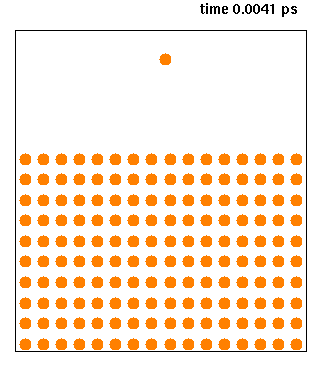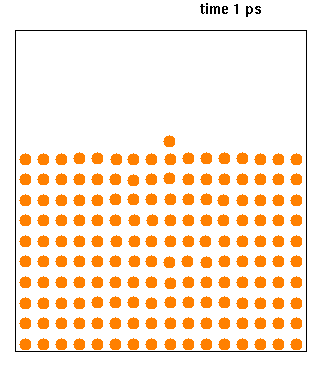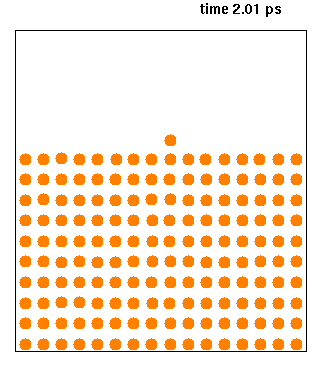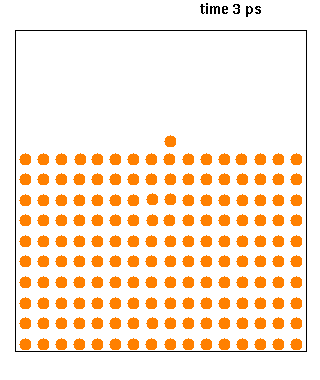
|
Molecular Imprinted Polymer
A molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) is a polymer that has been processed using the molecular imprinting technique which leaves cavities in the polymer matrix with an affinity for a chosen "template" molecule. The process usually involves initiating the polymerization of monomers in the presence of a template molecule that is extracted afterwards, leaving behind complementary cavities. These polymers have affinity for the original molecule and have been used in applications such as chemical separations, catalysis, or molecular sensors. Published works on the topic date to the 1930s. Molecular imprinting techniques (state of the art and perspectives) Molecular imprinting is the process of generating an impression within a solid or a gel, the size, shape and charge distribution of which corresponds to a template molecule (typically present during polymerisation). The result is a synthetic receptor capable of binding to a target molecule, which fits into the binding site with high affi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelation
In polymer chemistry, gelation (gel transition) is the formation of a gel from a system with polymers. Branched polymers can form links between the chains, which lead to progressively larger polymers. As the linking continues, larger branched polymers are obtained and at a certain extent of the reaction links between the polymer result in the formation of a single macroscopic molecule. At that point in the reaction, which is defined as gel point, the system loses fluidity and viscosity becomes very large. The onset of gelation, or gel point, is accompanied by a sudden increase in viscosity. This "infinite" sized polymer is called the gel or network, which does not dissolve in the solvent, but can swell in it. Background Gelation is promoted by gelling agents. Gelation can occur either by physical linking or by chemical crosslinking. While the physical gels involve physical bonds, chemical gelation involves covalent bonds. The first quantitative theories of chemical gelation w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Challenges Of Template Removal For Molecular Imprinted Polymers
Challenge may refer to: * Voter challenging or caging, a method of challenging the registration status of voters * Euphemism for disability * Peremptory challenge, a dismissal of potential jurors from jury duty Places Geography *Challenge, California, an unincorporated community * Challenge-Brownsville, California, a census-designated place in Yuba County, California, United States Structures *Challenge Stadium, former name of Perth Superdrome, a sports complex in Perth, Australia Books and publications * ''Challenge'' (anarchist periodical), American anarchist weekly tabloid, 1938–1939 * ''Challenge'' (Communist journal), British Young Communist League magazine, and also the name of the newspaper of the communist Progressive Labor Party (USA) * ''Challenge'' (game magazine), a role-playing game magazine * ''Challenge'' (economics magazine), a magazine covering economic affairs * ''Challenge'' (Bulldog Drummond), a Bulldog Drummond novel by H. C. McNeile * ''Challeng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecularly Imprinted Polymer
A molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) is a polymer that has been processed using the molecular imprinting technique which leaves cavities in the polymer matrix with an affinity for a chosen "template" molecule. The process usually involves initiating the polymerization of monomers in the presence of a template molecule that is extracted afterwards, leaving behind complementary cavities. These polymers have affinity for the original molecule and have been used in applications such as chemical separations, catalysis, or molecular sensors. Published works on the topic date to the 1930s. Molecular imprinting techniques (state of the art and perspectives) Molecular imprinting is the process of generating an impression within a solid or a gel, the size, shape and charge distribution of which corresponds to a template molecule (typically present during polymerisation). The result is a synthetic receptor capable of binding to a target molecule, which fits into the binding site with high affi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Phase Extraction
Solid-phase extraction (SPE) is an extractive technique by which compounds that are dissolved or suspended in a liquid mixture are separated from other compounds in the mixture according to their physical and chemical properties. Analytical laboratories use solid phase extraction to concentrate and purify samples for analysis. Solid phase extraction can be used to isolate analytes of interest from a wide variety of matrices, including urine, blood, water, beverages, soil, and animal tissue. SPE uses the affinity of solutes dissolved or suspended in a liquid (known as the mobile phase) for a solid through which the sample is passed (known as the stationary phase) to separate a mixture into desired and undesired components. The result is that either the desired analytes of interest or undesired impurities in the sample are retained on the stationary phase. The portion that passes through the stationary phase is collected or discarded, depending on whether it contains the desired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals are used against fungi. They can also be classified according to their function. Agents that kill microbes are microbicides, while those that merely inhibit their growth are called bacteriostatic agents. The use of antimicrobial medicines to treat infection is known as antimicrobial chemotherapy, while the use of antimicrobial medicines to prevent infection is known as antimicrobial prophylaxis. The main classes of antimicrobial agents are disinfectants (non-selective agents, such as bleach), which kill a wide range of microbes on non-living surfaces to prevent the spread of illness, antiseptics (which are applied to living tissue and help reduce infection during surgery), and antibiotics (which destroy microorganisms within the body). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scifinder
CAS (formerly Chemical Abstracts Service) is a division of the American Chemical Society. It is a source of chemical information. CAS is located in Columbus, Ohio, United States. Print periodicals ''Chemical Abstracts'' is a periodical index that provides numerous tools such as SciFinder as well as tagged keywords, summaries, indexes of disclosures, and structures of compounds in recently published scientific documents. Approximately 8,000 journals, technical reports, dissertations, conference proceedings, and new books, available in at least 50 different languages, are monitored yearly, as are patent specifications from 27 countries and two international organizations. ''Chemical Abstracts'' ceased print publication on January 1, 2010. Databases The two principal databases that support the different products are CAplus and Registry. CAS References CAS References consists of bibliographic information and abstracts for all articles in chemical journals worldwide, and chemistry-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coarse-grained Modeling
Coarse-grained modeling, coarse-grained models, aim at simulating the behaviour of complex systems using their coarse-grained (simplified) representation. Coarse-grained models are widely used for molecular modeling of biomolecules at various granularity levels. A wide range of coarse-grained models have been proposed. They are usually dedicated to computational modeling of specific molecules: proteins, nucleic acids, lipid membranes, carbohydrates or water. In these models, molecules are represented not by individual atoms, but by "pseudo-atoms" approximating groups of atoms, such as whole amino acid residue. By decreasing the degrees of freedom much longer simulation times can be studied at the expense of molecular detail. Coarse-grained models have found practical applications in molecular dynamics simulations. Another case of interest is the simplification of a given discrete-state system, as very often descriptions of the same system at different levels of detail are possible. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by numerically solving Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where forces between the particles and their potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanical force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics. Because molecular systems typically consist of a vast number of particles, it is impossible to determine the properties of such complex systems analytically; MD simulation circumvents this problem by using numerical methods. However, long MD simulations are mathematically ill-conditioned, generating cumulative errors in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Chemistry
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contributions to physical and chemical properties of Molecule, molecules, Material, materials, and solutions at the atomic level. These calculations include systematically applied approximations intended to make calculations computationally feasible while still capturing as much information about important contributions to the computed Wave function, wave functions as well as to observable properties such as structures, spectra, and thermodynamic properties. Quantum chemistry is also concerned with the computation of quantum effects on molecular dynamics and chemical kinetics. Chemists rely heavily on spectroscopy through which information regarding the Quantization (physics), quantization of energy on a molecular scale can be obtained. Common metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Mechanics
Molecular mechanics uses classical mechanics to model molecular systems. The Born–Oppenheimer approximation is assumed valid and the potential energy of all systems is calculated as a function of the nuclear coordinates using force fields. Molecular mechanics can be used to study molecule systems ranging in size and complexity from small to large biological systems or material assemblies with many thousands to millions of atoms. All-atomistic molecular mechanics methods have the following properties: * Each atom is simulated as one particle * Each particle is assigned a radius (typically the van der Waals radius), polarizability, and a constant net charge (generally derived from quantum calculations and/or experiment) * Bonded interactions are treated as ''springs'' with an equilibrium distance equal to the experimental or calculated bond length Variants on this theme are possible. For example, many simulations have historically used a ''united-atom'' representation in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Modelling
Molecular modelling encompasses all methods, theoretical and computational, used to model or mimic the behaviour of molecules. The methods are used in the fields of computational chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science to study molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and material assemblies. The simplest calculations can be performed by hand, but inevitably computers are required to perform molecular modelling of any reasonably sized system. The common feature of molecular modelling methods is the atomistic level description of the molecular systems. This may include treating atoms as the smallest individual unit (a molecular mechanics approach), or explicitly modelling protons and neutrons with its quarks, anti-quarks and gluons and electrons with its photons (a quantum chemistry approach). Molecular mechanics Molecular mechanics is one aspect of molecular modelling, as it involves the use of classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |