|
Modane Underground Laboratory
The Modane Underground Laboratory (LSM) (french: Laboratoire Souterrain de Modane; also known as the Fréjus Underground Laboratory) is a subterranean particle physics laboratory located within the Fréjus Road Tunnel near Modane, France. It is jointly operated by the French National Center for Scientific Research and the Atomic Energy and Alternative Energies Commission in partnership with the University of Savoie. The laboratory sits almost exactly in the middle of the road tunnel, which links Modane to Bardonecchia, Italy, below Fréjus Peak. This depth translates to a meter water equivalent depth of . , it is the deepest laboratory in the European Union. The LSM was built between 1981 and 1982 to host the "Fréjus" iron tracking calorimeter proton decay experiment. Today the site houses the Neutrino Ettore Majorana Observatory (NEMO) search for neutrinoless double beta decay, the EDELWEISS dark matter detector, and other particle detector In experimental and applied pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three generations of fermions, but ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even number are called mesons. Two baryons, the proton and the neutron, make up most of the mass of ordinary matter. Mesons are unstable and the longest-lived last for only a few hundredths of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been described as a '' sui generis'' political entity (without precedent or comparison) combining the characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.8per cent of the world population in 2020, the EU generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around trillion in 2021, constituting approximately 18per cent of global nominal GDP. Additionally, all EU states but Bulgaria have a very high Human Development Index according to the United Nations Development Programme. Its cornerstone, the Customs Union, paved the way to establishing an internal single market based on standardised legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states have agreed to act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Technology In Europe
Europe's achievements in science and technology have been significant and research and development efforts form an integral part of the European economy. Europe has been the home of some of the most prominent researchers in various scientific disciplines, notably physics, mathematics, chemistry and engineering. Scientific research in Europe is supported by industry, by the European universities and by several scientific institutions. All the raw output of scientific research from Europe consistently ranks among the world's best. Historical overview Mathematics flourished in the Greek world from 600 BC to 300 AD. However, the study of mathematics was de-emphasized when the Roman Empire was in power, and became even less important after the fall of Rome. Medieval Europeans were interested in mathematics for different reasons than modern mathematicians are; namely, they studied mathematics because they thought it was the basis to understand the created order of nature, as explain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics Facilities
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass. They vary greatly in size or quantity, from subatomic particles like the electron, to microscopic particles like atoms and molecules, to macroscopic particles like powders and other granular materials. Particles can also be used to create scientific models of even larger objects depending on their density, such as humans moving in a crowd or celestial bodies in motion. The term ''particle'' is rather general in meaning, and is refined as needed by various scientific fields. Anything that is composed of particles may be referred to as being particulate. However, the noun ''particulate'' is most frequently used to refer to pollutants in the Earth's atmosphere, which are a suspension of unconnected particles, rather than a connected particle aggregation. Conceptual properties The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
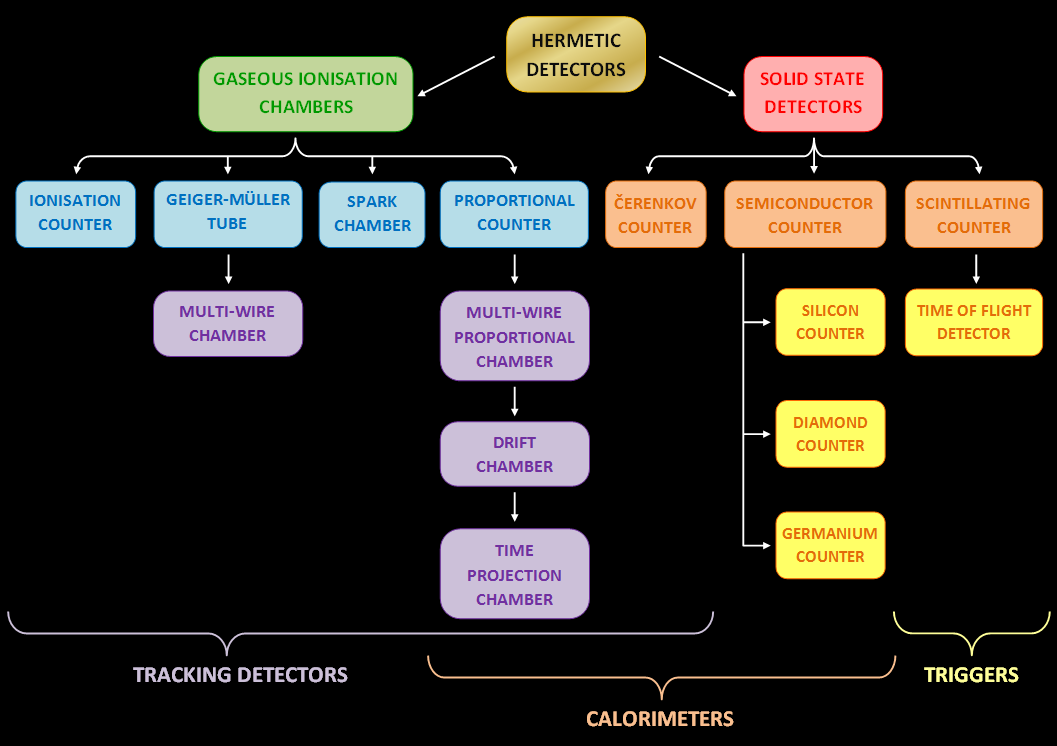
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. Examples and types Many of the detectors invented and used so far are ionization detectors (of which gaseous ionization detectors and semiconductor detectors are most typical) and scintillation detectors; but other, completely different principles have also been applied, like Čerenkov light and transition radiation. Historical examples *Bubble chamber * Wilson cloud chamber (diffusion chamber) * Photographic plate ;Detectors for radiation protection The following types of particle detector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark Matter
Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter thought to account for approximately 85% of the matter in the universe. Dark matter is called "dark" because it does not appear to interact with the electromagnetic field, which means it does not absorb, reflect, or emit electromagnetic radiation and is, therefore, difficult to detect. Various astrophysical observationsincluding gravitational effects which cannot be explained by currently accepted theories of gravity unless more matter is present than can be seenimply dark matter's presence. For this reason, most experts think that dark matter is abundant in the universe and has had a strong influence on its structure and evolution. The primary evidence for dark matter comes from calculations showing that many galaxies would behave quite differently if they did not contain a large amount of unseen matter. Some galaxies would not have formed at all and others would not move as they currently do. Other lines of evidence include observa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EDELWEISS
EDELWEISS (Expérience pour DEtecter Les WIMPs En Site Souterrain) is a dark matter search experiment located at the Modane Underground Laboratory in France. The experiment uses cryogenic detectors, measuring both the phonon and ionization signals produced by particle interactions in germanium crystals. This technique allows nuclear recoils events to be distinguished from electron recoil events. The EURECA project is a proposed future dark matter experiment, which will involve researchers from EDELWEISS and the CRESST dark matter search. Dark matter Dark matter is material which does not emit or absorb light. Measurements of the rotation curves of spiral galaxies suggest it makes up the majority of the mass of galaxies; and precision measurements of the cosmic microwave background radiation suggest it accounts for a significant fraction of the density of the Universe. A possible explanation of dark matter comes from particle physics. WIMP (Weakly Interacting Massive Particl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrinoless Double Beta Decay
The neutrinoless double beta decay (0νββ) is a commonly proposed and experimentally pursued theoretical radioactive decay process that would prove a Majorana nature of the neutrino particle. To this day, it has not been found. The discovery of the neutrinoless double beta decay could shed light on the absolute neutrino masses and on their mass hierarchy (Neutrino mass). It would mean the first ever signal of the violation of total lepton number conservation. A Majorana nature of neutrinos would confirm that the neutrino is its own antiparticle. To search for neutrinoless double beta decay, there are currently a number of experiments underway, with several future experiments for increased sensitivity proposed as well. Historical development of the theoretical discussion Back in 1939, Wendell H. Furry proposed the idea of the Majorana nature of the neutrino, which was associated with beta decays. Furry stated the transition probability to even be higher for the neutrino''les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino Ettore Majorana Observatory
The Neutrino Ettore Majorana Observatory (NEMO experiment) is an international collaboration of scientists searching for neutrinoless double beta decay (0νββ). The collaboration has been active since 1989. Observation of 0νββ would indicate neutrinos are Majorana particles and could be used to measure the neutrino mass. It is located in the Modane Underground Laboratory (LSM) in the Fréjus Road Tunnel. The experiment has (as of 2018) had 3 detectors, NEMO-1, NEMO-2, NEMO-3 (and a demonstrator module of SuperNEMO-detector) and is planning (as of 2018) to construct a new detector SuperNEMO. The NEMO-1 and NEMO-2 prototype detectors were used until 1997. Latest experiment NEMO-3 was under design and construction from 1994 onwards, took data from January 2003 to January 2011 and the final data analysis was published in 2018.http://www.rcnp.osaka-u.ac.jp/dbd18/Data/Prog/S0303_Patrick.pdf The NEMO-2 and NEMO-3 detectors produced measurements for double neutrino decays and lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Decay
In particle physics, proton decay is a hypothetical form of particle decay in which the proton decays into lighter subatomic particles, such as a neutral pion and a positron. The proton decay hypothesis was first formulated by Andrei Sakharov in 1967. Despite significant experimental effort, proton decay has never been observed. If it does decay via a positron, the proton's half-life is constrained to be at least years. According to the Standard Model, the proton, a type of baryon, is stable because baryon number (quark number) is conserved (under normal circumstances; see chiral anomaly for an exception). Therefore, protons will not decay into other particles on their own, because they are the lightest (and therefore least energetic) baryon. Positron emission and electron capture – forms of radioactive decay which sees a proton become a neutron – are not proton decay, since the proton interacts with other particles within the atom. Some beyond-the-Standard Model gran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durham, England
Durham ( , locally ), is a cathedral city and civil parish on the River Wear, County Durham, England. It is an administrative centre of the County Durham District, which is a successor to the historic County Palatine of Durham (which is different to both the ceremonial county and district of County Durham). The settlement was founded over the final resting place of St Cuthbert. Durham Cathedral was a centre of pilgrimage in medieval England while the Durham Castle has been the home of Durham University since 1832. Both built in 11th-century, the buildings were designated as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1986. HM Prison Durham is also located close to the city centre and was built in 1816. Name The name "Durham" comes from the Brythonic element , signifying a hill fort and related to -ton, and the Old Norse , which translates to island.Surtees, R. (1816) ''History and Antiquities of the County Palatine of Durham'' (Classical County Histories) The Lord Bishop of Durh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fréjus Road Tunnel
The Fréjus Road Tunnel is a tunnel that connects France and Italy. It runs under Col du Fréjus in the Cottian Alps between Modane in France and Bardonecchia in Italy. It is one of the major trans-Alpine transport routes between France and Italy being used for 80% of the commercial road traffic. Construction of the long tunnel started in 1974, and it came into service on 12 July 1980, leading to the closure of the motorail shuttle service in the Fréjus rail tunnel. It cost 2 billion francs (equivalent to €700 million at 2005 prices). It is the thirteenth longest road tunnel in the world. The French section is managed by the French company SFTRF, and the Italian section by the Italian company SITAF. (The French politician Pierre Dumas was chairman of SFTRF from 1962 to 1989). The tunnel can be reached from the Italian side by the A32 Torino-Bardonecchia motorway, or by SS335 from Oulx, which joins SS24 (“del Monginevro”), and reaches Bardonecchia after . From the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |