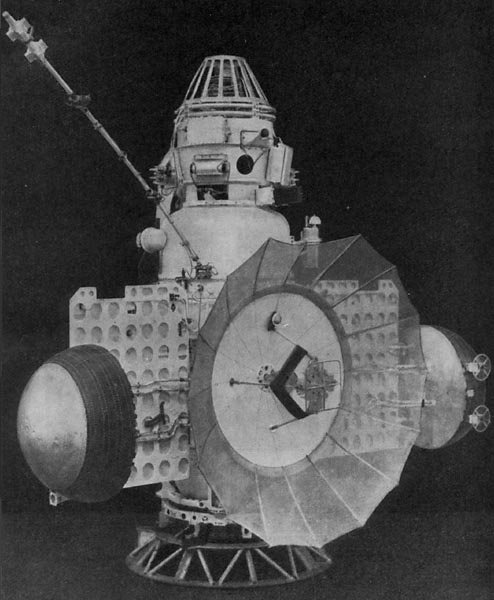
Molniya-1 No.2
Molniya-1 No.2, a Molniya (satellite), Molniya-1 satellite, was the first Soviet Union, Soviet communications satellite to be launched. However, it failed to achieve orbit due to a malfunction of the rocket which was carrying it. It was intended to operate in a Molniya orbit, from where it would be used to demonstrate communications between parts of the Soviet Union, USSR. Launch Molniya-1 No.2 was launched at 04:00 GMT on 4 June 1964, atop a Molniya (rocket), Molniya 8K78 launch vehicle, flying from Gagarin's Start, Site 1 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. A motor circuit in the Servomechanism, servo controlling the core stage throttle failed 104 seconds into the flight, resulting in the throttle becoming jammed closed and the fuel supply to the engines being stopped. Prior to the release of information about its mission, NASA had incorrectly identified the launch of Molniya-1 No.2 as a failed attempt to launch a Zond program, Zond spacecraft on a Circumlunar trajectory, circumlu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumlunar Trajectory
In orbital mechanics, a circumlunar trajectory, trans-lunar trajectory or lunar free return is a type of free return trajectory which takes a spacecraft from Earth, around the far side of the Moon, and back to Earth using only gravity once the initial trajectory is set. History The first spacecraft to fly a circumlunar trajectory was Luna 3. Circumlunar trajectories were also used by Apollo missions prior to lunar orbit insertion, to provide a free return to Earth in the event of a propulsion system malfunction on the way to the Moon. This was used on Apollo 13, when an oxygen tank rupture necessitated return to Earth without firing the Service Module engine, although a number of course corrections using the Lunar Module descent engine were used to refine the trajectory. A number of proposed, but not flown, crewed missions have been planned to intentionally conduct circumlunar flybys, including the Soviet Soyuz 7K-L1 or Zond programme, and several US proposals, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond Program
Zond (russian: Зонд, lit=probe) was the name given to two distinct series of Soviet robotic spacecraft launched between 1964 and 1970. The first series, based on the 3MV planetary probe, was intended to gather information about nearby planets. The second series of test spacecraft was intended as a precursor to remote-controlled robotic circumlunar loop flights, using a stripped-down variant of Soyuz spacecraft, consisting of the service and descent modules, but lacking the orbital module. Two tortoises and other lifeforms aboard Zond 5 were the first terrestrial organisms to travel around the Moon and return to Earth. Missions based on the 3MV planetary probe The first three missions were based on the model 3MV planetary probe, intended to explore Venus and Mars. After two failures, Zond 3 was sent on a test mission, becoming the second spacecraft to photograph the far side of the Moon (after Luna 3). It then continued out to the orbit of Mars in order to test telem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Servomechanism
In control engineering a servomechanism, usually shortened to servo, is an automatic device that uses error-sensing negative feedback to correct the action of a mechanism. On displacement-controlled applications, it usually includes a built-in encoder or other position feedback mechanism to ensure the output is achieving the desired effect. The term correctly applies only to systems where the feedback or error-correction signals help control mechanical position, speed, attitude or any other measurable variables. For example, an automotive power window control is not a servomechanism, as there is no automatic feedback that controls position—the operator does this by observation. By contrast a car's cruise control uses closed-loop feedback, which classifies it as a servomechanism. Applications Position control A common type of servo provides ''position control''. Commonly, servos are electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic. They operate on the principle of negative feedback, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, launch pads, supported by a missile launch control center, launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to large operating costs. An orbital spaceflight, orbital launch vehicle must lift its payload at least to the boundary of space, approximately and accelerate it to a horizontal velocity of at least . Suborbital spaceflight, Suborbital vehicles launch their payloads to lower velocity or are launched at elevation angles greater than horizontal. Practical orbital launch vehicles are multistage rockets which use chemical propellants such as Solid-propellant rocket, solid fuel, liquid hydrogen, kerosene, liquid oxygen, or Hypergolic propellants. Launch vehicles are cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molniya (satellite)
The Molniya ( rus, Молния, p=ˈmolnʲɪjə, a=Ru-молния.ogg, "Lightning") series satellites were military and communications satellites launched by the Soviet Union from 1965 to 2004. These satellites used highly eccentric elliptical orbits known as Molniya orbits, which have a long dwell time over high latitudes. They are suited for communications purposes in polar regions, in the same way that geostationary satellites are used for equatorial regions. There were 164 Molniya satellites launched, all in Molniya orbits with the exception of Molniya 1S which was launched into geostationary orbit for testing purposes. History In the early 1960s, when Europe and America were establishing geostationary communication satellites, the Russians found these orbits unsuitable. They were limited in the amount of rocket power available and it is extremely energy intensive to both launch a satellite to 40,000 km, and change its inclination to be over the equator, especially whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molniya Orbit
A Molniya orbit ( rus, Молния, p=ˈmolnʲɪjə, a=Ru-молния.ogg, "Lightning") is a type of satellite orbit designed to provide communications and remote sensing coverage over high latitudes. It is a highly elliptical orbit with an inclination of 63.4 degrees, an argument of perigee of 270 degrees, and an orbital period of approximately half a sidereal day. The name comes from the ''Molniya'' satellites, a series of Soviet/Russian civilian and military communications satellites which have used this type of orbit since the mid-1960s. The Molniya orbit has a long dwell time over the hemisphere of interest, while moving very quickly over the other. In practice, this places it over either Russia or Canada for the majority of its orbit, providing a high angle of view to communications and monitoring satellites covering these high-latitude areas. Geostationary orbits, which are necessarily inclined over the equator, can only view these regions from a low angle, hamperin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geocentric Orbit
A geocentric orbit or Earth orbit involves any object orbiting Earth, such as the Moon or artificial satellites. In 1997, NASA estimated there were approximately 2,465 artificial satellite payloads orbiting Earth and 6,216 pieces of space debris as tracked by the Goddard Space Flight Center. More than 16,291 objects previously launched have undergone orbital decay and entered Earth's atmosphere. A spacecraft enters orbit when its centripetal acceleration due to gravity is less than or equal to the centrifugal acceleration due to the horizontal component of its velocity. For a low Earth orbit, this velocity is about ; by contrast, the fastest crewed airplane speed ever achieved (excluding speeds achieved by deorbiting spacecraft) was in 1967 by the North American X-15. The energy required to reach Earth orbital velocity at an altitude of is about 36 MJ/kg, which is six times the energy needed merely to climb to the corresponding altitude. Spacecraft with a perigee belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |