|
Molecules In Stars
Stellar molecules are molecules that exist or form in stars. Such formations can take place when the temperature is low enough for molecules to form – typically around 6000 K or cooler. Otherwise the stellar matter is restricted to atoms (chemical elements) in the forms of gas or – at very high temperatures – plasma. Background Matter is made up by atoms (formed by protons and other subatomic particles). When the environment is right, atoms can join together and form molecules, which give rise to most materials studied in materials science. But certain environments, such as high temperatures, don't allow atoms to form molecules. Stars have very high temperatures, primarily in their interior, and therefore there are few molecules formed in stars. For this reason, a typical chemist (who studies atoms and molecules) would not have much to study in a star, so stars are better explained by astrophysicists or astrochemists. However, low abundance of molecules in stars i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it is the oldest continuously published magazine in the United States. ''Scientific American'' is owned by Springer Nature, which in turn is a subsidiary of Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History ''Scientific American'' was founded by inventor and publisher Rufus Porter (painter), Rufus Porter in 1845 as a four-page weekly newspaper. The first issue of the large format newspaper was released August 28, 1845. Throughout its early years, much emphasis was placed on reports of what was going on at the United States Patent and Trademark Office, U.S. Patent Office. It also reported on a broad range of inventions including perpetual motion machines, an 1860 device for buoying vessels by Abraham Lincoln, and the universal joint which now can be found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Monoxide
Titanium(II) oxide ( Ti O) is an inorganic chemical compound of titanium and oxygen. It can be prepared from titanium dioxide and titanium metal at 1500 °C. It is non-stoichiometric in a range TiO0.7 to TiO1.3 and this is caused by vacancies of either Ti or O in the defect rock salt structure. In pure TiO 15% of both Ti and O sites are vacant, as the vacancies allow metal-metal bonding between adjacent Ti centres. Careful annealing can cause ordering of the vacancies producing a monoclinic form which has 5 TiO units in the primitive cell that exhibits lower resistivity. A high temperature form with titanium atoms with trigonal prismatic coordination is also known. Acid solutions of TiO are stable for a short time then decompose to give hydrogen: :2 Ti2+(aq) + 2 H+(aq) → 2 Ti3+(aq) + H2(g) Gas-phase TiO shows strong bands in the optical spectra of cool ( M-type) stars. In 2017, TiO was claimed to be detected in an exoplanet An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium Monoxide
Vanadium(II) oxide is the inorganic compound with the idealized formula VO. It is one of the several binary vanadium oxides. It adopts a distorted NaCl structure and contains weak V−V metal to metal bonds. VO is a semiconductor owing to delocalisation of electrons in the t2g orbitals. VO is a non-stoichiometric compound In chemistry, non-stoichiometric compounds are chemical compounds, almost always solid inorganic compounds, having elemental composition whose proportions cannot be represented by a ratio of small natural numbers (i.e. an empirical formula); m ..., its composition varying from VO0.8 to VO1.3. Diatomic VO is one of the molecules found in the spectrum of relatively cool M-type stars. References Vanadium(II) compounds Non-stoichiometric compounds Transition metal oxides Rock salt crystal structure {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Monohydride
Silylidyne is a chemical substance occurring as a molecule found in stars and probably existing in interstellar space, or as a monolayer on the surface of solid silicon. The SiH molecule is a radical, and can be made experimentally by striking an electric arc to silicon on a low pressure hydrogen gas. Surface As a surface layer, silicon hydrides form when the silicon is cleaned with hydrofluoric acid. These hydrides decompose to SiH when heated to 750 K. Other ways to coat a silicon surface in hydrogen is via reaction with atomic hydrogen, or hot silane. A (111) crystal face will become covered in the pure monohydride, but other faces on a silicon crystal will also have the dihydride and trihydride groups. Group The silylidyne group, not to be confused with silylidyne, is a ≡SiH group that is bonded with a triple bond. The hydrogen can be substituted by other groups to make a more generic family of silylidynes. It is known as a ligand on molybdenum. Natural occurrence Silylid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
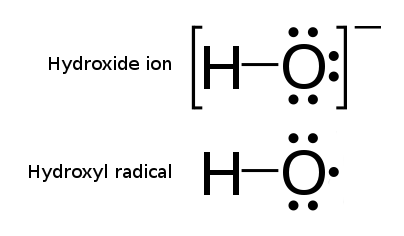
Hydroxyl Radical
The hydroxyl radical is the diatomic molecule . The hydroxyl radical is very stable as a dilute gas, but it decays very rapidly in the condensed phase. It is pervasive in some situations. Most notably the hydroxyl radicals are produced from the decomposition of hydroperoxides (ROOH) or, in atmospheric chemistry, by the reaction of excited atomic oxygen with water. It is also important in the field of radiation chemistry, since it leads to the formation of hydrogen peroxide and oxygen, which can enhance corrosion and SCC in coolant systems subjected to radioactive environments. In organic synthesis, hydroxyl radicals are most commonly generated by photolysis of 1-hydroxy-2(1''H'')-pyridinethione. Notation The unpaired electron of the hydroxyl radical is officially represented by a middle dot, •, beside the O. Biology Hydroxyl radicals can occasionally be produced as a byproduct of immune action. Macrophages and microglia most frequently generate this compound when exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium Monohydride
Chromium(I) hydride, systematically named chromium hydride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula (also written as or CrH). It occurs naturally in some kinds of stars where it has been detected by its spectrum. However, molecular chromium(I) hydride with the formula CrH has been isolated in solid gas matrices. The molecular hydride is very reactive. As such the compound is not well characterised, although many of its properties have been calculated via computational chemistry. Molecular forms A. G. Gaydon first created CrH gas with an electric arc between chromium electrodes in a hydrogen air flame. CrH can be formed by the reaction of chromium metal vapour, created by an electrical discharge in the presence of hydrogen. The electric discharge breaks up the H2 molecules into reactive H atoms. So the reaction then proceeds as Cr(g) + H → CrH. Another method to make CrH is to react chromium carbonyl (Cr(CO)6) vapour with atomic hydrogen generated by an electri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Monohydride
Iron(I) hydride, systematically named iron hydride and poly(hydridoiron) is a solid inorganic compound with the chemical formula (also written or FeH). It is both thermodynamically and kinetically unstable toward decomposition at ambient temperature, and as such, little is known about its bulk properties. Iron(I) hydride is the simplest polymeric iron hydride. Due to its instability, it has no practical industrial uses. However, in metallurgical chemistry, iron(I) hydride is fundamental to certain forms of iron-hydrogen alloys. Nomenclature The systematic name ''iron hydride'', a valid IUPAC name, is constructed according to the compositional nomenclature. However, as the name is compositional in nature, it does not distinguish between compounds of the same stoichiometry, such as molecular species, which exhibit distinct chemical properties. The systematic names ''poly(hydridoiron)'' and ''poly errane(1)', also valid IUPAC names, are constructed according to the additive an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Monohydride
Calcium monohydride is a molecule composed of calcium and hydrogen with formula CaH. It can be found in stars as a gas formed when calcium atoms are present with hydrogen atoms. Discovery Calcium monohydride was first discovered when its spectrum was observed in Alpha Herculis and ο Ceti by Alfred Fowler in 1907. It was observed in sunspots the following year by C. M. Olmsted. Next, it was made in a laboratory in 1909 by A. Eagle, and with early research by Hulthèn, and Watson and Weber in 1935. It was further observed in M dwarfs by Y. Öhman in 1934. Öhman proposed its use as a proxy for stellar luminosity, similar to magnesium monohydride (MgH), in being more apparent in the spectra of compact, cool, high surface gravity stars such as M dwarfs than in cool, low surface gravity stars such as M giants of non-negligible, or even comparable, metallicity. Calcium monohydride is the first molecular gas that was cooled by a cold buffer gas and then trapped by a magnetic field. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Monohydride
Magnesium monohydride is a molecular gas with formula MgH that exists at high temperatures, such as the atmospheres of the Sun and stars. It was originally known as magnesium hydride, although that name is now more commonly used when referring to the similar chemical magnesium dihydride. History George Downing Liveing and James Dewar are claimed to be the first to make and observe a spectral line from MgH in 1878. However they did not realise what the substance was. Formation A laser can evaporate magnesium metal to form atoms that react with molecular hydrogen gas to form MgH and other magnesium hydrides. An electric discharge through hydrogen gas at low pressure (20 pascals) containing pieces of magnesium can produce MgH. Thermally produced hydrogen atoms and magnesium vapour can react and condense in a solid argon matrix. This process does not work with solid neon, probably due to the formation of instead. A simple way to produce some MgH is to burn magnesium in a bunsen b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Spot
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. Sunspots appear within active regions, usually in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity. Their number varies according to the approximately 11-year solar cycle. Individual sunspots or groups of sunspots may last anywhere from a few days to a few months, but eventually decay. Sunspots expand and contract as they move across the surface of the Sun, with diameters ranging from to . Larger sunspots can be visible from Earth without the aid of a telescope. They may travel at relative speeds, or proper motions, of a few hundred meters per second when they first emerge. Indicating intense magnetic activity, sunspots accompany other active region phenomena such as coronal loops, prominences, and reconnection events. Most solar flares and coronal mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes from the emission of residual thermal energy; no fusion takes place in a white dwarf. The nearest known white dwarf is at 8.6 light years, the smaller component of the Sirius binary star. There are currently thought to be eight white dwarfs among the hundred star systems nearest the Sun. The unusual faintness of white dwarfs was first recognized in 1910. The name ''white dwarf'' was coined by Willem Luyten in 1922. White dwarfs are thought to be the final evolutionary state of stars whose mass is not high enough to become a neutron star or black hole. This includes over 97% of the other stars in the Milky Way. After the hydrogen- fusing period of a main-sequence star of low or medium mass ends, such a star will expand to a red giant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_2007-04-30_T001456.gif)