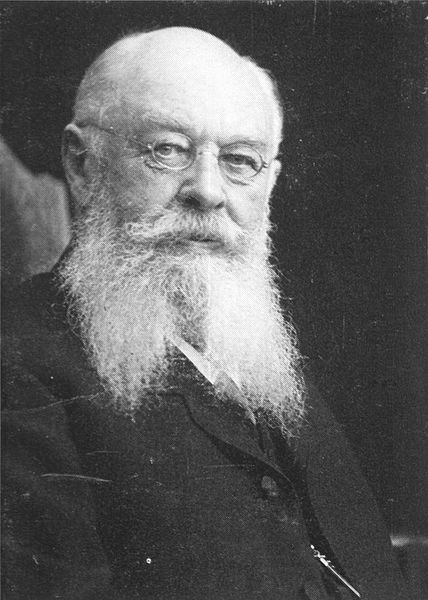|
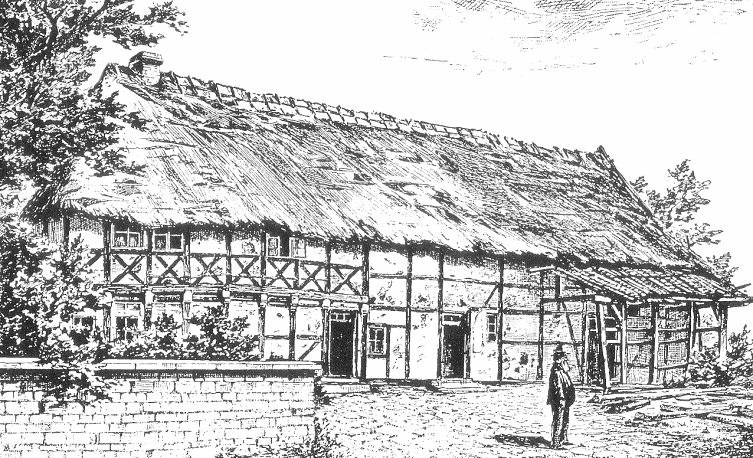
Middle German House
The Middle German house (german: mitteldeutsches Haus, Ernhaus) is a style of traditional German farmhouse which is predominantly found in Central Germany. It is known by a variety of other names, many of which indicate its regional distribution: * ''Ernhaus'' (hall house, hall kitchen house) * ''Oberdeutsches Haus'' (Upper German house) * ''Thüringisches Haus'' (Thuringian house) * ''Fränkisches Haus'' (Franconian house) The Middle German house first emerged in the Middle Ages as a type of farmhouse built either using timber framing or stone. It is an 'all-in-one' house (''Einhaus'') with living quarters and livestock stalls under one roof. This rural type of farmstead still forms part of the scene in many villages in the central and southern areas of Germany. The northern boundary of its distribution area is roughly where the Central Uplands merge into the North German Plain. There, its place is gradually taken by the Low German house (''Fachhallenhaus''), known colloquially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jettying
Jettying (jetty, jutty, from Old French ''getee, jette'') is a building technique used in medieval timber-frame buildings in which an upper floor projects beyond the dimensions of the floor below. This has the advantage of increasing the available space in the building without obstructing the street. Jettied floors are also termed ''jetties''. In the U.S., the most common surviving colonial version of this is the garrison house. Most jetties are external, but some early medieval houses were built with internal jetties. Structure A jetty is an upper floor that depends on a cantilever system in which a horizontal beam, the jetty bressummer, supports the wall above and projects forward beyond the floor below (a technique also called ''oversailing''). The bressummer (or breastsummer) itself rests on the ends of a row of jetty beams or joists which are supported by jetty plates. Jetty joists in their turn were slotted sideways into the diagonal dragon beams at angle of 45° by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Styles
{{disambiguation ...
House style may refer to: * Standards for writing as specified in the internal style guide of a particular institution, for example, a book publishing company, newspaper, professional organization, or university * Standards for illustration or graphic design, as an aspect of corporate or organizational identity, or as used for the overall output of a comic book publisher or animation studio * Types of residential structures (see List of house styles) See also * House organ A house organ (also variously known an in-house magazine, in-house publication, house journal, shop paper, plant paper, or employee magazine) is a magazine or periodical A periodical literature (also called a periodical publication or simp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture In Germany
The architecture of Germany has a long, rich and diverse history. Every major European style from Roman to Postmodern is represented, including renowned examples of Carolingian, Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance, Baroque, Classical, Modern and International Style architecture. Centuries of fragmentation of Germany into principalities and kingdoms caused a great regional diversity and favoured vernacular architecture. This made for a heterogeneous and diverse architectural style, with architecture differing from town to town. While this diversity may still be witnessed in small towns, the devastation of architectural heritage in the larger cities during World War II resulted in extensive rebuilding characterized by simple modernist architecture. In this context, however, it must be emphasized that many German cities had already changed their face in the course of industrialization in the 19th and 20th centuries. Cities like Munich or Berlin (population around 1500: 13000/8000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houses In Germany
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Andree
Richard Andree (26 February 1835 – 22 February 1912) was a German geographer and cartographer, noted for devoting himself especially to ethnographic studies. He wrote numerous books on this subject, dealing notably with the races of his own country, while an important general work was ''Ethnographische Parallelen und Vergleiche'' (Stuttgart, 1878). Biography Andree was born in Braunschweig, the son of geographer Karl Andree (1808–1875). He followed in the footsteps of his father, studied natural sciences at the Braunschweig Collegium Carolinum and Leipzig University, and temporarily worked in a Bohemian ironworks. As a director of the geography bureau of publisher Velhagen & Klasing in Leipzig from 1873 to 1890, he also took up cartography, having a chief share in the production of the ''Physikalisch-Statistischer Atlas des Deutschen Reichs'' (together with Oscar Peschel, Leipzig, 1877) and the ''Allgemeiner Historischer Handatlas'', (with Gustav Droysen, son of Johann Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernacular Architecture
Vernacular architecture is building done outside any academic tradition, and without professional guidance. This category encompasses a wide range and variety of building types, with differing methods of construction, from around the world, both historical and extant, representing the majority of buildings and settlements created in pre-industrial societies. Vernacular architecture constitutes 95% of the world's built environment, as estimated in 1995 by Amos Rapoport, as measured against the small percentage of new buildings every year designed by architects and built by engineers. Vernacular architecture usually serves immediate, local needs; is constrained by the materials available in its particular region; and reflects local traditions and cultural practices. Traditionally, the study of vernacular architecture did not examine formally schooled architects, but instead that of the design skills and tradition of local builders, who were rarely given any attribution for the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geestharden House
The Geestharden house (german: Geesthardenhaus), also called the Cimbrian house (''Cimbrisches Haus''), Schleswig house (''Schleswiger Haus''), Slesvig house ( da, Slesvigsk gård) or Southern Jutland house (''Sønderjysk gård'') due to its geographical spread in Jutland, is one of three basic forms on which the many farmhouse types in the north German state of Schleswig-Holstein are based. The other two basic designs are the Gulf house (including its variant, the Haubarg) and the Low German hall house. By far the best known variant of the Geestharden house is the Uthland-Frisian house (''Uhtlandfriesische Haus'' or ''Frisergård''), which is also referred to as the Frisian house (''Friesenhaus''). Geographical spread In spite of its description, the Geestharden house is not just found on geest, a rolling landscape that was formed as a result of ice age glacial deposition, but also in the ''Marsch'', the flat marshlands on the North Sea coast of Germany.Vollmer, Manfred et al. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Frisian Farmhouse
An Old Frisian farmhouse (german: Altfriesisches Bauernhaus) is a small unit farmhouse (''Wohnstallhaus'') that combined the farmer's living area and animals' stalls, and had limited space for storing harvest products. It was widely distributed across the North German Plain until the middle of the 17th century and was the forerunner of the Gulf house. Gallery File:Exterieur overzicht kop-hals-romp boerderij - 20000310 - RCE.jpg, Exterior of a headneck trunk farm File:Overzicht voorgevel en rechter zijgevel, boerderij - Boksum - 20346097 - RCE.jpg, View of facade and right side wall, farm at Boksum, Netherlands File:Exterieur KOP, HALS EN ROMPBOERDERIJ - Burum - 20315014 - RCE.jpg, House and barn, Burum, Netherlands File:Voorgevel album 3, blz. 76 - Follega - 20467952 - RCE.jpg, Frisian farmhouse, Netherlands File:Kop-hals-rompboerderij Twijzel.JPG, Head-neck-trunk farm, Twijzel, Netherlands See also * Old Frisian longhouse Old Frisian longhouses were, as the name indicates, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf House
A Gulf house (german: Gulfhaus), also called a Gulf farmhouse (''Gulfhof'') or East Frisian house (''Ostfriesenhaus''), is a type of byre-dwelling that emerged in the 16th and 17th centuries in North Germany.Vollmer, Manfred et al., ''Landscape and Cultural Heritage in the Wadden Sea Region'', Wadden Sea Ecosystem No. 12 - 2001, CWSS, Wilhelmshaven, 2001. ISSN 0946-896X. It is timber-framed and built using post-and-beam construction. Initially Gulf houses appeared in the marshes, but later spread to the Frisian geest. They were distributed across the North Sea coastal regions from West Flanders through the Netherlands, East Frisia and Oldenburg as far as Schleswig-Holstein (as a variant called the Haubarg). This spread was interrupted by the Elbe-Weser Triangle which developed a type of Low German house instead, better known as the Low Saxon house. Historically, the Gulf house belongs to a larger group of aisled barns, which also include medieval tithe barns, monastery gran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byre-dwelling
A byre-dwelling ("byre"+ "dwelling") is a farmhouse in which the living quarters are combined with the livestock and/or grain barn under the same roof. In the latter case, the building is mostly called an housebarn. This kind of construction is found in archaeological sites in northwestern Europe from the Bronze Age. It was also used in more modern times by Mennonites in Flanders and the Netherlands. Distribution Austria The Bregenzerwälderhaus from the Bregenz Forest in Vorarlberg is an example for a byre-dwelling. The stable and the usually two-storey house are under one roof. Germany The generic German term is ''Wohnstallhaus'' from ''Wohnung'' ("dwelling"), ''Stall'' ("byre", " sty)" and ''Haus'' ("house"). From the Iron Age onwards the longhouse, developed from the byre-dwellings of the Bronze Age with its domestic area and adjacent cattle bays, was found across the North German Plain. As a result of the keeping of ever larger herds of cattle, these buildings be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocklestove
A masonry heater (also called a masonry stove) is a device for warming an interior space through radiant heating, by capturing the heat from periodic burning of fuel (usually wood), and then radiating the heat at a fairly constant temperature for a long period. Masonry heaters covered in tile are called cocklestoves (also tile stoves or ceramic stoves). The technology has existed in different forms, from back into the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods. Archaeological digs have revealed excavations of ancient inhabitants utilizing hot smoke from fires in their subterranean dwellings, to radiate into the living spaces. These early forms have evolved into modern systems. Evidence found from 5,000 B.C. of massive blocks of masonry used to retain heat foreshadowed early forms of fire hearths that were used as multifunctional heating sources. Later evolutions came in the Roman ''hypocaust'' and Austro-German cocklestove (''Kachelofen'', literally "tile oven", or ''Steinofen'', "ston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |