|
Mitchelstown Cave
Mitchelstown Cave (also known as New Cave) is a limestone cave near Burncourt, County Tipperary, Ireland. Situated from Mitchelstown, County Cork, it became the first cave in Ireland to be developed for the public in 1972. The cave is located near Mitchelstown, County Cork, but is actually in Tipperary off the R639 Mitchelstown. It is a privately owned local landmark and tourist destination, with a number of caverns open to the public through a guided tour. Noteworthy speleothems include the Tower of Babel column. The largest cavern, known as the Tír na Nóg has hosted musical events including a performance by the Celtic Tenors. History While the presence of a nearby cave (referred to variously as Old Cave, Old Mitchelstown Cave or Desmond Cave) has been known in the area at least as far back as 1777, Mitchelstown Cave aka "New Cave" was discovered accidentally by Laura Condon, a farm worker on 3 May 1833. The Mitchelstown Caves are so called, in spite of their distance fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
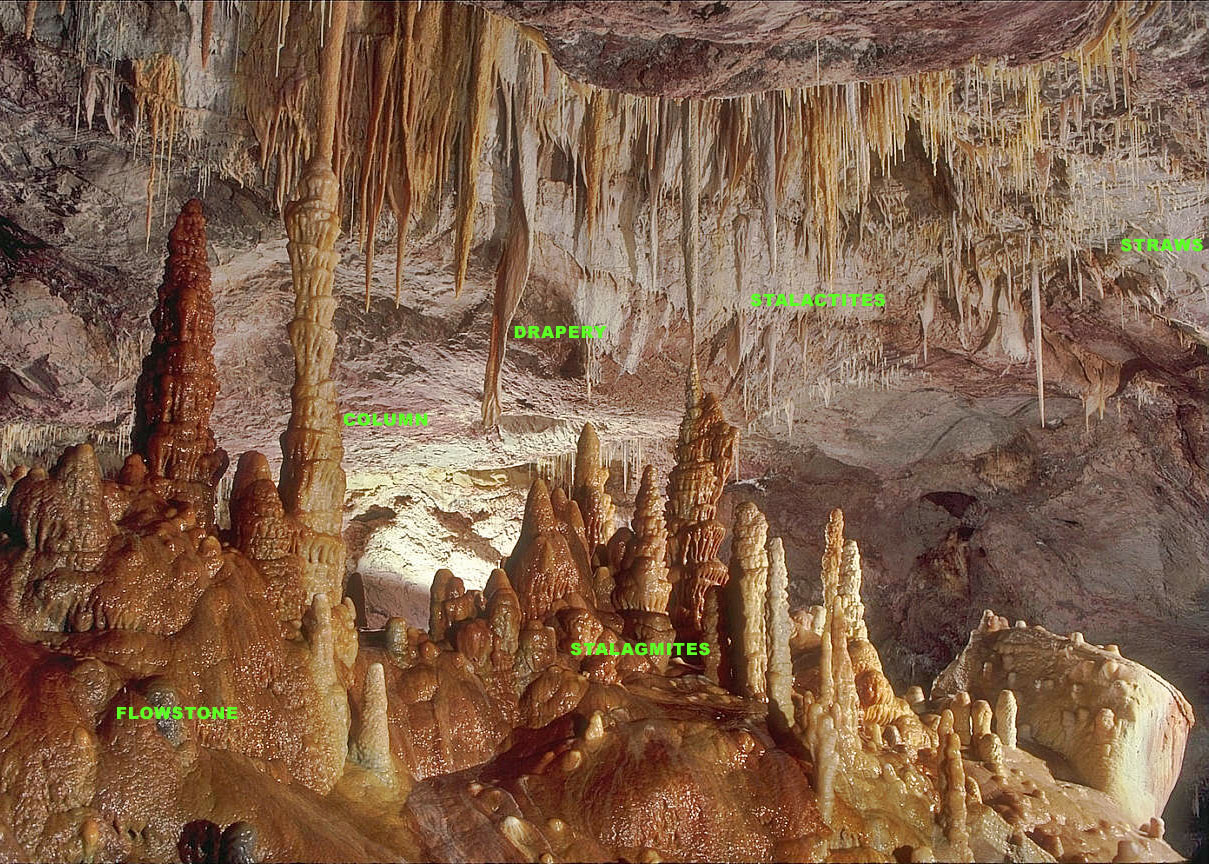
Speleothem
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety of forms, depending on their depositional history and environment. Their chemical composition, gradual growth, and preservation in caves make them useful paleoclimatic proxies. Chemical and physical characteristics More than 300 variations of cave mineral deposits have been identified. The vast majority of speleothems are calcareous, composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) minerals (calcite or aragonite). Less commonly, speleothems are made of calcium sulfate (gypsum or mirabilite) or opal. Speleothems of pure calcium carbonate or calcium sulfate are translucent and colorless. The presence of iron oxide or copper provides a reddish brown color. The presence of manganese oxide can create darker colors such as black or dark brown. Speleothems can also be brown d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert King, 1st Baron Kingsborough
Robert King, 1st Baron Kingsborough (18 February 1724 – 22 May 1755), known as Sir Robert King, Bt, between 1740 and 1748, was an Irish landowner and politician. King was the elder son of Sir Henry King, 3rd Baronet, by Isabella Wingfield, daughter of Edward Wingfield and sister of Richard Wingfield, 1st Viscount Powerscourt. He succeeded his father in the baronetcy in 1740. In 1744 he was returned to the Irish Parliament for Boyle, a seat he held until 1748, when, aged only 24, he was raised to the Irish peerage as Baron Kingsborough. He was also Custos Rotulorum of Roscommon. Lord Kingsborough died in May 1755, aged 31. He never married and the barony died with him. He was succeeded in the baronetcy by his younger brother, Edward, who was created Earl of Kingston in 1768. References , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Kingsborough, Robert King, 1st Baron 1724 births 1755 deaths Barons in the Peerage of Ireland Peers of Ireland created by George II King Robert Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Lloyd Praeger
Robert Lloyd Praeger (25 August 1865 – 5 May 1953) was an Irish naturalist, writer and librarian. Biography From a Unitarian background, he was born and raised in Holywood, County Down. He attended the school of the Reverend McAlister and then the nearby Sullivan Upper School. He worked in the National Library of Ireland in Dublin from 1893 to 1923. He co-founded and edited the '' Irish Naturalist'', and wrote papers on the flora and other aspects of the natural history of Ireland. He organised the Lambay Survey in 1905/06 and, from 1909 to 1915, the wider Clare Island Survey. He was an engineer by qualification, a librarian by profession and a naturalist by inclination. He was awarded the Veitch Memorial Medal of the Royal Horticultural Society in 1921. He became the first President of both An Taisce and the Irish Mountaineering Club in 1948, and served as President of the Royal Irish Academy for 1931–34. He is buried in Deansgrange Cemetery, Dublin, together with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yorkshire Ramblers' Club
The Yorkshire Ramblers' Club (YRC) is the second-oldest mountaineering club in England, the oldest being the Alpine Club. Founded in 1892, the YRC is still a highly active club mountaineering and caving in the UK and all over the world. History On 13 July 1892 four Yorkshire gentlemen met at the home of a Mr. Herbert Slater in Leeds to discuss the idea of forming a club for individuals interested in promoting the idea of walking and the study of the countryside. At an open meeting held at the Skyrack Inn, Headingley on 6 October 1892 it was unanimously decided to form a club to organise walking and mountaineering expeditions and encourage the study of nature. The name of the club was picked from others including The Three Peaks Club, but Yorkshire understatement prevailed and the name Yorkshire Ramblers' Club was chosen. Consequently, "greater attention was paid to climbing the Lake District", in both the club's earliest days and today with the adjoining Scottish Borders a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Survey
A cave survey is a map of all or part of a cave system, which may be produced to meet differing standards of accuracy depending on the cave conditions and equipment available underground. Cave surveying and cartography, i.e. the creation of an accurate, detailed map, is one of the most common technical activities undertaken within a cave and is a fundamental part of speleology. Surveys can be used to compare caves to each other by length, depth and volume, may reveal clues on speleogenesis, provide a spatial reference for other areas of scientific study and assist visitors with route-finding. Traditionally, cave surveys are produced in two-dimensional form due to the confines of print, but given the three-dimensional environment inside a cave, modern techniques using computer aided design are increasingly used to allow a more realistic representation of a cave system. History The first known plan of a cave dates from 1546, and was of a man-made cavern in tufa called the Stufe di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Édouard-Alfred Martel
Édouard-Alfred Martel (1 July 1859, Pontoise, Val-d'Oise – 3 June 1938, Montbrison), the 'father of modern speleology', was a world pioneer of cave exploration, study, and documentation. Martel explored thousands of caves in his native France and many other countries, popularised the pursuit of cave exploration, introduced the concept of speleology as a distinct area of scientific study, maintained an extensive archive, and in 1895 founded , the first organisation devoted to cave science in the world. Life and Exploration Édouard-Alfred Martel was born in Pontoise, Seine-et-Oise on 1 July 1859. Born into a family of lawyers, he studied at the Lycée Condorcet in Paris. Early on, he became passionate about geography and the natural sciences and in 1877 he won first prize in an open competition for geography. He was a great reader of the works of Jules Verne. In 1866, while holidaying with his parents, he visited the Caves of Gargas in the Pyrenees. Other trips allowed him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Greek equivalent of fauna. ''Fauna'' is also the word for a book that catalogues the animals in such a manner. The term was first used b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Review
''The Natural History Review'' was a short-lived, quarterly journal devoted to natural history. It was published in Dublin and London between 1854 and 1865. The ''Natural History Review'' included the transactions of the Belfast Natural History and Philosophical Society, Cork Cuvierian Society, Dublin Natural History Society, Dublin University Zoological Association, and the Literary and Scientific Institution of Kilkenny, as authorised...It was founded by Edward Perceval Wright who was also the editor. The parts are: Vols 1-4, 1854–57; title concludes: ...by the Councils of these Societies (Geological Society of Dublin later added to list) This was continued as ''Natural History Review, and quarterly journal of science''. Edited by Edward Percival Wright, William Henry Harvey, Joseph Reay Greene, Samuel Haughton and Alexander Henry Haliday London, Vols 5-7, 1858-60. In turn continued as ''Natural History Review'': a quarterly journal of biological science. Edited by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Percival Wright
Edward Percival (Perceval) Wright (27 December 1834, Donnybrook – 2 March 1910) FRGSI was an Irish ophthalmic surgeon, botanist and zoologist. Family, education and career He was the eldest son of barrister, Edward Wright and Charlotte Wright. One of his brothers was Charles Henry Hamilton Wright. Edward was educated by a private tutor, and was taught natural history by George James Allman. From 1852 he studied at Trinity College, Dublin, graduating BA in 1857. In that same year he became Curator of the University Museum at Trinity and, the following year, 1858, Lecturer in Zoology, a post which he held for ten years. At the same time he undertook medical studies and lectured in botany at the medical school of Dr Steevens' Hospital, Dublin gaining an M.A. (University of Dublin) in 1859 and an MA Ad eundem degree (University of Oxford). He graduated M.D in 1862. Wright was also a founding editor of the Journal of Anatomy and Physiology in 1867. Wright next studied ophthalmic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Henry Haliday
Alexander Henry Haliday (1806–1870, also known as Enrico Alessandro Haliday, Alexis Heinrich Haliday, or simply Haliday) was an Irish entomologist. He is primarily known for his work on Hymenoptera, Diptera, and Thysanoptera, but worked on all insect orders and on many aspects of entomology. Haliday was born in Carnmoney, Co. Antrim later living in Holywood, County Down, Ireland. A boyhood friend of Robert Templeton, he divided his time between Ireland and Lucca, where he co-founded the Italian Entomological Society with Camillo Rondani and Adolfo Targioni Tozzetti. He was a member of the Royal Irish Academy, the Belfast Natural History Society, the Microscopical Society of London, and the Galileiana Academy of Arts and Science, as well as a fellow of the (now Royal) Entomological Society of London. Alexander Haliday was among the greatest dipterists of the 19th century and one of the most renowned British entomologists. His achievements were in four main fields: desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speleologist
Speleology is the scientific study of caves and other karst features, as well as their make-up, structure, physical properties, history, life forms, and the processes by which they form (speleogenesis) and change over time (speleomorphology). The term ''speleology'' is also sometimes applied to the recreational activity of exploring caves, but this is more properly known as ''caving'', ''potholing'' (British English), or ''spelunking''. Speleology and caving are often connected, as the physical skills required for ''in situ'' study are the same. Speleology is a cross-disciplinary field that combines the knowledge of chemistry, biology, geology, physics, meteorology, and cartography to develop portraits of caves as complex, evolving systems. History Before modern speleology developed, John Beaumont wrote detailed descriptions of some Mendip caves in the 1680s. The term speleology was coined by Émile Rivière in 1890. Prior to the mid-nineteenth century the scientific valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.png)



