|
Microhedylacea
Acochlidiacea, common name acochlidians, are a taxonomic clade of very unusual sea snails and sea and freshwater slugs, aquatic gastropod mollusks within the large clade Heterobranchia. Acochlidia is a variant spelling. Description These are mostly very small animals, without a shell or gills, distinguished by the visceral mass being sharply set off from the rest of the body. Being a small group with only 30 species worldwide known in 2010, and 32 species described in 2011, and 33 in 2012 (+9 undescribed ''Pontohedyle'' species), these slugs are morphologically and biologically highly aberrant and diverse, comprising a series of unusual characters (e.g. secondary gonochorism, lack of copulatory organs, asymmetric radulae). Most acochlidians live interstitially in marine sands, while some have conquered limnic systems (uniquely within opisthobranch gastropods). Taxonomy Nils Hjalmar Odhner established this taxon as a family in 1937, when he created the families Microhedylid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microhedylacea
Acochlidiacea, common name acochlidians, are a taxonomic clade of very unusual sea snails and sea and freshwater slugs, aquatic gastropod mollusks within the large clade Heterobranchia. Acochlidia is a variant spelling. Description These are mostly very small animals, without a shell or gills, distinguished by the visceral mass being sharply set off from the rest of the body. Being a small group with only 30 species worldwide known in 2010, and 32 species described in 2011, and 33 in 2012 (+9 undescribed ''Pontohedyle'' species), these slugs are morphologically and biologically highly aberrant and diverse, comprising a series of unusual characters (e.g. secondary gonochorism, lack of copulatory organs, asymmetric radulae). Most acochlidians live interstitially in marine sands, while some have conquered limnic systems (uniquely within opisthobranch gastropods). Taxonomy Nils Hjalmar Odhner established this taxon as a family in 1937, when he created the families Microhedylid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedylopsacea
Acochlidiacea, common name acochlidians, are a taxonomic clade of very unusual sea snails and sea and freshwater slugs, aquatic gastropod mollusks within the large clade Heterobranchia. Acochlidia is a variant spelling. Description These are mostly very small animals, without a shell or gills, distinguished by the visceral mass being sharply set off from the rest of the body. Being a small group with only 30 species worldwide known in 2010, and 32 species described in 2011, and 33 in 2012 (+9 undescribed ''Pontohedyle'' species), these slugs are morphologically and biologically highly aberrant and diverse, comprising a series of unusual characters (e.g. secondary gonochorism, lack of copulatory organs, asymmetric radulae). Most acochlidians live interstitially in marine sands, while some have conquered limnic systems (uniquely within opisthobranch gastropods). Taxonomy Nils Hjalmar Odhner established this taxon as a family in 1937, when he created the families Microhedylid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
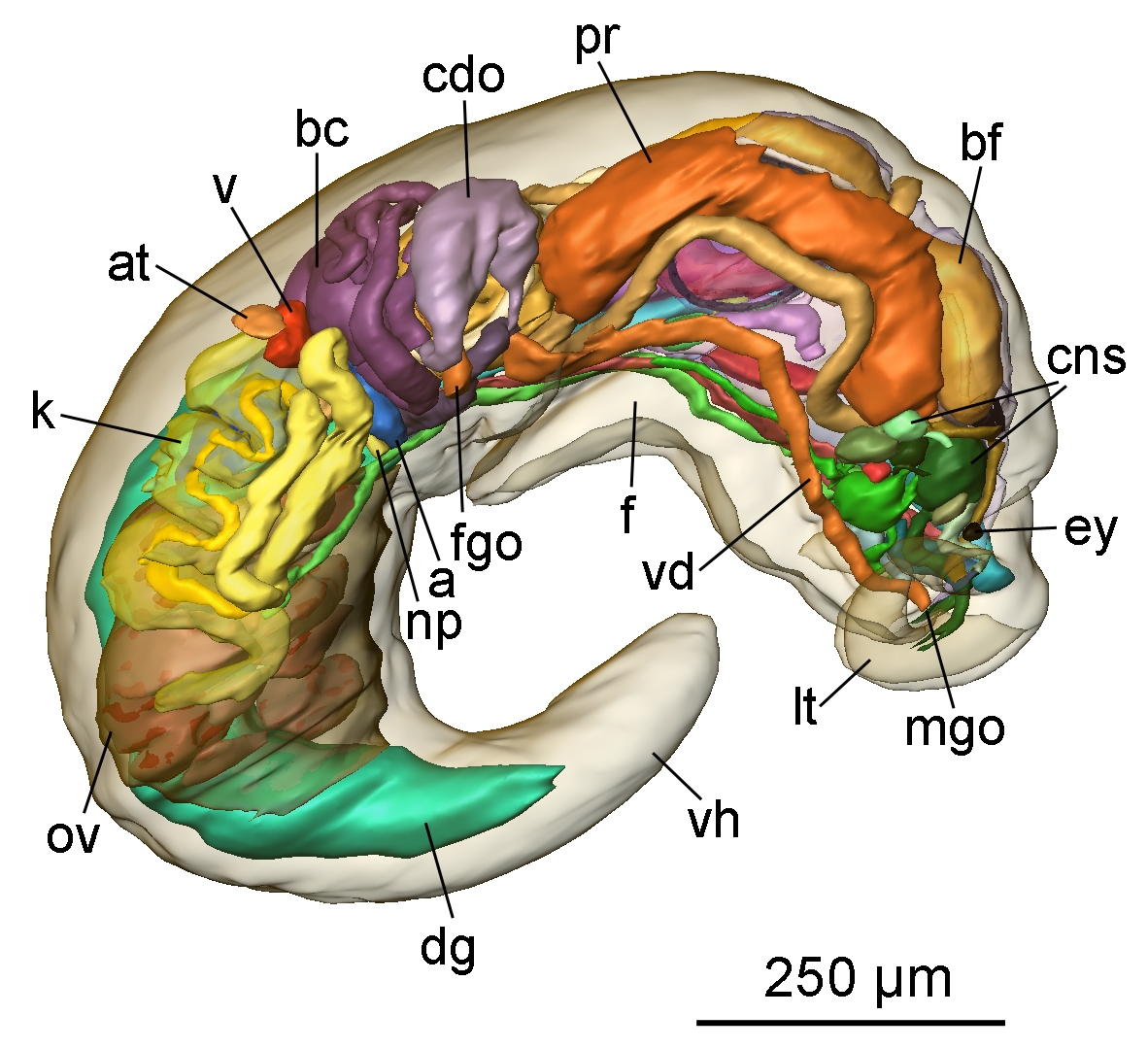
Pontohedyle
''Pontohedyle'' is a genus of sea slugs, acochlidians, shell-less marine gastropod mollusks in the family Microhedylidae. Sea slugs in this genus are highly simplified and uniform. Distribution The genus ''Pontohedyle'' shows a circumtropical distribution with a single derived species (Mediterranean/ Black Sea ''Pontohedyle milaschewitchii'') inhabiting temperate waters. In the absence of a fossil record for meiofaunal slugs, the only available estimate for divergence times derives from a molecular clock approach, calibrated with shelled heterobranch fossils. Jörger et al. (2010)Jörger K. M., Stöger I., Kano Y., Fukuda H., Knebelsberger T. & Schrödl M. (2010). "On the origin of Acochlidia and other enigmatic euthyneuran gastropods, with implications for the systematics of Heterobranchia". ''BMC Evolutionary Biology'' 10: 323. . estimated the origin of the genus ''Pontohedyle'' to the late Cretaceous, 84 mya (95% confidence interval ranging from 160–60 mya), providing a rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontohedyle Milaschewitchii
''Pontohedyle milaschewitchii'' is a species of sea slug, an acochlidian, a shell-less marine gastropod mollusk in the family Microhedylidae.Jörger K. M., Norenburg J. L., Wilson N. G. & Schrödl M. (2012). "Barcoding against a paradox? Combined molecular species delineations reveal multiple cryptic lineages in elusive meiofaunal sea slugs". ''BMC Evolutionary Biology'' 12: 245. . Ecology The life cycle of all Acochlidiacea is not well known. ''Pontohedyle milaschewitchii'' lays a maximum of 40 eggs. References External links * Jörger K. M., Neusser T. P. & Schrödl M. (2007). "Re-description of a female ''Pontohedyle brasilensis'' (Rankin, 1979), a junior synonym of the Mediterranean ''P. milaschewitchii'' (Kowalevsky, 1901) (Acochlidia, Gastropoda)". ''Bonner Zoologische Beiträge'' 55(3/4): 283-290PDF * Jörger K. M., Neusser T. P., Haszprunar G. & Schrödl M. (2008). "Undersized and underestimated: 3D-visualization of the Mediterranean interstitial acochlidian gastro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microhedylidae
Parhedylidae are a taxonomic family of sea slugs, marine gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Parhedyloidea. MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Parhedylidae Thiele, 1931. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=411947 on 2021-06-17 2005 taxonomy Microhedylidae has been listed as a synonym of Parhedylidae in the taxonomy of Bouchet & Rocroi (2005). Ganitidae Rankin, 1979 has been listed as a sole family within Hedylopsoidea. The type genus of Livorniellidae was ''Livorniella'' Rankin, 1979. 2010 taxonomy Sensu Schrödl & Neusser (2010)Schrödl M. & Neusser T. P. (2010). "Towards a phylogeny and evolution of Acochlidia (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Opisthobranchia)". ''Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society'' 158: 124–154. . is Microhedylidae within the clade Microhedylacea. Parhedylidae is a synonym of Microhedylidae. Microhedylidae s.l. may informally include Ganitidae, but inclusion of Ganitidae within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asperspinidae
''Asperspina'' is a genus of sea slugs, marine gastropod mollusks within the clade Acochlidiacea. Taxonomy Asperspinidae has been listed as a synonym of Parhedylidae in the taxonomy of Bouchet & Rocroi (2005). Sensu Schrödl & Neusser (2010)Schrödl M. & Neusser T. P. (2010). "Towards a phylogeny and evolution of Acochlidia (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Opisthobranchia)". ''Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society'' 158: 124-154. . is ''Asperspina'' is the only genus in the family Asperspinidae. Minicheviellidae is a junior synonym of Asperspinidae. Species Species within the genus ''Asperspina'' include: * '' Asperspina brambelli'' (Swedmark, 1968) * '' Asperspina murmanica'' (Kudinskaya & Minichev, 1978) - synonym: ''Minicheviella murmanica'' (Kuchinskaja & Minichev, 1978) * '' Asperspina rhopalotecta'' Salvini-Plawen, 1973 * '' Asperspina loricata'' (Swedmark, 1968) * '' Asperspina riseri'' (Morse, 1976) References Further reading * "Heartless and primitive? 3D reconstruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudunela Cornuta
''Pseudunela cornuta'' is a species of minute sea slug, an acochlidian, a shell-less marine and temporarily brackishNeusser T. P., Jörger K. M. & Schrödl M. (2011). "Cryptic Species in Tropic Sands – Interactive 3D Anatomy, Molecular Phylogeny and Evolution of Meiofaunal Pseudunelidae (Gastropoda, Acochlidia)". '' PLoS ONE'' 6(8): e23313. figure 12. . gastropod mollusk in the family Pseudunelidae. Adults are about 3 mm long and live in the spaces between sand grains. A complex interactive 3D reconstruction (a 3D visualization based on 420 paraffin histological sections) of the body of an individual of this species has been available since 2009. Taxonomy ''Pseudunela cornuta'' is the type species of the genus '' Pseudunela''. Challis, who described the species in 1970, claimed to have deposited the holotype of ''Pseudunela cornuta'', 20 paratypes and a slide with the radula of a further paratype in the Natural History Museum, London; furthermore, he claimed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusc Shell
The mollusc (or molluskOften spelled mollusk shell in the USA; the spelling "mollusc" are preferred by ) shell is typically a calcareous exoskeleton which encloses, supports and protects the soft parts of an animal in the phylum Mollusca, which includes snails, clams, tusk shells, and several other classes. Not all shelled molluscs live in the sea; many live on the land and in freshwater. The ancestral mollusc is thought to have had a shell, but this has subsequently been lost or reduced on some families, such as the squid, octopus, and some smaller groups such as the caudofoveata and solenogastres. Today, over 100,000 living species bear a shell; there is some dispute as to whether these shell-bearing molluscs form a monophyletic group (conchifera) or whether shell-less molluscs are interleaved into their family tree. Malacology, the scientific study of molluscs as living organisms, has a branch devoted to the study of shells, and this is called conchology—although these te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist. The microscopic structure of a gill presents a large surface area to the external environment. Branchia (pl. branchiae) is the zoologists' name for gills (from Ancient Greek ). With the exception of some aquatic insects, the filaments and lamellae (folds) contain blood or coelomic fluid, from which gases are exchanged through the thin walls. The blood carries oxygen to other parts of the body. Carbon dioxide passes from the blood through the thin gill tissue into the water. Gills or gill-like organs, located in different parts of the body, are found in various groups of aquatic animals, including mollusks, crustaceans, insects, fish, and amphibians. Semiterrestrial marine animals such as crabs and mudskippers have gill cham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acochlidium Fijiiensis
''Acochlidium'' is a genus of freshwater slugs, an aquatic gastropod molluscs in the family Acochlidiidae. ''Acochlidium'' species have no shell. Species Species within the genus ''Acochlidium'' include: * ''Acochlidium amboinense'' Strubell, 1892Rudman W. B. (17 June 2006). "Comment on Are there freshwater sea slugs? by Dave". ''Sea Slug Forum''. Australian Museum, Sydney. Available fromhttp://www.seaslugforum.net/find/16865 accessed 23 May 2010. * '' Acochlidium bayerfehlmanni'' Wawra, 1980 * ''Acochlidium fijiiensis'' Haynes & Kenchington, 1991 synonyms: * ''Acochlidium paradoxum'' Strubell is a synonym for ''Strubellia paradoxa'' (Strubell, 1892) * ''Acochlidium sutteri'' WawraWawra E. (1979). "''Acochlidium sutteri'' nov. spec. (Gastropoda, Opisthobranchia, Acochlidiacea) von Sumba, Indonesien". ''Ann. Naturhistor. Mus. Wien'' 82: 595-60PDF/ref> is a synonym for ''Palliohedyle sutteri'' * ''Acochlidium weberi'' Bergh, 1896 is a synonym for ''Palliohedyle weberi ''Pallioh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscera
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerves that innervate the parenchyma, the blood vessels that oxygenate and nourish it and carry away its metabolic wastes, and the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |