|
Mojmír Dynasty
The Moymirid dynasty (Latin: ''Moimarii'', Czech and Slovak: ''Mojmírovci'') was a Moravian ruling dynasty that ruled over Moravia in the 9th and early 10th century. On one hand, it is named after the first known member, Mojmir I, but on the other hand the Latin form of the dynasty's name is first mentioned in a letter from the year 900. The last known members presumably died in the first decade of the 10th century during one of the invasions of Hungarian tribes. The developments of the family before Mojmír I and after 906 are unknown. Known members Disputed members *Pribina Pribina (c. 800861) was a Slavic prince whose adventurous career, recorded in the ''Conversion of the Bavarians and the Carantanians'' (a historical work written in 870), illustrates the political volatility of the Franco–Slavic frontie ... * Predslav References {{Reflist Moravian noble families Great Moravia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Language
Czech (; Czech ), historically also Bohemian (; ''lingua Bohemica'' in Latin), is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. Spoken by over 10 million people, it serves as the official language of the Czech Republic. Czech is closely related to Slovak, to the point of high mutual intelligibility, as well as to Polish to a lesser degree. Czech is a fusional language with a rich system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval period, and the standardization of Czech and Slovak within the Czech–Slovak dialect continuum emerged in the early modern period. In the later 18th to mid-19th century, the modern written standard became codified in the context of the Czech National Revival. The main non-standard variety, known as Common Czech, is based on the vernacular of Prague, but is now spoken as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak Language
Slovak () , is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Slovak is closely related to Czech, to the point of mutual intelligibility to a very high degree, as well as Polish. Like other Slavic languages, Slovak is a fusional language with a complex system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German and other Slavic languages. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval period, and the standardization of Czech and Slovak within the Czech–Slovak dialect continuum emerged in the early modern period. In the later mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moravians (tribe)
The Moravians ( Old Slavic self-designation ''Moravljane'', sk, Moravania, cz, Moravané) were a West Slavic tribe in the Early Middle Ages. Although it is not known exactly when the Moravian tribe was founded, Czech historian Dušan Třeštík claimed that the tribe was formed between the turn of the 6th century to the 7th century, around the same time as the other Slavic tribes. In the 9th century Moravians settled mainly around the historic region of Moravia and Western Slovakia, but also in parts of Lower Austria (up to the Danube) and Upper Hungary. The first known mention of the Moravians was in the Annales Regni Francorum in 822 AD. The tribe was located by the Bavarian Geographer (as ''Marharii'') between the tribe of the Bohemians and the tribe of the Bulgarians. In the 9th century Moravians gain control over neighbouring Nitra and founded the realm of Great Moravia, ruled by the Mojmír dynasty until the 10th century. After the breakup of the Moravian realm the Mora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavs, West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Austria, Germany, Poland, Romania, Croatia, Serbia and Ukraine. The only formation preceding it in these territories was Samo's Empire, Samo's tribal union known from between 631 and 658 AD. Its core territory is the region now called Moravia in the eastern part of the Czech Republic alongside the Morava (river), Morava River, which gave its name to the kingdom. The kingdom saw the rise of the first ever Slavic literary culture in the Old Church Slavonic language as well as the expansion of Christianity, first via missionaries from East Francia, and later after the arrival of Saints Cyril and Metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mojmir I Of Moravia
Mojmir I, Moimir I or Moymir I (Latin: ''Moimarus'', ''Moymarus'', Czech and Slovak: ''Mojmír I.'') was the first known ruler of the Moravian Slavs (820s/830s–846) and eponym of the House of Mojmir. In modern scholarship, the creation of the early medieval state known as Great Moravia is attributed either to his or to his successors' expansionist policy. He was deposed in 846 by Louis the German, king of East Francia. Background From the 570s the Avars dominated the large area stretching from the Eastern Carpathians to the Eastern Alps in Central Europe. The local Slavic tribes were obliged to pay tribute to their overlords, but they began to resist in the early 7th century.Spiesz ''et al.'' 2006, p. 17. First those who inhabited the region of today's Vienna (Austria) threw off the yoke of the Avars in 623–624. They were led by a Frankish merchant named Samo whose reign would last for at least 35 years. However, when he died some time between 658 and 669, hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranked below princess nobility and grand dukes. The title comes from French ''duc'', itself from the Latin ''dux'', 'leader', a term used in republican Rome to refer to a military commander without an official rank (particularly one of Germanic or Celtic origin), and later coming to mean the leading military commander of a province. In most countries, the word ''duchess'' is the female equivalent. Following the reforms of the emperor Diocletian (which separated the civilian and military administrations of the Roman provinces), a ''dux'' became the military commander in each province. The title ''dux'', Hellenised to ''doux'', survived in the Eastern Roman Empire where it continued in several contexts, signifying a rank equivalent to a captai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rastislav Of Moravia
