|
Mixed-phenotype Acute Leukemia
Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) is a group of blood cancers (leukemia) which have combined features of myeloid and lymphoid cancers. It is a rare disease, constituting about 2–5% of all leukemia cases. It mostly involve myeloid with either of T lymphocyte or B lymphocyte progenitors, but in rare cases all the three cell lineages. Knowledge on the cause, clinical features and cellular mechanism is poor, making the treatment and management (prognosis) difficult. The name "mixed-phenotype acute leukemia" was adopted by the World Health Organization in 2008 to include leukemias of ambiguous lineage, acute undifferentiated leukemias and natural killer lymphoblastic leukemias. According to WHO criteria, myeloid lineage is characterised by the presence of myeloperoxidase, while B and T lymphoid lineages are indicated by the expression of CD19 and cytoplasmic CD3. __TOC__ Molecular biology The fundamental feature of MPAL involves two types of tranlocations that occur in chromoso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ''leukemia cells''. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, petrochemicals (such as benzene), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia— acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myeloi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Death
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as diseases, localized injury, or the death of the organism of which the cells are part. Apoptosis or Type I cell-death, and autophagy or Type II cell-death are both forms of programmed cell death, while necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury. Programmed cell death Programmed cell death (PCD) is cell death mediated by an intracellular program. PCD is carried out in a regulated process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's life-cycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and metazoa (multicellula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonal Antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies can have monovalent affinity, binding only to the same epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes and are usually made by several different antibody-secreting plasma cell lineages. Bispecific monoclonal antibodies can also be engineered, by increasing the therapeutic targets of one monoclonal antibody to two epitopes. It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to virtually any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it. This capability has become an investigative tool in biochemistry, molecular biology, and medicine. Monoclonal antibodies are being used on a clinical level for both the diagnosis and therapy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidney & Lois Eskenazi Hospital
The Sidney & Lois Eskenazi Hospital is a public hospital located in Indianapolis, Indiana. The hospital is the flagship medical center for Eskenazi Health, founded in 1859 as Indiana's oldest public healthcare system. The hospital is operated by Health and Hospital Corporation of Marion County. The current hospital opened December 7, 2013, less than to the west of the original campus, replacing Wishard Memorial Hospital. Many of Eskenazi Hospital's 4,620 medical staff are provided by a mix of faculty, residents, and students of the adjacent Indiana University School of Medicine. The hospital is an Adult Level I Trauma Center and serves about 1 million outpatients annually. History The hospital was founded as Indianapolis City Hospital in 1859 in response to a smallpox epidemic in the city. During the Civil War, the hospital was used by the Union Army to treat some 13,000 sick and wounded soldiers. The hospital reverted to community control after the war. In 1943, the hosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Infirmary
The Western Infirmary was a teaching hospital situated in the West End of Glasgow, Scotland, that was managed by NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde. It was opened in 1874 and closed in 2015. History After the University of Glasgow moved from the city centre to the West End in the 1870s, distancing itself from the Royal Infirmary, a new teaching hospital was commissioned for the new university site and opened in 1874. The Western Infirmary opened as a voluntary hospital relying upon donations and bequests from members of the public. By 1890 there had already been 877 operations performed in the hospital. Although the hospital initially had only 150 beds, by 1911 this had increased to over six hundred. In 1936 the decision was taken to establish a medical department. In 1930 a radiology department opened and, in 1936, a new ophthalmology department was officially opened, named the Tennent Memorial, with an entrance on Church Street. In 1938 the research capacity increased with the openi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Findlay
Leonard Findlay (5 February 1878, in Glasgow – 14 June 1947) was the pediatrician who was the first Leonard Gow Lecturer on the Medical Diseases of Infancy and Childhood. Findlay was also the first person to hold the Samson Gemmell Chair of Child Health at the University of Glasgow. Findlay married Gertrude Findlay née Binning in 1905. The couple had two daughters. Life Findlay was the son of a doctor, Dr William Findlay who was also an essayist who wrote under the pen name, George Umber. His mother was Margaret Findlay née Carruthers. Findlay took his early education at Allan Glen's School before moving to Glasgow University. He graduated Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery in 1900 and Doctor of Medicine in 1904 both with commendations. Findlay passed the DSc in 1912. Career Findlay's first post was at the outpatient's department of Western Infirmary in Glasgow before moving to the Department of Pathology under Sir Robert Muir. After several years gaining experience ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
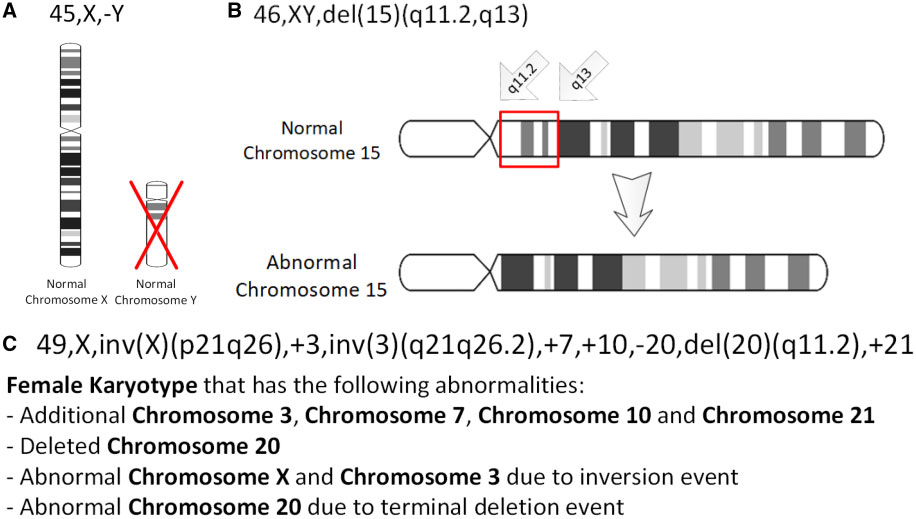
Chromosomal Inversion
An inversion is a chromosome rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome becomes inverted within its original position. An inversion occurs when a chromosome undergoes a two breaks within the chromosomal arm, and the segment between the two breaks inserts itself in the opposite direction in the same chromosome arm. The breakpoints of inversions often happen in regions of repetitive nucleotides, and the regions may be reused in other inversions. Chromosomal segments in inversions can be as small as 100 kilobases or as large as 100 megabases. The number of genes captured by an inversion can range from a handful of genes to hundreds of genes. Inversions can happen either through ectopic recombination, chromosomal breakage and repair, or non-homologous end joining. Inversions are of two types: paracentric and pericentric. Paracentric inversions do not include the centromere, and both breakpoints occur in one arm of the chromosome. Pericentric inversions span the centromere, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Methyltransferases
Histone methyltransferases (HMT) are histone-modifying enzymes (e.g., histone-lysine N-methyltransferases and histone-arginine N-methyltransferases), that catalyze the transfer of one, two, or three methyl groups to lysine and arginine residues of histone proteins. The attachment of methyl groups occurs predominantly at specific lysine or arginine residues on histones H3 and H4. Two major types of histone methyltranferases exist, lysine-specific (which can be SET (Su(var)3-9, Enhancer of Zeste, Trithorax) domain containing or non-SET domain containing) and arginine-specific. In both types of histone methyltransferases, S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) serves as a cofactor and methyl donor group. The genomic DNA of eukaryotes associates with histones to form chromatin. The level of chromatin compaction depends heavily on histone methylation and other post-translational modifications of histones. Histone methylation is a principal epigenetic modification of chromatin that determines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Methylation
Histone methylation is a process by which methyl groups are transferred to amino acids of histone proteins that make up nucleosomes, which the DNA double helix wraps around to form chromosomes. Methylation of histones can either increase or decrease transcription of genes, depending on which amino acids in the histones are methylated, and how many methyl groups are attached. Methylation events that weaken chemical attractions between histone tails and DNA increase transcription because they enable the DNA to uncoil from nucleosomes so that transcription factor proteins and RNA polymerase can access the DNA. This process is critical for the regulation of gene expression that allows different cells to express different genes. Function Histone methylation, as a mechanism for modifying chromatin structure is associated with stimulation of neural pathways known to be important for formation of long-term memories and learning. Animal models have shown methylation and other epigenetic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HOX Genes
Hox genes, a subset of homeobox genes, are a group of related genes that specify regions of the body plan of an embryo along the head-tail axis of animals. Hox proteins encode and specify the characteristics of 'position', ensuring that the correct structures form in the correct places of the body. For example, Hox genes in insects specify which appendages form on a segment (for example, legs, antennae, and wings in fruit flies), and Hox genes in vertebrates specify the types and shape of vertebrae that will form. In segmented animals, Hox proteins thus confer segmental or positional identity, but do not form the actual segments themselves. Studies on Hox genes in ciliated larvae have shown they are only expressed in future adult tissues. In larvae with gradual metamorphosis the Hox genes are activated in tissues of the larval body, generally in the trunk region, that will be maintained through metamorphosis. In larvae with complete metamorphosis the Hox genes are mainly express ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KMT2A
Histone-lysine ''N''-methyltransferase 2A also known as acute lymphoblastic leukemia 1 (ALL-1), myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1), or zinc finger protein HRX (HRX) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''KMT2A'' gene. MLL1 is a histone methyltransferase deemed a positive global regulator of gene transcription. This protein belongs to the group of histone-modifying enzymes comprising transactivation domain 9aaTAD; ; and is involved in the epigenetic maintenance of transcriptional memory. Its role as an epigenetic regulator of neuronal function is an ongoing area of research. Function Transcriptional regulation KMT2A gene encodes a transcriptional coactivator that plays an essential role in regulating gene expression during early development and hematopoiesis. The encoded protein contains multiple conserved functional domains. One of these domains, the SET domain, is responsible for its histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferase activity which medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.Kimball's Biology Pages. "Oncogenes" Free full text Most normal cells will undergo a programmed form of rapid cell death ( apoptosis) when critical functions are altered and malfunctioning. Activated oncogenes can cause those cells designated for apoptosis to survive and proliferate instead. Most oncogenes began as proto-oncogenes: normal genes involved in cell growth and proliferation or inhibition of apoptosis. If, through mutation, normal genes promoting cellular growth are up-regulated (gain-of-function mutation), they will predispose the cell to cancer; thus, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |