|
Migma
Migma, sometimes migmatron or migmacell, was a proposed colliding beam fusion reactor designed by Bogdan Maglich in 1969. Migma uses self-intersecting beams of ions from small particle accelerators to force the ions to fuse. Similar systems using larger collections of particles, up to microscopic dust sized, were referred to as " macrons". Migma was an area of some research in the 1970s and early 1980s, but lack of funding precluded further development. Conventional fusion Fusion takes place when atoms come into close proximity and the nuclear strong force pulls their nuclei together. Counteracting this process is the fact that the nuclei are all positively charged, and thus repel each other due to the electrostatic force. In order for fusion to occur, the nuclei must have enough energy to overcome this coulomb barrier. The barrier is lowered for atoms with less positive charge, those with the fewest protons, and the strong force is increased with additional nucleons, the total num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colliding Beam Fusion
Colliding beam fusion (CBF), or colliding beam fusion reactor (CBFR), is a class of fusion power concepts that are based on two or more intersecting beams of fusion fuel ions that are independently accelerated to fusion energies using a variety of particle accelerator designs or other means. One of the beams may be replaced by a static target, in which case the approach is termed ''accelerator based fusion'' or ''beam-target fusion'', but the physics is the same as colliding beams. CBFRs face several problems that have limited their ability to be seriously considered as candidates for fusion power. When two ions collide, they are more likely to scatter than to fuse. Magnetic confinement fusion reactors overcome this problem using a bulk plasma and confining it for some time so that the ions have many thousands of chances to collide. Two beams colliding give ions little time to interact before the beams fly apart. This limits how much fusion power a beam-beam machine can make. CB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogdan Maglich
Bogdan Castle Maglich (also spelled Maglic or Maglić) (August 5, 1928, Sombor, Yugoslavia – November 25, 2017, Newport Beach, California, US) was a Serbian experimental nuclear physicist and the leading advocate of a purported non-radioactive aneutronic fusion energy source. Maglich built four models of ''Migma'', devices producing fusion of deuterium atoms in colliding ion beams. Education and academic work Maglich received his Bachelor of Science degree from the University of Belgrade in 1951, his Master of Science from the University of Liverpool in 1955, and his Ph.D. in high-energy physics and nuclear engineering from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1959. Upon receiving his Ph.D., Maglich joined Dr. Luis Walter Alvarez's research group at Lawrence Berkeley Lab. During this time, he, along with Fred Kirsten, invented the "sonic spark chamber", the first film-less spark chamber particle detector system. Maglich participated in the discovery of the omega mes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles ( neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises due to the difference in nuclear binding energy between the atomic nuclei before and after the reaction. Nuclear fusion is the process that powers active or main-sequence stars and other high-magnitude stars, where large amounts of energy are released. A nuclear fusion process that produces atomic nuclei lighter than iron-56 or nickel-62 will generally release energy. These elements have a relatively small mass and a relatively large binding energy per nucleon. Fusion of nuclei lighter than these releases energy (an exothermic process), while the fusion of heavier nuclei results in energy retained by the product nucleons, and the resulting reaction is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Confinement Fusion
Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) is a fusion energy process that initiates nuclear fusion reactions by compressing and heating targets filled with thermonuclear fuel. In modern machines, the targets are small spherical pellets about the size of a pinhead typically containing a mixture of about 10 milligrams of deuterium 2H and tritium 3H. To compress and heat the fuel, energy is deposited in the outer layer of the target using high-energy beams of photons, electrons or ions, although almost all ICF devices used lasers. The beams heat the outer layer, which explodes outward. This produces a reaction force against the remainder of the target, which accelerates it inwards and compresses the fuel. This process also creates shock waves that travel inward through the target. Sufficiently powerful shock waves can compress and heat the fuel at the center such that fusion occurs. ICF is one of two major branches of fusion energy research, the other is magnetic confinement fusion. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bremsstrahlung
''Bremsstrahlung'' (), from "to brake" and "radiation"; i.e., "braking radiation" or "deceleration radiation", is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into radiation (i.e., photons), thus satisfying the law of conservation of energy. The term is also used to refer to the process of producing the radiation. ''Bremsstrahlung'' has a continuous spectrum, which becomes more intense and whose peak intensity shifts toward higher frequencies as the change of the energy of the decelerated particles increases. Broadly speaking, ''bremsstrahlung'' or braking radiation is any radiation produced due to the deceleration (negative acceleration) of a charged particle, which includes synchrotron radiation (i.e., photon emission by a relativistic particle), cyclotron radiation (i.e. photon emission by a no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
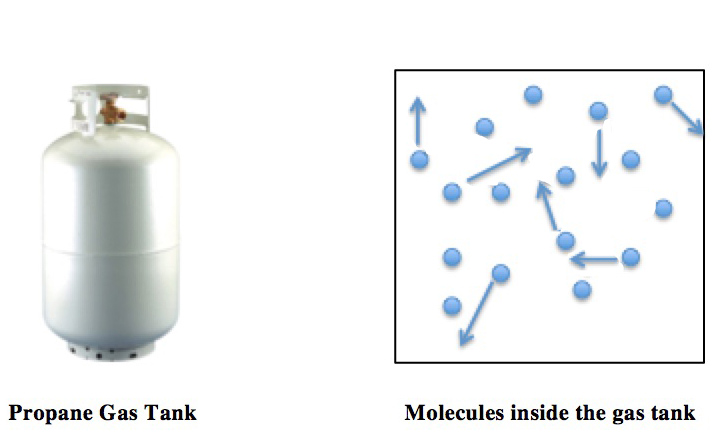
Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form: pV = nRT where p, V and T are the pressure, volume and Thermodynamic temperature, temperature; n is the amount of substance; and R is the ideal gas constant. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory of gases, kinetic theory, as was achieved (apparently independently) by August Krönig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857. Equation The state function, state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. The temperature used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta (plasma Physics)
The beta of a plasma, symbolized by ''β'', is the ratio of the plasma pressure (''p'' = ''n'' ''k''B ''T'') to the magnetic pressure (''p''mag = ''B''²/2 ''μ''0). The term is commonly used in studies of the Sun and Earth's magnetic field, and in the field of fusion power designs. In the fusion power field, plasma is often confined using strong magnets. Since the temperature of the fuel scales with pressure, reactors attempt to reach the highest pressures possible. The costs of large magnets roughly scales like ''β½''. Therefore, beta can be thought of as a ratio of money out to money in for a reactor, and beta can be thought of (very approximately) as an economic indicator of reactor efficiency. For tokamaks, betas of larger than 0.05 or 5% are desired for economically viable electrical production. The same term is also used when discussing the interactions of the solar wind with various magnetic fields. For example, beta in the corona of the Sun is about 0.01. Backgroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Scientist (magazine)
''The Scientist'' is a professional magazine intended for life scientists. Coverage includes articles on recently published research papers, current research, techniques, important career news, profiles of established and up and coming scientists, publishing, research integrity and best practices, as well as other columns and reports of interest to its readers. The editor-in-chief is Bob Grant. Overview The main purpose of the magazine is to provide print and online coverage of the latest developments in life sciences research, technology, careers, and business. Subject matter covered by the magazine includes: groundbreaking research, industry innovations, careers, financial topics, economics of science, scientific ethics, profiles of scientists, lab tools, scientific publishing, techniques, product spotlight, and guides History ''The Scientist'' was founded by Eugene Garfield in 1986. In 1988, Garfield sold ''The Scientist'', part of the ''Institute for Scientific Infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aneutronic Fusion
Aneutronic fusion is any form of fusion power in which very little of the energy released is carried by neutrons. While the lowest-threshold nuclear fusion reactions release up to 80% of their energy in the form of neutrons, aneutronic reactions release energy in the form of charged particles, typically protons or alpha particles. Successful aneutronic fusion would greatly reduce problems associated with neutron radiation such as damaging ionizing radiation, neutron activation, reactor maintenance, and requirements for biological shielding, remote handling and safety. Since it is simpler to convert the energy of charged particles into electrical power than it is to convert energy from uncharged particles, an aneutronic reaction would be attractive for power systems. Some proponents see a potential for dramatic cost reductions by converting energy directly to electricity, as well as in eliminating the radiation from neutrons, which are difficult to shield against. However, the cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirograph
Spirograph is a geometric drawing device that produces mathematical roulette curves of the variety technically known as hypotrochoids and epitrochoids. The well-known toy version was developed by British engineer Denys Fisher and first sold in 1965. The name has been a registered trademark of Hasbro Inc. since 1998 following purchase of the company that had acquired the Denys Fisher company. The Spirograph brand was relaunched worldwide in 2013, with its original product configurations, by Kahootz Toys. History In 1827, Greek-born English architect and engineer Peter Hubert Desvignes developed and advertised a "Speiragraph", a device to create elaborate spiral drawings. A man named J. Jopling soon claimed to have previously invented similar methods. When working in Vienna between 1845 and 1848, Desvignes constructed a version of the machine that would help prevent banknote forgeries, as any of the nearly endless variations of roulette patterns that it could produce were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precess
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called ''nutation''. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced. In astronomy, ''precession'' refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters. An important example is the steady change in the orientation of the axis of rotation of the Earth, known as the precession of the equinoxes. Torque-free Torque-free precession implies that no external moment (torque) is applied to the body. In torque-free precession, the angular momentum is a constant, but the angular veloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Texas
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 graduate students and 3,133 teaching faculty as of Fall 2021, it is also the largest institution in the system. It is ranked among the top universities in the world by major college and university rankings, and admission to its programs is considered highly selective. UT Austin is considered one of the United States's Public Ivies. The university is a major center for academic research, with research expenditures totaling $679.8 million for fiscal year 2018. It joined the Association of American Universities in 1929. The university houses seven museums and seventeen libraries, including the LBJ Presidential Library and the Blanton Museum of Art, and operates various auxiliary research facilities, such as the J. J. Pickle Research C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |