|
Minimal-entropy Martingale Measure
In probability theory, the minimal-entropy martingale measure (MEMM) is the risk-neutral probability measure that minimises the entropy difference between the objective probability measure, P, and the risk-neutral measure, Q. In incomplete markets, this is one way of choosing a risk-neutral measure (from the infinite number available) so as to still maintain the no-arbitrage conditions. The MEMM has the advantage that the measure Q will always be equivalent to the measure P by construction. Another common choice of equivalent martingale measure is the minimal martingale measure, which minimises the variance of the equivalent martingale. For certain situations, the resultant measure Q will not be equivalent to P. In a finite probability model, for objective probabilities p_i and risk-neutral probabilities q_i then one must minimise the Kullback–Leibler divergence In mathematical statistics, the Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence (also called relative entropy and I-divergence), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Theory
Probability theory or probability calculus is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set of axioms of probability, axioms. Typically these axioms formalise probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure (mathematics), measure taking values between 0 and 1, termed the probability measure, to a set of outcomes called the sample space. Any specified subset of the sample space is called an event (probability theory), event. Central subjects in probability theory include discrete and continuous random variables, probability distributions, and stochastic processes (which provide mathematical abstractions of determinism, non-deterministic or uncertain processes or measured Quantity, quantities that may either be single occurrences or evolve over time in a random fashion). Although it is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. Entropy is central to the second law of thermodynamics, which states that the entropy of an isolated system left to spontaneous evolution cannot decrease with time. As a result, isolated systems evolve toward thermodynamic equilibrium, where the entropy is highest. A consequence of the second law of thermodynamics is that certain processes are irreversible. The thermodynami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incomplete Market
In economics, incomplete markets are markets in which there does not exist an Arrow–Debreu security for every possible state of nature. In contrast with complete markets, this shortage of securities will likely restrict individuals from transferring the desired level of wealth among states. An Arrow security purchased or sold at date ''t'' is a contract promising to deliver one unit of income in one of the possible contingencies which can occur at date ''t'' + 1. If at each date-event there exists a complete set of such contracts, one for each contingency that can occur at the following date, individuals will trade these contracts in order to insure against future risks, targeting a desirable and budget feasible level of consumption in each state (i.e. consumption smoothing). In most set ups when these contracts are not available, optimal risk sharing between agents will not be possible. For this scenario, agents (homeowners, workers, firms, investors, etc.) will lack the instrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk-neutral Measure
In mathematical finance, a risk-neutral measure (also called an equilibrium measure, or '' equivalent martingale measure'') is a probability measure such that each share price is exactly equal to the discounted expectation of the share price under this measure. This is heavily used in the pricing of financial derivatives due to the fundamental theorem of asset pricing, which implies that in a complete market, a derivative's price is the discounted expected value of the future payoff under the unique risk-neutral measure. Such a measure exists if and only if the market is arbitrage-free. A risk-neutral measure is a probability measure The easiest way to remember what the risk-neutral measure is, or to explain it to a probability generalist who might not know much about finance, is to realize that it is: # The probability measure of a transformed random variable. Typically this transformation is the utility function of the payoff. The risk-neutral measure would be the measure co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martingale Measure
In mathematical finance, a risk-neutral measure (also called an equilibrium measure, or ''equivalent martingale measure'') is a probability measure such that each share price is exactly equal to the discounted expectation of the share price under this measure. This is heavily used in the pricing of financial derivatives due to the fundamental theorem of asset pricing, which implies that in a complete market, a derivative's price is the discounted expected value of the future payoff under the unique risk-neutral measure. Such a measure exists if and only if the market is arbitrage-free. A risk-neutral measure is a probability measure The easiest way to remember what the risk-neutral measure is, or to explain it to a probability generalist who might not know much about finance, is to realize that it is: # The probability measure of a transformed random variable. Typically this transformation is the utility function of the payoff. The risk-neutral measure would be the measure cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martingale (probability Theory)
In probability theory, a martingale is a stochastic process in which the expected value of the next observation, given all prior observations, is equal to the most recent value. In other words, the conditional expectation of the next value, given the past, is equal to the present value. Martingales are used to model fair games, where future expected winnings are equal to the current amount regardless of past outcomes. History Originally, ''martingale (betting system), martingale'' referred to a class of betting strategy, betting strategies that was popular in 18th-century France. The simplest of these strategies was designed for a game in which the gambler wins their stake if a coin comes up heads and loses it if the coin comes up tails. The strategy had the gambler double their bet after every loss so that the first win would recover all previous losses plus win a profit equal to the original stake. As the gambler's wealth and available time jointly approach infinity, their pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
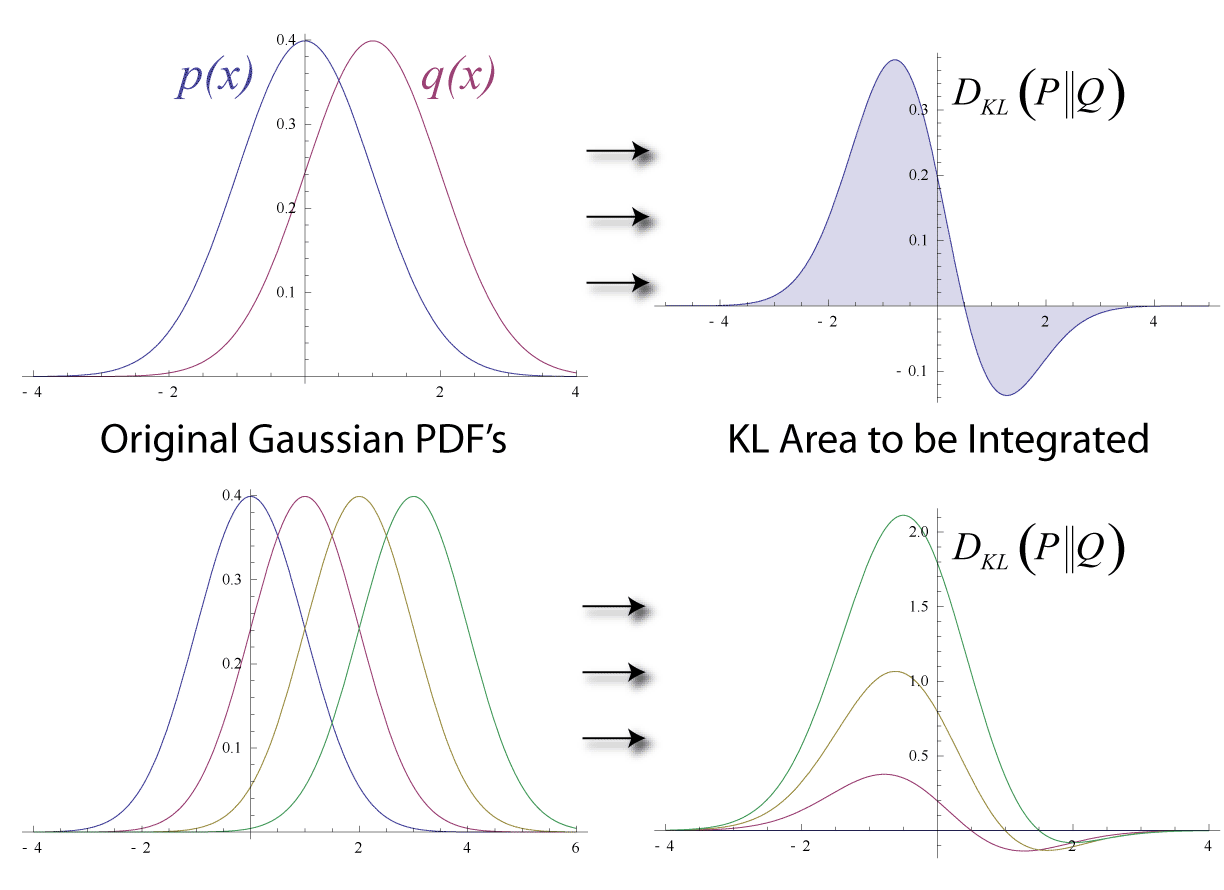
Kullback–Leibler Divergence
In mathematical statistics, the Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence (also called relative entropy and I-divergence), denoted D_\text(P \parallel Q), is a type of statistical distance: a measure of how much a model probability distribution is different from a true probability distribution . Mathematically, it is defined as D_\text(P \parallel Q) = \sum_ P(x) \, \log \frac\text A simple interpretation of the KL divergence of from is the expected excess surprise from using as a model instead of when the actual distribution is . While it is a measure of how different two distributions are and is thus a distance in some sense, it is not actually a metric, which is the most familiar and formal type of distance. In particular, it is not symmetric in the two distributions (in contrast to variation of information), and does not satisfy the triangle inequality. Instead, in terms of information geometry, it is a type of divergence, a generalization of squared distance, and for cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |