|
Mogounus
Mogons or Moguns was a Celtic god worshiped in Roman Britain and Gaul. The main evidence is from altars dedicated to the god by Roman soldiers. Etymology According to J.T. Koch at the University of Wales, the various alternations of the name ''Moguns'' derive from the Romano-Celtic dialectal reflexes of Proto-Celtic *''mogont-s'' (a derivative of the Proto-Indo-European root ''*megH2-'' "to be great, mighty"), an Indo-European *''-nt-'' -stem cognate with Sanskrit ''mahānt'' and Avestan ''mazant'' ‘great’.Koch, J.T. (2005:1300) ''Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia'' ABC-CLIO Ltd (15 Mar 2006); 978-1851094400 Centres of worship Altar-stones raised to Mogons have been recovered in the United Kingdom, such as the stones found at the following locations. The number is the catalog number of the artifact and the name in parentheses is the word as it appears on the stone, not necessarily (and probably not) in the nominative case. Most are datives, to be translated as "t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grannus
Grannus (also ''Granus'', ''Mogounus,'' and ''Amarcolitanus'') was a Celtic deity of classical antiquity. He was regularly identified with Apollo as Apollo Grannus and frequently worshipped in conjunction with Sirona, and sometimes with Mars and other deities. Name Etymology The theonym ''Grannus'' is a latinized form of Gaulish ''Grannos''. The same stem appears in the personal names ''Grania'', ''Grannia'', ''Grannicus'', and ''Grannica'', as well as in the place names ''Grignols'' (from an earlier *''Granno-ialon'' 'Grannus' clearing'), ''Aquae Granni'' (> '' Aachen''), and ''Granéjouls''. Its etymology remains debated. The name could be connected to Proto-Celtic *''grand''-''/grend-'', meaning 'beard' (cf. Middle Irish ''grend'', Middle Welsh ''grann'' 'chin, beard, cheek', Middle Breton ''grann'' 'eyebrow'), although some scholars have pointed that the god is never actually portrayed with a beard. Old French ''grenon'' ('small beard'), Old Spanish ''greñon'' ('beard') and Oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main (river), Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Mainz on the left bank, and Wiesbaden, the capital of the neighbouring state Hesse, on the right bank. Mainz is an independent city with a population of 218,578 (as of 2019) and forms part of the Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Frankfurt Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region. Mainz was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans in the 1st century BC as a military fortress on the northernmost frontier of the empire and provincial capital of Germania Superior. Mainz became an important city in the 8th century AD as part of the Holy Roman Empire, capital of the Electorate of Mainz and seat of the Elector of Mainz, Archbishop-Elector of Mainz, the Primate (bishop), Primate of Germany. Mainz is famous as the birthplace of Johannes Gutenberg, the inventor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
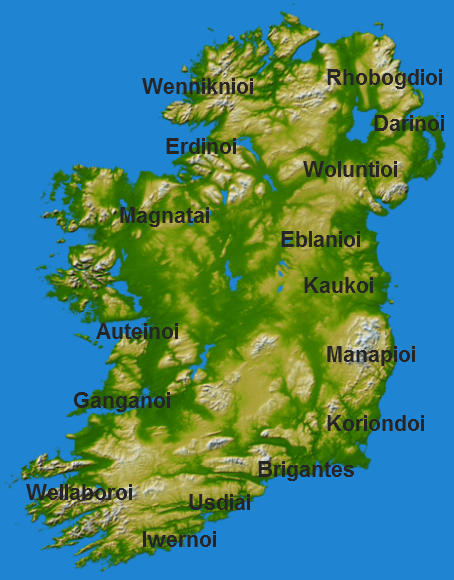
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was raised to the status of a Roman province. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by other Celtic tribes during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells ('' musculi'') according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over the sea. Three years later, Claudius directed four legi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vindolanda
Vindolanda was a Roman auxiliary fort (''castrum'') just south of Hadrian's Wall in northern England, which it originally pre-dated.British windo- 'fair, white, blessed', landa 'enclosure/meadow/prairie/grassy plain' (the modern Welsh word would be something like ''gwynlan'', and the modern Gaelic word ''fionnlann'' ld Gaelic word ''Fiondland''). Archaeological excavations of the site show it was under Roman occupation from roughly 85 AD to 370 AD. Located near the modern village of Bardon Mill in Northumberland, it guarded the Stanegate, the Roman road from the River Tyne to the Solway Firth. It is noted for the Vindolanda tablets, a set of wooden leaf-tablets that were, at the time of their discovery, the oldest surviving handwritten documents in Britain. Early accounts The first post-Roman record of the ruins at Vindolanda was made by the antiquarian William Camden, in his ''Britannia'' (1586). Occasional travellers reached the site over the next two hundred years, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penrith, Cumbria
Penrith (, , ) is a market town and civil parish in the county of Cumbria, England, about south of Carlisle. It is less than outside the Lake District, Lake District National Park, in between the Rivers River Petteril, Petteril and River Eamont, Eamont and just north of the River Lowther. It had a population of 15,181 at the 2011 Census. Historic counties of England, Historically in Cumberland, Penrith's current local authority, local authorities are the Eden, Cumbria, Eden District Council, which is based in the town, and Cumbria County Council. In 2023, Penrith will become part of the Westmorland and Furness unitary authority area. From 1974 to 2015, it was an unparished area with no local council. A civil parish was reintroduced as Penrith Town Council and first elected on 7 May 2015. Toponymy The etymology of "Penrith" has been debated. Several writers argue for the Cumbric or Welsh language, Welsh "head, chief, end" (both noun and adjective) with the Cumbric , Wels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had a population of 1,898,533. Alsatian culture is characterized by a blend of Germanic and French influences. Until 1871, Alsace included the area now known as the Territoire de Belfort, which formed its southernmost part. From 1982 to 2016, Alsace was the smallest administrative ''région'' in metropolitan France, consisting of the Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin departments. Territorial reform passed by the French Parliament in 2014 resulted in the merger of the Alsace administrative region with Champagne-Ardenne and Lorraine to form Grand Est. On 1 January 2021, the departments of Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin merged into the new European Collectivity of Alsace but remained part of the region Grand Est. Alsatian is an Alemannic dialect closely related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gael
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising Irish, Manx and Scottish Gaelic. Gaelic language and culture originated in Ireland, extending to Dál Riata in western Scotland. In antiquity, the Gaels traded with the Roman Empire and also raided Roman Britain. In the Middle Ages, Gaelic culture became dominant throughout the rest of Scotland and the Isle of Man. There was also some Gaelic settlement in Wales, as well as cultural influence through Celtic Christianity. In the Viking Age, small numbers of Vikings raided and settled in Gaelic lands, becoming the Norse-Gaels. In the 9th century, Dál Riata and Pictland merged to form the Gaelic Kingdom of Alba. Meanwhile, Gaelic Ireland was made up of several kingdoms, with a High King often claiming lordship over them. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jedburgh
Jedburgh (; gd, Deadard; sco, Jeddart or ) is a town and former royal burgh in the Scottish Borders and the traditional county town of the historic county of Roxburghshire, the name of which was randomly chosen for Operation Jedburgh in support of the D-Day invasion. Location Jedburgh lies on the Jed Water, a tributary of the River Teviot. It is from the border with England, and is dominated by the substantial ruins of Jedburgh Abbey. Other notable buildings in the town include Queen Mary's House, Jedburgh Castle Jail, now a museum, and the Jedburgh Library. Other places nearby are Ancrum, Bairnkine, Bonjedward, Camptown, Crailing, Edgerston, Ferniehirst Castle, Nisbet and Oxnam. History Jedburgh began as ''Jedworð'', the "worth" or enclosed settlement on the Jed. Later the more familiar word "burgh" was substituted for this, though the original name survives as Jeddart/Jethart. Bishop Ecgred of Lindisfarne founded a church at Jedburgh in the 9th century, and King D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treveri
The Trēverī (Gaulish: *''Trēueroi'') were a Celtic tribe of the Belgae group who inhabited the lower valley of the Moselle from around 150 BCE, if not earlier, until their displacement by the Franks. Their domain lay within the southern fringes of the ''Silva Arduenna'' ( Ardennes Forest), a part of the vast Silva Carbonaria, in what are now Luxembourg, southeastern Belgium and western Germany; its centre was the city of Trier (''Augusta Treverorum''), to which the Treveri give their name. Celtic in language, according to Tacitus they claimed Germanic descent.Tacitus writes, "The Treveri and Nervii are even eager in their claims of a German origin, thinking that the glory of this descent distinguishes them from the uniform level of Gallic effeminacy." ''Germania'' XXVIII. They possibly contained both Gallic and Germanic influences. Although early adopters of Roman material culture, the Treveri had a chequered relationship with Roman power. Their leader Indutiomarus led them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aresaces
The Aresaces were Belgic tribe. They were closely related to, and probably originally part of, the Treveri. They inhabited the left bank of the Rhine in the Mainz -Bingen area, which was once the easternmost part of Treveran territory. Written sources The Aresaces are not mentioned by ancient writers, such as geographers or Julius Caesar, but are known from three inscriptions dating to the 1st and 2nd centuries CE. Two of these come from Rhenish Hesse, while the third is from Augusta Treverorum (Trier), the capital of the Treveri. A grave monument from Mainz-Weisenau that identifies the two deceased children as Treveri has been explained as evidence that the Aresaces continued to regard themselves as a subdivision of the Treveri. Another Celtic tribe in Rhenish Hesse, known from an inscription as well as ancient literature, was the Cairacates. Settlement area of the Aresaces According to current scholarship, the Aresaces would have been organized as a ''pagus'' or sub-unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germania Superior
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon ('' Vesontio''), Strasbourg (''Argentoratum''), Wiesbaden ('' Aquae Mattiacae''), and Germania Superior's capital, Mainz (''Mogontiacum''). It comprised the Middle Rhine, bordering on the ''Limes Germanicus'', and on the Alpine province of Raetia to the south-east. Although it had been occupied militarily since the reign of Augustus, Germania Superior (along with Germania Inferior) was not made into an official province until c. 85 AD. Origin Initial Roman involvement The terms, "Upper Germania" and "Lower Germania" do not appear in the ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' of Julius Caesar, yet he writes about reports that the people who lived in those regions were referred to as "Germani" locally, a term used for a tribe that the Romans called the Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhaetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west with Transalpine Gaul and on the south with Venetia et Histria, a region of Roman Italy. It thus comprised the districts occupied in modern times by eastern and central Switzerland (containing the Upper Rhine and Lake Constance), southern Germany (Bavaria and most of Baden-Württemberg), Vorarlberg and the greater part of Tyrol in Austria, and part of northern Lombardy in Italy. The region of Vindelicia (today eastern Württemberg and western Bavaria) was annexed to the province at a later date than the others. The northern border of Raetia during the reigns of emperors Augustus and Tiberius was the River Danube. Later the Limes Germanicus marked the northern boundary, stretching for 166 km north of the Danube. Raetia linked to Italy across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |