|
Mission Beach, Queensland
Mission Beach is a coastal town and Suburbs and localities (Australia), locality in the Cassowary Coast Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , the locality of Mission Beach had a population of 815 people. Geography Mission Beach is bounded on the east by the Coral Sea. Clump Point () is the northern end of a sandy beach long facing the Coral Sea which runs south to Tam O'Shanter Point in South Mission Beach at the southern end. History Djiru The region has been inhabited for at least the past 5,000 years by a rainforest dwelling people collectively known as the Djiru people. Remains of middens, fish traps, rock-shelter paintings and ceremonial sites are located around Mission Beach and Dunk Island. Djiru people made large wooden swords and built wet-season villages consisting of dome-shaped huts thatched with palm fronds and paperbark. British exploration Lieutenant James Cook sailed through the area in 1770, naming Dunk Island. Clump Point was descriptively named in 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
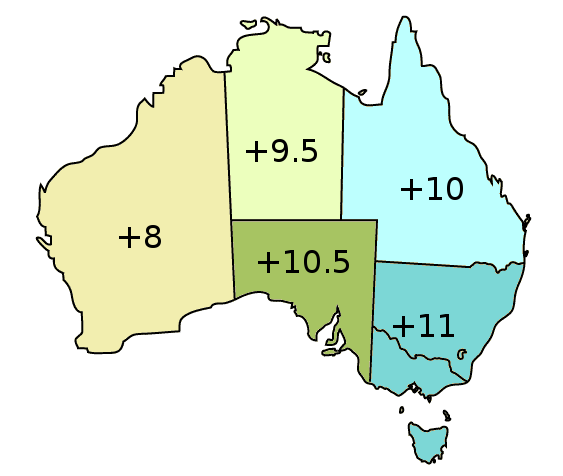
AEST
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones. Standard time was introduced in the 1890s when all of the Australian colonies adopted it. Before the switch to standard time zones, each local city or town was free to determine its local time, called local mean time. Now, Western Australia uses Western Standard Time; South Australia and the Northern Territory use Central Standard Time; while New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Jervis Bay Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory use Eastern Standard Time. Daylight saving time (+1 hour) is used in jurisdictions in the south and south-east: South Australia, New South Wales, Vict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and to New Zealand and Australia in particular. He made detailed maps of Newfoundland prior to making three voyages to the Pacific, during which he achieved the first recorded European contact with the eastern coastline of Australia and the Hawaiian Islands, and the first recorded circumnavigation of New Zealand. Cook joined the British merchant navy as a teenager and joined the Royal Navy in 1755. He saw action in the Seven Years' War and subsequently surveyed and mapped much of the entrance to the St. Lawrence River during the siege of Quebec, which brought him to the attention of the Admiralty and the Royal Society. This acclaim came at a crucial moment for the direction of British overseas exploration, and it led to his commission in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schooner also has a square topsail on the foremast, to which may be added a topgallant. Differing definitions leave uncertain whether the addition of a fore course would make such a vessel a brigantine. Many schooners are gaff-rigged, but other examples include Bermuda rig and the staysail schooner. The origins of schooner rigged vessels is obscure, but there is good evidence of them from the early 17th century in paintings by Dutch marine artists. The name "schooner" first appeared in eastern North America in the early 1700s. The name may be related to a Scots word meaning to skip over water, or to skip stones. The schooner rig was used in vessels with a wide range of purposes. On a fast hull, good ability to windward was useful for priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Moresby
Rear Admiral John Moresby (15 March 1830 – 12 July 1922) was a British naval officer who explored the coast of New Guinea and was the first European to discover the site of Port Moresby. Life and career Moresby was born in Allerford, Somerset, England, the son of Eliza Louisa and Admiral of the Fleet Sir Fairfax Moresby. He joined the navy at an early age as a Volunteer 1st Class in HMS ''Victor'', and rose to be in charge of the 1,031 ton paddle steamer cruiser HMS ''Basilisk'' in which he made hydrological surveys around eastern New Guinea. During the survey of the southern coast he discovered the harbour which he named Fairfax after his father. The town established there, based on already existing native villages (principally Hanuabada) was named Port Moresby and is now the nation's capital. John Moresby was also searching for a shorter route between Australia and China and on the eastern tip of the island he discovered the China Strait. He continued exploring along the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Police
Australian native police units, consisting of Aboriginal troopers under the command (usually) of at least one white officer, existed in various forms in all Australian mainland colonies during the nineteenth and, in some cases, into the twentieth centuries. The Native Mounted Police utilised horses as their transportation mode in the days before motor cars, and patrolled huge geographic areas. The introduction of a Police presence helped provide law & order to areas which were already struggling with crime issues. From established base camps they patrolled vast areas to investigate law breaches, including alleged murders. Often armed with rifles, carbines and swords, they sometimes also escorted surveying groups, pastoralists and prospectors through country considered to be dangerous. The Aboriginal men within the Native Police were routinely recruited from areas that were very distant from the locations in which they were deployed. As the troopers were Aboriginal, this benefit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Arthur Johnstone
Robert Arthur Johnstone (1843 – 16 January 1905) was an officer in the Native Police paramilitary force which operated in the British imperial colony of Queensland. He was stationed at various locations in central and northern Queensland between 1867 and 1880 conducting regular punitive expeditions against clans of Indigenous Australians who resisted colonisation. He also participated in several surveying expeditions in Far North Queensland, including those under the leadership of George Elphinstone Dalrymple, providing well-armed protection for the expeditionary memers. As a result of being at the frontier of British colonial expansion in this region of Australia, a number of geographical and zoological entities are named after him, such as the Johnstone River and the freshwater crocodile. After resigning from the Native Police in 1880, Johnstone was a police magistrate in various locations around Queensland before he retired from government service in 1891. In his years of du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardwell, Queensland
Cardwell is a coastal town and rural locality in the Cassowary Coast Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , the locality of Cardwell had a population of 1,309 people. Geography The Bruce Highway National Highway 1 and the North Coast railway line are the dominant transport routes; connecting with the Queensland provincial cities of Cairns and Townsville. Cardwell railway station in Bowen Street serves the town (). The town is a long narrow strip hugging the coast with Greenwood Hill immediately to the west of the town () rising to above sea level. West of Cardwell the rugged topography of the Cardwell Range intercepts the trade winds resulting in high rainfall. The coastal escarpment is covered in rainforest which transitions to the west to eucalypt woodland and tropical savanna. Cardwell Range biodiversity has been protected by the introduction of Forestry Reserves, National Parks and Queensland World Heritage Wet Tropics Areas. Seaward lies the Hinchinbrook Channel () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea). It is a simplified version of Motu, from the Austronesian l ...: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Mainland Australia, Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua (province), Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua (province), West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Kennedy
Edmund Besley Court Kennedy J. P. (5 September 1818 – December 1848) was an explorer in Australia in the mid nineteenth century. He was the Assistant-Surveyor of New South Wales, working with Sir Thomas Mitchell. Kennedy explored the interior of Queensland and northern New South Wales, including the Thomson River, the Barcoo River, Cooper Creek, and Cape York Peninsula. He died in December 1848 after being speared by Aboriginal Australians in far north Queensland near Cape York. Early life Kennedy was born on 5 September 1818 on Guernsey in the Channel Islands to Colonel Thomas Kennedy (British Army) and Mary Ann (Smith) Kennedy. He was the sixth born of nine children, comprising five boys and four girls. Kennedy was educated at Elizabeth College Guernsey, and expressed an early interest in surveying. In 1837 he went to Rio de Janeiro, returning to England in 1838 when the business house in which he worked closed down. A naval officer friend of the family, Captain Charl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape York Peninsula
Cape York Peninsula is a large peninsula located in Far North Queensland, Australia. It is the largest unspoiled wilderness in northern Australia.Mittermeier, R.E. et al. (2002). Wilderness: Earth’s last wild places. Mexico City: Agrupación Sierra Madre, S.C. The land is mostly flat and about half of the area is used for grazing cattle. The relatively undisturbed eucalyptus-wooded savannahs, tropical rainforests and other types of habitat are now recognised and preserved for their global environmental significance. Although much of the peninsula remains pristine, with a diverse repertoire of endemic flora and fauna, some of its wildlife may be threatened by industry and overgrazing as well as introduced species and weeds.Mackey, B. G., Nix, H., & Hitchcock, P. (2001). The natural heritage significance of Cape York Peninsula. Retrieved 15 January 2008, froepa.qld.gov.au. The northernmost point of the peninsula is Cape York (). The land has been occupied by a number of Abor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Rattlesnake (1822)
HMS ''Rattlesnake'' was an 28-gun sixth-rate corvette of the Royal Navy launched in 1822. She made a historic voyage of discovery to the Cape York and Torres Strait areas of northern Australia. Construction Launched at Chatham Dockyard on 26 March 1822, ''Rattlesnake'' was 114 feet (34.7 m) long and 32 feet (9.7 m) abeam. She carried twenty 32-pounder carronades, six 18-pounder carronades and two 9-pounder long guns. Service in the Greek War of Independence For most of the years 1827 to 1829 ''Rattlesnake'' was cruising off the coasts of Greece, under the command of Captain the Hon. Charles Orlando Bridgeman. During that period her log was kept by Midshipman Talavera Vernon Anson and survives in a collection at the New York Public Library. Both men went on to become admirals. On 31 January 1828, ''Rattlesnake'' was part of a force of five British and two French ships that attacked the Greek island of Gramvousa, used as a base for piracy. While most of the pirat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |