|
Missaguash River
The Missaguash River (French: Rivière Missaguash) is a small Canadian river that forms the southern portion of the inter-provincial boundary between Nova Scotia and New Brunswick on the Isthmus of Chignecto. It had historic significance in the 18th century as the ''de facto'' border between French (to the west) and English-controlled territories. History The river's name is from the ''Mi'kmaq'' language, likely meaning "marsh river", in reference to the Tantramar Marshes through which it flows. The name can be translated as "muskrat". Musaguash (Morris, 1750); Mesiguash (DesBarres, 1781); Missaguash from 1901 onward. The river flows south into Cumberland Basin. Its source is in the Missaguash Bog, several kilometres to the north. About 1672 a small group of Acadians from Port Royal, led by Jacques Bourgeois, formed a settlement on the south bank of the Missaguash near its mouth named Beaubassin. The settlers reclaimed the salt marsh bordering the Missaquash for cultivation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missaguash River
The Missaguash River (French: Rivière Missaguash) is a small Canadian river that forms the southern portion of the inter-provincial boundary between Nova Scotia and New Brunswick on the Isthmus of Chignecto. It had historic significance in the 18th century as the ''de facto'' border between French (to the west) and English-controlled territories. History The river's name is from the ''Mi'kmaq'' language, likely meaning "marsh river", in reference to the Tantramar Marshes through which it flows. The name can be translated as "muskrat". Musaguash (Morris, 1750); Mesiguash (DesBarres, 1781); Missaguash from 1901 onward. The river flows south into Cumberland Basin. Its source is in the Missaguash Bog, several kilometres to the north. About 1672 a small group of Acadians from Port Royal, led by Jacques Bourgeois, formed a settlement on the south bank of the Missaguash near its mouth named Beaubassin. The settlers reclaimed the salt marsh bordering the Missaquash for cultivation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dike (construction)
A levee (), dike ( American English), dyke ( Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually earthen and that often runs parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastlines. The purpose of a levee is to keep the course of rivers from changing and to protect against flooding of the area adjoining the river or coast. Levees can be naturally occurring ridge structures that form next to the bank of a river, or be an artificially constructed fill or wall that regulates water levels. Ancient civilizations in the Indus Valley, ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia and China all built levees. Today, levees can be found around the world, and failures of levees due to erosion or other causes can be major disasters. Etymology Speakers of American English (notably in the Midwest and Deep South) use the word ''levee'', from the French word (from the feminine past participle of the French verb , 'to raise'). It ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
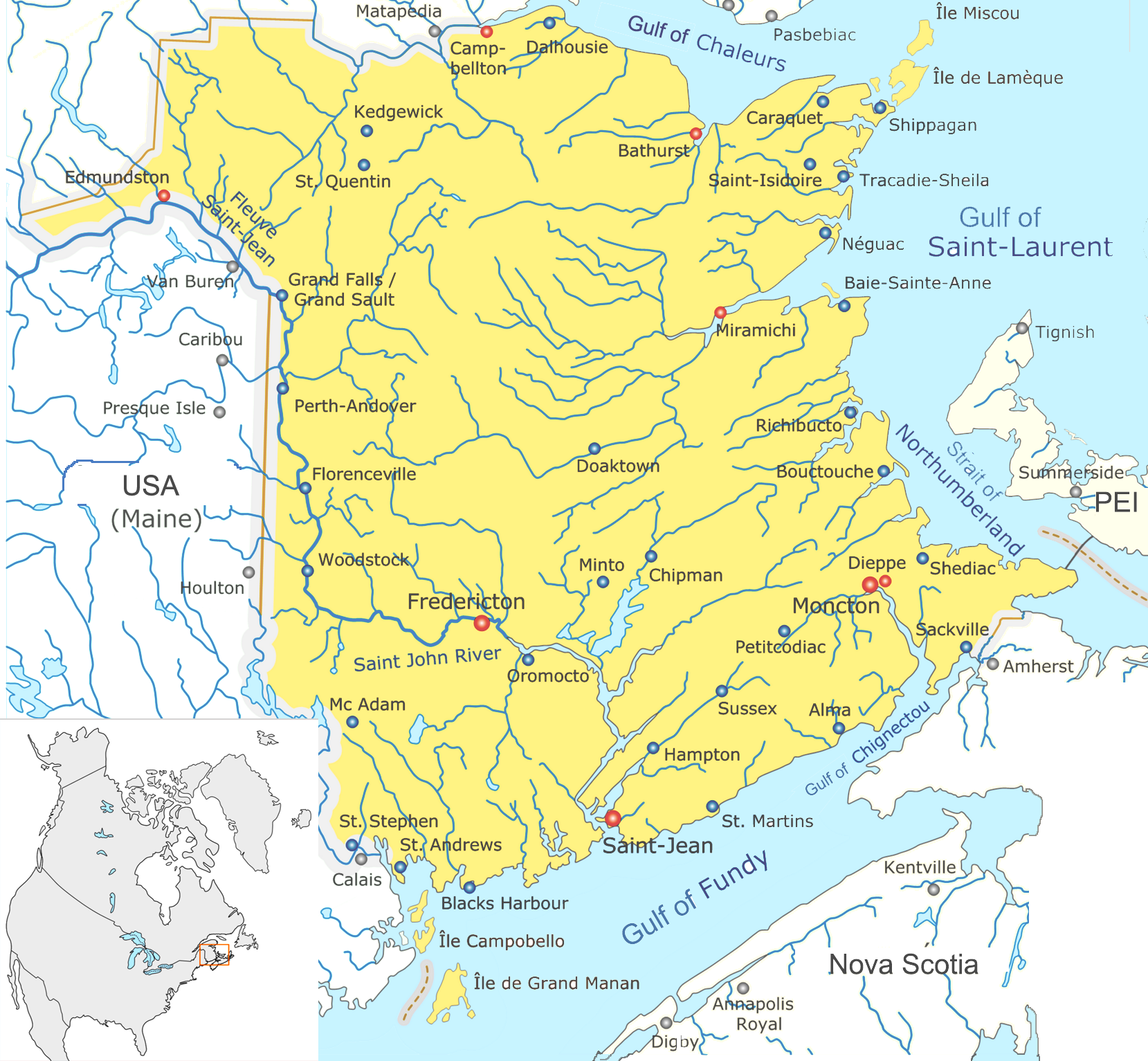
Rivers Of New Brunswick
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as creek, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague. Rivers are part of the water cycle. Water generally collects in a river from precipitation through a drainage basin from surface runoff and other sources such as groundwater recharge, springs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivers Of Nova Scotia
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as creek, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague. Rivers are part of the water cycle. Water generally collects in a river from precipitation through a drainage basin from surface runoff and other sources such as groundwater recharge, sprin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rivers Of Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia's rivers all flow into the Atlantic Ocean through four unique watersheds: the Gulf of Maine, the Northumberland Strait, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and into the Atlantic Ocean itself. Gulf of Maine The Gulf of Maine system includes the Bay of Fundy, which includes the Cumberland and Minas Basins. In Nova Scotia, the system occupies the shores from Fort Lawrence to Cape St. Mary (44°05′N). Bay of Fundy The Bay of Fundy coastline in Nova Scotia begins at Fort Lawrence and circles Cape Chignecto eastward to Truro. It then follows west along the Annapolis Valley as far as Brier Island on the Digby Neck. Within the Bay of Fundy are two basins: Chignecto Bay which begins at Fort Lawrence and ends at Cape Chignecto, and the Minas Basin that encompasses everything east of Ramshead Point (near Diligent River) and Cape Split. *Apple River (Note: westernmost river on the north coast of the Bay of Fundy) *Fox River *Ramshead River *Diligent River (Note: easternmost r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bodies Of Water Of New Brunswick
This is a List of bodies of water in the Canadian province of New Brunswick, including waterfalls. New Brunswick receives precipitation year-round, which feeds numerous streams and rivers. There are two main discharge basins: the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the east and north and the Bay of Fundy to the south. The major rivers are the Saint John River (Wolastoq) and the Miramichi River. Bodies of water See also *List of bays in New Brunswick *List of lakes in New Brunswick *List of mountains in New Brunswick *List of islands of New Brunswick *List of waterfalls in Canada References External links * *Map of New Brunswick Watershed Groups and Provisional Water Classification* * Map of the main rivers of New Brunswick in French * {{Rivers of New Brunswick New Brunswick * Bodies of water New Brunswick New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
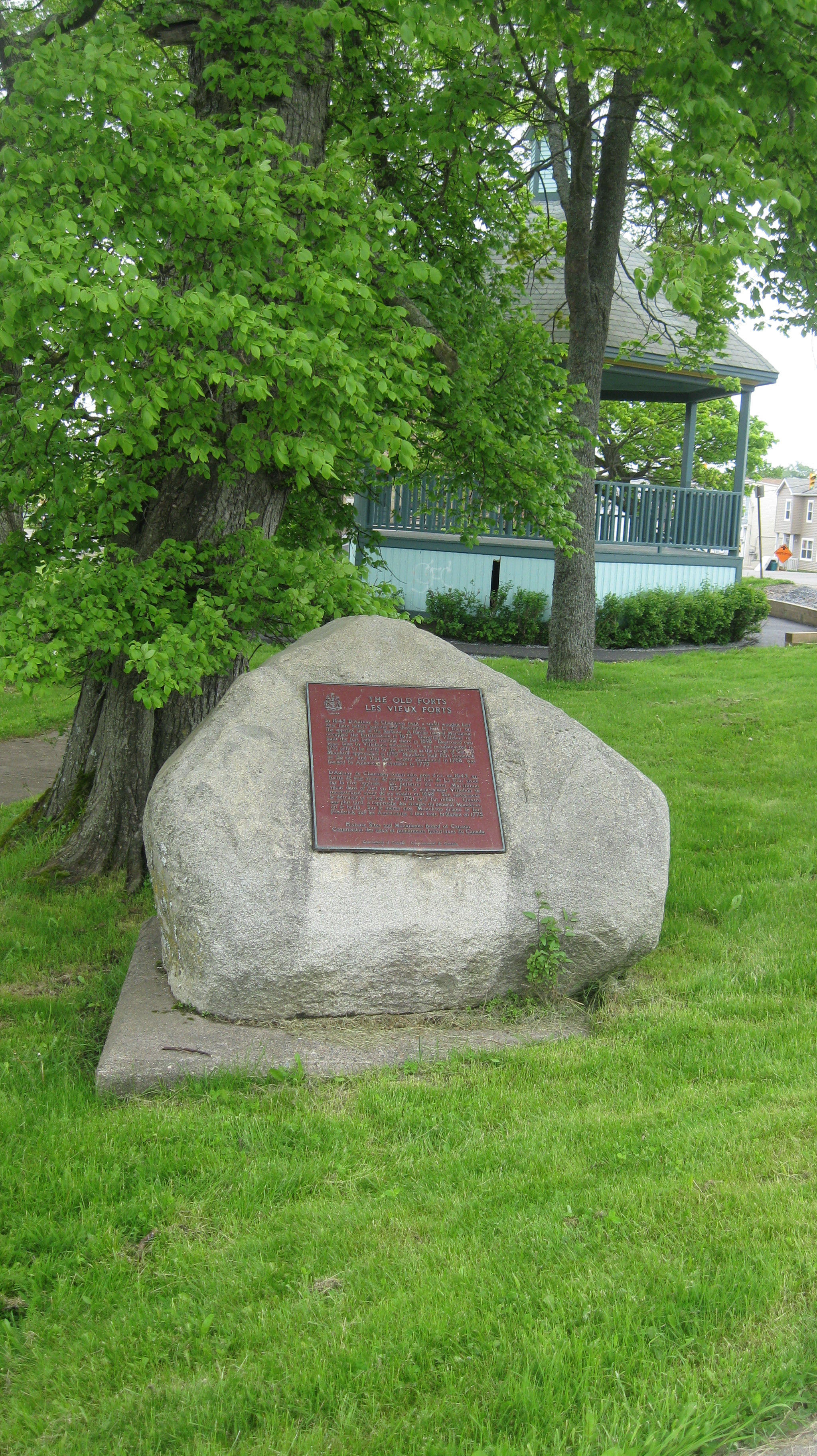
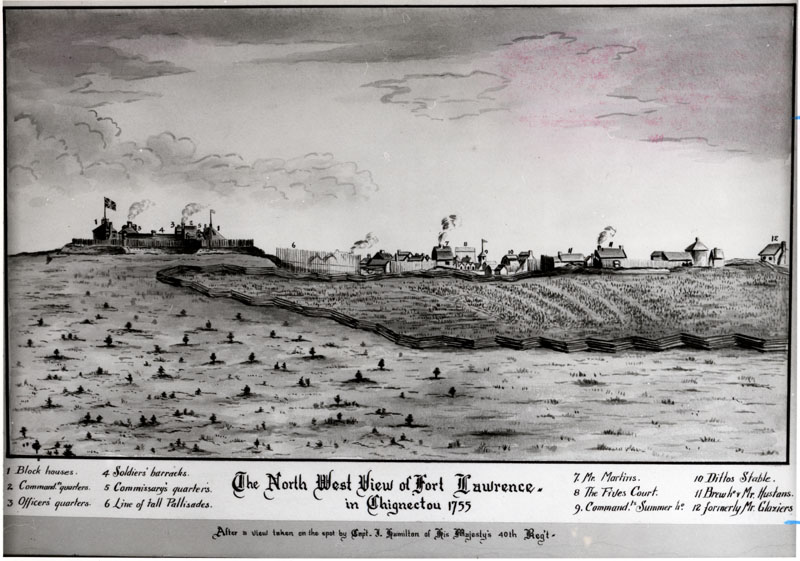
Fort Lawrence
Fort Lawrence was a British fort built during Father Le Loutre's War and located on the Isthmus of Chignecto (in the modern-day community of Fort Lawrence). Father Le Loutre's War Despite the British Conquest of Acadia in 1710, Nova Scotia remained primarily occupied by Catholic Acadians and Mi'kmaq. Father Le Loutre's War began after Edward Cornwallis arrived to establish Halifax with 13 transports on June 21, 1749. The British quickly began to build other settlements. To guard against Mi'kmaq, Acadian and French attacks on the new Protestant settlements, British fortifications were erected in Halifax (1749), Bedford (Fort Sackville) (1749), Dartmouth (1750), Lunenburg (1753), and Lawrencetown (1754). Within 18 months of establishing Halifax, the British also took firm control of peninsula Nova Scotia by building fortifications in all the major Acadian communities: present-day Windsor ( Fort Edward); Grand-Pré (Fort Vieux Logis) and Chignecto (Fort Lawrence). A British fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lawrence (British Army Officer)
Brigadier-General Charles Lawrence (14 December 1709 – 19 October 1760) was a British military officer who, as lieutenant governor and subsequently governor of Nova Scotia, is perhaps best known for overseeing the Expulsion of the Acadians and settling the New England Planters in Nova Scotia. He was born in Plymouth, England, and died in Halifax, Nova Scotia. According to historian Elizabeth Griffiths, Lawrence was seen as a "competent", "efficient" officer with a "service record that had earned him fairly rapid promotion, a person of considerable administrative talent who was trusted by both Cornwallis and Hopson." He is buried in the crypt of St. Paul's Church (Halifax). Early career Lawrence was born in Plymouth (Devon) on 14 December 1709. He followed his father, General Charles John Lawrence, who is said to have served in Flanders under John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, into a military career. Charles Lawrence's earlier life is obscure. He was commissioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Army
The English Army existed while was an independent state and was at war with other states, but it was not until the Interregnum and the New Model Army (raised by Parliament to defeat the Royalists in the ) that England acquired a peacetime professional |
Siege Of Annapolis Royal (1744)
The siege of Annapolis Royal (also known as the siege of Fort Anne) in 1744 involved two of four attempts by the French, along with their Acadian and native allies, to regain the capital of Nova Scotia/Acadia, Annapolis Royal, during King George's War. The siege is noted for Governor of Nova Scotia Paul Mascarene successfully defending the last British outpost in the colony and for the first arrival of New England Ranger John Gorham to Nova Scotia. The French and Mi'kmaq land forces were thwarted on both attempts on the capital because of the failure of French naval support to arrive. Historical context The conquest of Acadia by Great Britain began with the 1710 capture of the provincial capital, Port Royal. In the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht, France formally ceded Acadia to Britain. However, there was disagreement about the provincial boundaries, and some Acadians also resisted British rule. With renewed war imminent in 1744, the leaders of New France formulated plans to retake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Deschamps De Boishébert Et De Raffetot
Charles Deschamps de Boishébert (also known as Courrier du Bois, Bois Hebert) was a member of the Compagnies Franches de la Marine and was a significant leader of the Acadian militia's resistance to the Expulsion of the Acadians. He settled and tried to protect Acadians refugees along the rivers of New Brunswick. At Beaubears National Park on Beaubears Island, New Brunswick he settled refugee Acadians during the Expulsion of the Acadians. King George's War Siege of Annapolis Royal From October until 3 November 1746, Boishebert took part in the unsuccessful Siege of Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia (N.S.), the British administrative and military headquarters in Acadia. Battle at Port-la-Joye After the first Siege of Louisbourg in May–June 1745, a British force composed largely of New England irregulars proceeded to seize Île Saint-Jean (present day Prince Edward Island) and its capital Port-la-Joye, which had a French garrison consisting of about 15 soldiers and 100 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mi'kmaq People
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the northeastern region of Maine. The traditional national territory of the Mi'kmaq is named Miꞌkmaꞌki (or Miꞌgmaꞌgi). There are 170,000 Mi'kmaq people in the region, (including 18,044 members in the recently formed Qalipu First Nation in Newfoundland.) Nearly 11,000 members speak Miꞌkmaq, an Eastern Algonquian language. Once written in Miꞌkmaw hieroglyphic writing, it is now written using most letters of the Latin alphabet. The Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and Pasamaquoddy nations signed a series of treaties known as the Covenant Chain of Peace and Friendship Treaties with the British Crown throughout the eighteenth century; the first was signed in 1725, and the last in 1779. The Miꞌkmaq maintain that they did not cede or give up the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_by_Dominic_Serres%2C_c._1765.jpg)