Rastislav or Rostislav, also known as St. Rastislav, (Latin: ''Rastiz'', Greek: Ῥασισθλάβος / ''Rhasisthlábos'') was the second known ruler of Moravia (846–870).Spiesz ''et al.'' 2006, p. 20. Although he started his reign as vassal to Louis the German, king of East Francia, he consolidated his rule to the extent that after 855 he was able to repel a series of Frankish attacks. Upon his initiative, brothers Cyril and Methodius, sent by the Byzantine Emperor Michael III in 863, translated the most important Christian liturgical books into Slavonic. Rastislav was dethroned by his nephew Svatopluk I of Moravia, who handed him over to the Franks. He was canonized by the Eastern Orthodox Church in 1994. Early life According to the ''Annals of Fulda'', Rastislav was a nephew of Mojmir I, the first known ruler of Moravia. His career before 846 is unknown,The Slovakian historian Stanislav J. Kirschbaum refers to Rastislav as prince of Nitra in the period before 846 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svatopluk I Of Moravia
Svatopluk I or Svätopluk I, also known as Svatopluk the Great (Latin: ''Zuentepulc'', ''Zuentibald'', ''Sventopulch'', ''Zvataplug''; Old Church Slavic: Свѧтопълкъ and transliterated ''Svętopъłkъ''; Polish: ''Świętopełk''; Greek: Σφενδοπλόκος, ''Sphendoplókos''), was a ruler of Great Moravia, which attained its maximum territorial expansion during his reign (870–871, 871–894). Svatopluk's career started in the 860s, when he governed a principality within Moravia, the location of which is still a matter of debate among historians, under the suzerainty of his uncle, Rastislav. In 870 Svatopluk dethroned Rastislav, who was a vassal of Louis the German, and betrayed him to the Franks. Within a year, however, the Franks also imprisoned Svatopluk. After the Moravians rebelled against the Franks, Svatopluk was released and led the rebels to victory over the invaders. Although he was obliged to pay tribute to East Francia under the peace treaty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavomir Of Moravia
Slavomir (Latin: ''Sclagamarus'', Czech and Slovak: ''Slavomír'') was a duke of Moravia (871). He led a revolt against the Franks who had annexed Moravia during the incarceration of his relative, Svatopluk I. Early life Slavomir, according to the '' Annals of Fulda'', was a member of the Moravian ruling dynasty. He seems to have been a disciple of Saints Cyril and Methodius who had in 863 arrived in Moravia where they established an institution of higher education. It is possible that Slavomir was one of the "high-ranking hostages" whom his relative, Rastislav, the duke of Moravia, turned over to the Franks in 864, because in that year Bishop Otgar of Eichstätt granted an estate near the Frankish–Moravian border to a certain Slav, Sleimar, whose name may be a variant spelling of his name. It is conceivable that Louis the German, the king of East Francia, placed Slavomir-Sleimar under Bishop Otgar's supervision and granted him an estate as a prebend while he served as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mojmir II Of Moravia
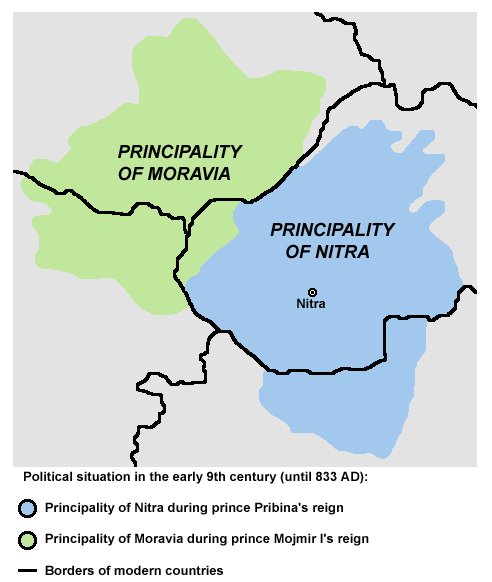
Mojmir II (Latin: ''Moymirus'', Czech and Slovak: ''Mojmír II.'', born after 871, died after 901) was a member of the House of Mojmir and since 894 the last known ruler of Great Moravia. He probably died in the beginning of the 10th century in a battle against the Magyars. Biography Mojmir II ruled at the same time as the son of Svatopluk I and grandson (according to Simon of Kéza) of Morot (a Prince of Poland who had subdued Bractari and ruled as Emperor of the Bulgars and Moravians). Prince Morot conquered Crișana and the people that are called Cozar inhabiting that land. This grandson of Prince Morot through Svatopluk I was called Menumorout (Stallion of Morout)."Anonymus Notary of King Bela The Deeds of the Hungarians" edited translated and anotated by Martyn Rady and László Veszprémy. CEU Press, 2010. P.33 As in the Hungarian "Menumarot" version of history, Mojmir II succeeded his father Svatopluk I as the king of Great Moravia in 894. At the same time, the Principa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svatopluk II
Svatopluk II or Svätopluk II (Latin: ''Zentobolchus'') was a member of the House of Mojmír and Prince in Moravia (maybe of Nitra) from 894 to 899, as which he strove to control all of Great Moravia. He was the son of Svatopluk I son of Morot. Biography Svatopluk II was a younger son of Svatopluk I and grandson (according to Simon of Kéza) of Morot. As Prince of Nitra, Svatopluk II was subordinated to Mojmír II, the King of Great Moravia which contained the principality as its province. Svatopluk II rebelled against Mojmír II in 898 in an attempt to take over control of Great Moravia. Their conflict climaxed when Bavarian troops intervened in the winter of 898/899. Mojmír II defeated the Bavarians and captured Svatopluk II, but the Bavarians managed to rescue him and brought him to East Francia. Svatopluk II returned to the Principality of Nitra in 901. He probably died in 906 in fights with the Hungarians, who began to invade the Carpathian Basin The Pannonian Basin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |