|
Mir Asadollah Madani
Mir Asadollah Madani Dehkharghani (1914 – 11 September 1981) was an Iran, Iranian politician and Shia cleric. He was the second Imam Jumu'ah of Tabriz, the Imam Jumu'ah of Hamadan, the representative of the Supreme Leader of Iran, Supreme Leader in East Azerbaijan for less than a year, and a member of the Muslim People's Republic Party. Madani was also Hamadan Province's representative in the first term of the Assembly of Experts. He was Assassination, assassinated on 11 September 1981. According to Tehran radio, he was killed by a guerrilla with a grenade. Iranian government press sometimes refers to him as "the second martyr of Mihrab." Political activity In 1970, Mir Asadollah Madani returned to Iran in opposition to the rule of Mohammad Reza Pahlavi. However, his actions resulted in him being exiled to Bandar Kangan. He was later arrested by SAVAK and was deported several times in the 1960s. He used SAVAK to escape the pressures of the religious spectrum in 1972, banis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, serve as community leaders, and provide religious guidance. Thus for Sunnis, anyone can study the basic Islamic sciences and become an Imam. For most Shia Muslims, the Imams are absolute infallible leaders of the Islamic community after the Prophet. Shias consider the term to be only applicable to the members and descendents of the '' Ahl al-Bayt'', the family of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In Twelver Shiasm there are 14 infallibles, 12 of which are Imams, the final being Imam Mahdi who will return at the end of times. The title was also used by the Zaidi Shia Imams of Yemen, who eventually founded the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen (1918–1970). Sunni imams Sunni Islam does not have imams in the same sense as the Shi'a, an importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleric
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the terms used for individual clergy are clergyman, clergywoman, clergyperson, churchman, and cleric, while clerk in holy orders has a long history but is rarely used. In Christianity, the specific names and roles of the clergy vary by denomination and there is a wide range of formal and informal clergy positions, including deacons, elders, priests, bishops, preachers, pastors, presbyters, ministers, and the pope. In Islam, a religious leader is often known formally or informally as an imam, caliph, qadi, mufti, mullah, muezzin, or ayatollah. In the Jewish tradition, a religious leader is often a rabbi (teacher) or hazzan (cantor). Etymology The word ''cleric'' comes from the ecclesiastical Latin ''Clericus'', for those belonging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
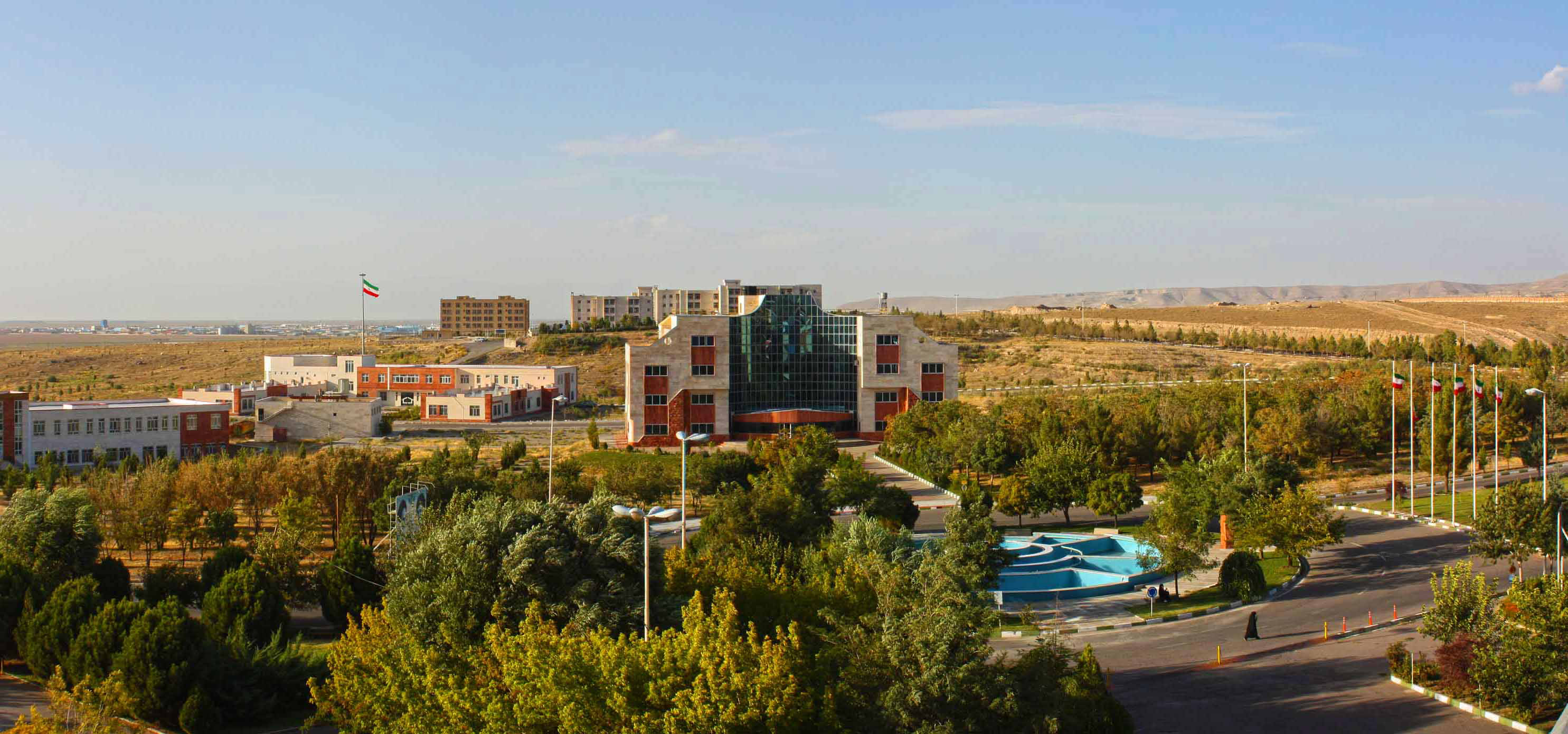
Azarbaijan Shahid Madani University
Azarbaijan Shahid Madani University, ( fa, دانشگاه شهید مدنی آذربایجان, ''Danushgah-e Shihid-e Midâni-ye Âzerbaijan'') commonly called only ''Azarbaijan University'', is a public university located near Tabriz, East Azerbaijan Province, Iran, founded in 1987. The university provides both undergraduate and graduate education to approximately 7,500 students at a wide range of fields including engineering, basic sciences, literature and theology. The university has got Research Gate's total impact point of 1716.47 from 61 publications, according to the latest statistics. History Azarbaijan University was founded in 1987 in Tabriz as a branch of Tehran's Tarbiat Moallem (teacher education) University. The initial objective of the university was to train teachers in different area for the fulfillment of Iranian government educational development policies and the major concern of the university was focused on training teachers for high schools and technical scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
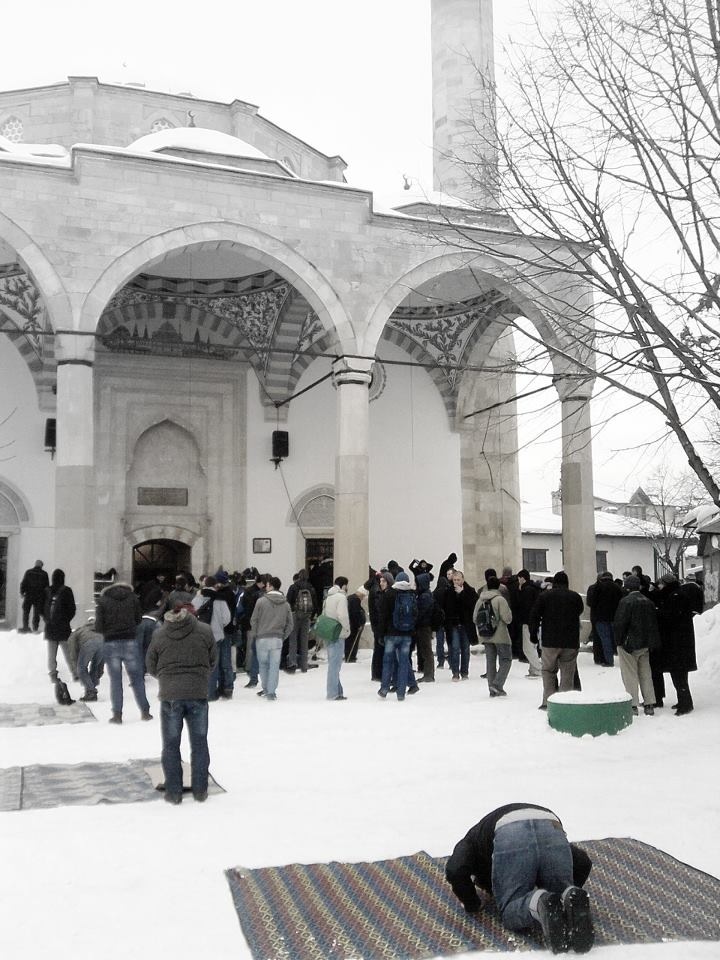
Mihrab
Mihrab ( ar, محراب, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "qibla wall". The ''minbar'', which is the raised platform from which an imam (leader of prayer) addresses the congregation, is located to the right of the mihrab. Etymology The origin of the word ''miḥrāb'' is complicated and multiple explanations have been proposed by different sources and scholars. It may come from Old South Arabian (possibly Sabaic) ''mḥrb'' meaning a certain part of a palace, as well as "part of a temple where ''tḥrb'' (a certain type of visions) is obtained," from the root word ''ḥrb'' "to perform a certain religious ritual (which is compared to combat or fighting and described as an overnight retreat) in the ''mḥrb'' of the temple." It may also possibly be related to Ethiopic ''məkʷrab'' "temple, sanctua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friday Prayer
In Islam, Friday prayer or Congregational prayer ( ar, صَلَاة ٱلْجُمُعَة, ') is a prayer ('' ṣalāt'') that Muslims hold every Friday, after noon instead of the Zuhr prayer. Muslims ordinarily pray five times each day according to the sun's sky path regardless of time zones. ''Jumu’ah'' means Friday in the Arabic language. In many Muslim countries, the weekend is inclusive of Fridays, while in others, Fridays are half-days for schools and some workplaces. Meaning It is one of the most exalted Islamic rituals and one of its confirmed obligatory acts. Obligation There is consensus among Muslims regarding the Friday prayer (''salat al-jum‘ah'') being ''wajib'' - required - in accordance with the Quranic verse, as well as the many traditions narrated both by Shi’i and Sunni sources. According to the majority of Sunni schools and some Shiite jurists, Friday prayer is a religious obligation, but their differences were based on whether its obligation is condit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynasty under Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, and the replacement of his government with an Islamic republic under the rule of Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, a leader of one of the factions in the revolt. The revolution was supported by various leftist and Islamist organizations. After the 1953 Iranian coup d'état, Pahlavi had aligned with the United States and the Western Bloc to rule more firmly as an authoritarian monarch. He relied heavily on support from the United States to hold on to power which he held for a further 26 years. This led to the 1963 White Revolution and the arrest and exile of Ayatollah Khomeini in 1964. Amidst massive tensions between Khomeini and the Shah, demonstrations began in October 1977, developing into a campaign of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamedan
Hamadan () or Hamedan ( fa, همدان, ''Hamedān'') (Old Persian: Haŋgmetana, Ecbatana) is the capital city of Hamadan Province of Iran. At the 2019 census, its population was 783,300 in 230,775 families. The majority of people living in Hamadan identify as ethnic Persians. Hamedan is believed to be among the oldest Iranian cities. It is possible that it was occupied by the Assyrians in 1100 BCE; the Ancient Greek historian, Herodotus, states that it was the capital of the Medes, around 700 BCE. Hamedan has a green mountainous area in the foothills of the 3,574-meter Alvand Mountain, in the midwest part of Iran. The city is 1,850 meters above sea level. The highly cultural nature of this old city and its historic sites attract tourists during the summer to this city, located approximately southwest of Tehran. The major sights of this city are the Ganj Nameh inscription, the Avicenna monument and the Baba Taher monument. The main language in the city is Persian. History A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAVAK
SAVAK ( fa, ساواک, abbreviation for ''Sâzemân-e Ettelâ'ât va Amniat-e Kešvar'', ) was the secret police, domestic security and intelligence service in Iran during the reign of the Pahlavi dynasty. SAVAK operated from 1957 until prime minister Shapour Bakhtiar ordered its dissolution during the climax of the 1979 Iranian Revolution. SAVAK had 5,000 agents at its peak. Gholam Reza Afkhami estimates SAVAK staffing at between 4,000 and 6,000. ''Time'' magazine's 19 February 1979 publication also states that it had 5,000 members.SAVAK: "Like the CIA". Feb. 19, 1979 . History 1957–1971 After the |
Bandar Kangan
Bandar Kangan ( fa, بندر كنگان, also Romanized as Bandar-e Kangān; also known as Kangān and Kangun) is a city in the Central District of Kangan County, Bushehr province, Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ..., and serves as capital of the county. At the 2006 census, its population was 23,921 in 5,200 households. The following census in 2011 counted 76,329 people in 9,304 households. The latest census in 2016 showed a population of 60,187 people in 19,225 households. Language The linguistic composition of the city: References Cities in Bushehr Province Populated places in Kangan County {{Kangan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohammad Reza Pahlavi
, title = Shahanshah Aryamehr Bozorg Arteshtaran , image = File:Shah_fullsize.jpg , caption = Shah in 1973 , succession = Shah of Iran , reign = 16 September 1941 – 11 February 1979 , coronation = 26 October 1967 , predecessor = Reza Shah , successor = ''Monarchy abolished''Ruhollah Khomeini as Supreme Leader , birth_date = , birth_place = Tehran, Sublime State of Persia , death_date = , death_place = Cairo, Egypt , burial_place = 29 July 1980Al-Rifa'i Mosque, Cairo, Egypt , spouse = , issue = , regnal name = Mohammad Reza Shah fa, محمدرضا شاه , native_lang1 = Alma mater , native_lang1_name1 = , house = Pahlavi , father = Reza Shah , mother = Tadj ol-Molouk , religion = Twelver Shi’ism , signature = , module = Mohammad Reza Pahlavi ( fa, محمدرضا پهلوی, ; 26 October 1919 – 27 July 1980), also known as Mohammad Reza Shah (), was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mashregh
The Mashriq ( ar, ٱلْمَشْرِق), sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", the name is derived from the verb ''sharaqa'' ( ar, شرق, link=no "to shine, illuminate, radiate" and "to rise"), from sh-r-q root (ش-ر-ق), referring to the east, where the sun rises. The region includes the Arab states of Bahrain, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Geography As the word ''Mashriq'' refers to Arab countries located between the Mediterranean Sea and Iran, it is the companion term to '' Maghreb'' ( ar, ٱلْمَغْرِب), the western part of North Africa. Libya may be regarded as straddling the two regions, receiving influences from both the Maghreb and the Mashriq, with its eastern part ( Cyrenaica) being linked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihrab
Mihrab ( ar, محراب, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "qibla wall". The ''minbar'', which is the raised platform from which an imam (leader of prayer) addresses the congregation, is located to the right of the mihrab. Etymology The origin of the word ''miḥrāb'' is complicated and multiple explanations have been proposed by different sources and scholars. It may come from Old South Arabian (possibly Sabaic) ''mḥrb'' meaning a certain part of a palace, as well as "part of a temple where ''tḥrb'' (a certain type of visions) is obtained," from the root word ''ḥrb'' "to perform a certain religious ritual (which is compared to combat or fighting and described as an overnight retreat) in the ''mḥrb'' of the temple." It may also possibly be related to Ethiopic ''məkʷrab'' "temple, sanctua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)