|
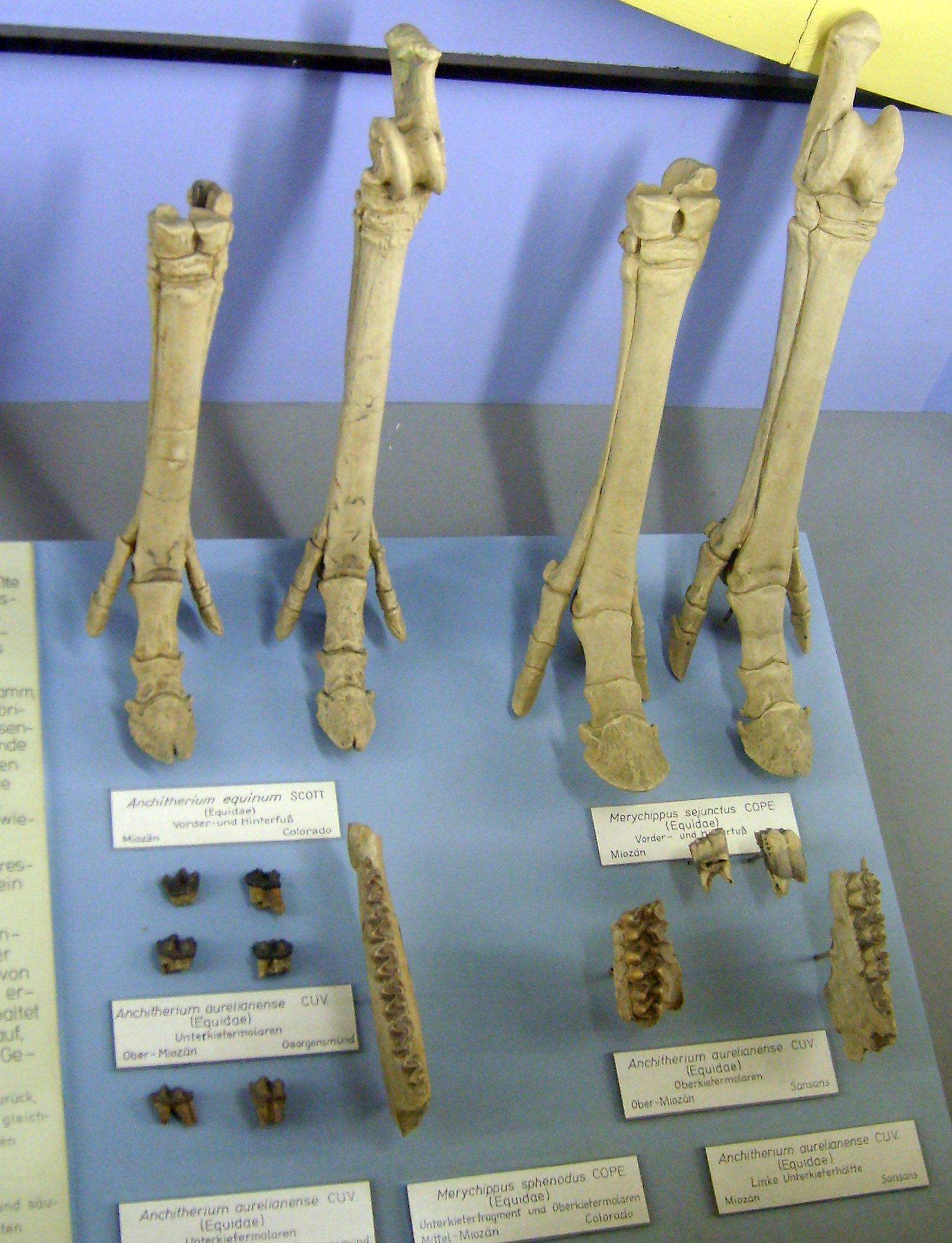
Merychippus
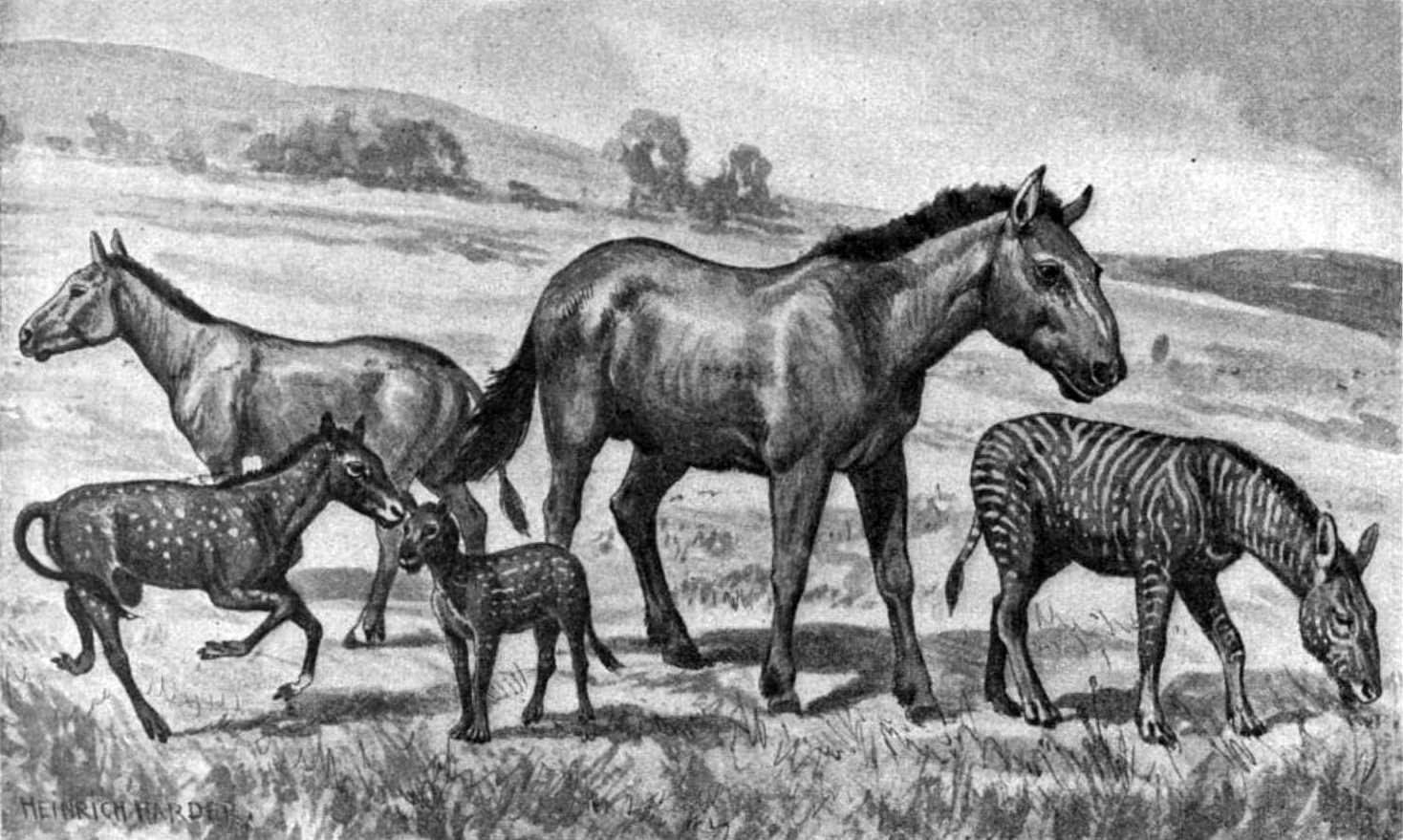
''Merychippus'' is an extinct proto-horse of the family Equidae that was endemic to North America during the Miocene, 15.97–5.33 million years ago. It had three toes on each foot and is the first horse known to have grazed. Discovery and naming ''Merychippus'' was named by Joseph Leidy (1856). Numerous authors assigned the type species – ''Merychippus insignis'' – to ''Protohippus'', but this is ignored. It was assigned to the Equidae by Leidy (1856) and Carroll (1988), and to the Equinae by MacFadden (1998) and Bravo-Cuevas and Ferrusquía-Villafranca (2006). Its name means "ruminant horse", but current evidence does not support ''Merychippus'' ruminating. Description ''Merychippus'' lived in groups. It was about tall and at the time it was the tallest equine to have existed. Its muzzle was longer, deeper jaw, and eyes wider apart than any other horse-like animal to date. The brain was also much larger, making it smarter and more agile. ''Merychippus'' was the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
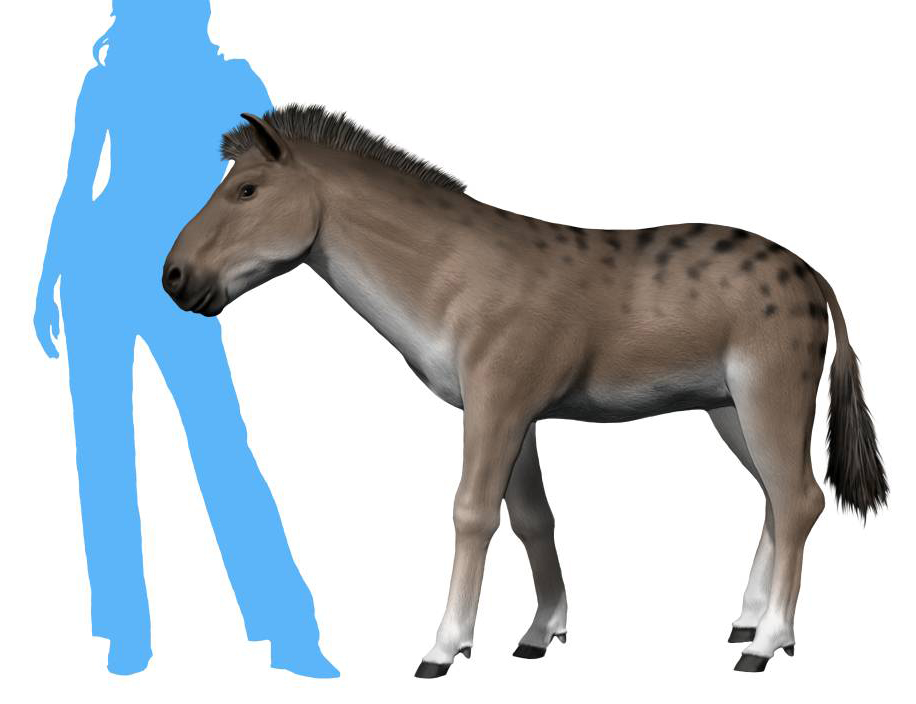
Merychippus Insignis Life Restoration
''Merychippus'' is an extinct proto-horse of the family Equidae that was endemic to North America during the Miocene, 15.97–5.33 million years ago. It had three toes on each foot and is the first horse known to have grazed. Discovery and naming ''Merychippus'' was named by Joseph Leidy (1856). Numerous authors assigned the type species – ''Merychippus insignis'' – to ''Protohippus'', but this is ignored. It was assigned to the Equidae by Leidy (1856) and Carroll (1988), and to the Equinae by MacFadden (1998) and Bravo-Cuevas and Ferrusquía-Villafranca (2006). Its name means "ruminant horse", but current evidence does not support ''Merychippus'' ruminating. Description ''Merychippus'' lived in groups. It was about tall and at the time it was the tallest equine to have existed. Its muzzle was longer, deeper jaw, and eyes wider apart than any other horse-like animal to date. The brain was also much larger, making it smarter and more agile. ''Merychippus'' was the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merychippus
''Merychippus'' is an extinct proto-horse of the family Equidae that was endemic to North America during the Miocene, 15.97–5.33 million years ago. It had three toes on each foot and is the first horse known to have grazed. Discovery and naming ''Merychippus'' was named by Joseph Leidy (1856). Numerous authors assigned the type species – ''Merychippus insignis'' – to ''Protohippus'', but this is ignored. It was assigned to the Equidae by Leidy (1856) and Carroll (1988), and to the Equinae by MacFadden (1998) and Bravo-Cuevas and Ferrusquía-Villafranca (2006). Its name means "ruminant horse", but current evidence does not support ''Merychippus'' ruminating. Description ''Merychippus'' lived in groups. It was about tall and at the time it was the tallest equine to have existed. Its muzzle was longer, deeper jaw, and eyes wider apart than any other horse-like animal to date. The brain was also much larger, making it smarter and more agile. ''Merychippus'' was the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equinae
Equinae is a subfamily of the family Equidae, which have lived worldwide (except Indonesia and Australia) from the Hemingfordian stage of the Early Miocene (16 million years ago) onwards. They are thought to be a monophyletic grouping.B. J. MacFadden. 1998. Equidae. In C. M. Janis, K. M. Scott, and L. L. Jacobs (eds.), Evolution of Tertiary Mammals of North America Members of the subfamily are referred to as equines; the only extant equines are the horses, asses, and zebras of the genus ''Equus''. The subfamily contains two tribes, the Equini and the Hipparionini, as well as two unplaced genera, ''Merychippus'' and ''Scaphohippus''. Sister taxa * Anchitheriinae * Hyracotheriinae ''Hyracotherium'' ( ; "hyrax-like beast") is an extinct genus of very small (about 60 cm in length) perissodactyl ungulates that was found in the London Clay formation. This small, fox-sized animal was once considered to be the earliest know ... References Miocene horses Pliocene o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equid
Equidae (sometimes known as the horse family) is the taxonomic family of horses and related animals, including the extant horses, asses, and zebras, and many other species known only from fossils. All extant species are in the genus '' Equus'', which originated in North America. Equidae belongs to the order Perissodactyla, which includes the extant tapirs and rhinoceros, and several extinct families. The term equid refers to any member of this family, including any equine. Evolution The oldest known fossils assigned to Equidae were found in North America, and date from the early Eocene epoch, 54 million years ago. They were once assigned to the genus '' Hyracotherium'', but the type species of that genus is now regarded as a palaeothere. The other species have been split off into different genera. These early equids were fox-sized animals with three toes on the hind feet, and four on the front feet. They were herbivorous browsers on relatively soft plants, and already a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equidae
Equidae (sometimes known as the horse family) is the taxonomic family of horses and related animals, including the extant horses, asses, and zebras, and many other species known only from fossils. All extant species are in the genus '' Equus'', which originated in North America. Equidae belongs to the order Perissodactyla, which includes the extant tapirs and rhinoceros, and several extinct families. The term equid refers to any member of this family, including any equine. Evolution The oldest known fossils assigned to Equidae were found in North America, and date from the early Eocene epoch, 54 million years ago. They were once assigned to the genus ''Hyracotherium'', but the type species of that genus is now regarded as a palaeothere. The other species have been split off into different genera. These early equids were fox-sized animals with three toes on the hind feet, and four on the front feet. They were herbivorous browsers on relatively soft plants, and already adapt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchitherium
''Anchitherium'' (meaning ''near beast'') was a fossil horse with a three- toed hoof. ''Anchitherium'' was a browsing (leaf eating) horse that originated in the early Miocene of North America and subsequently dispersed to Europe and Asia,(in Chinese with English summary).MacFadden, B.J. 2001. Three-toed browsing horse ''Anchitherium clarencei'' from the early Miocene (Hemingfordian) Thomas Farm, Florida. Bulletin of the Florida Museum of Natural History, 43(3):79-109. where it gave rise to the larger bodied genus ''Sinohippus ''Sinohippus'' ("Chinese horse") is an extinct equid genus belonging to the subfamily Anchitheriinae The Anchitheriinae are an extinct subfamily of the Perissodactyla family Equidae, the same family which includes modern horses, zebras and d ...''. It was around high at the shoulder, and probably represented a side-branch of horse evolution that left no modern descendants. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q542119 Miocene horses Prehistoric place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypsodont
Hypsodont is a pattern of dentition with high-crowned teeth and enamel extending past the gum line, providing extra material for wear and tear. Some examples of animals with hypsodont dentition are cows and horses; all animals that feed on gritty, fibrous material. The opposite condition is called brachydont. Evolution Since the morphology of the hypsodont tooth is suited to a more abrasive diet, hypsodonty was thought to have evolved concurrently with the spread of grasslands. Grass contains phytoliths, silica-rich granules, which wear away dental tissue more quickly. Analysis has shown however, that the development of this morphology is out of sync with the flourishing of grasslands. Instead, the ingestion of grit and soil is hypothesized to be the primary driver of hypsodonty (the Grit, not grass hypothesis). Morphology Hypsodont dentition is characterized by: * high-crowned teeth * A rough, flattish occlusal surface adapted for crushing and grinding * Cementum both abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to roam around and consume wild vegetations in order to convert the otherwise indigestible (by human gut) cellulose within grass and other forages into meat, milk, wool and other animal products, often on land unsuitable for arable farming. Farmers may employ many different strategies of grazing for optimum production: grazing may be continuous, seasonal, or rotational within a grazing period. Longer rotations are found in ley farming, alternating arable and fodder crops; in rest rotation, deferred rotation, and mob grazing, giving grasses a longer time to recover or leaving land fallow. Patch-burn sets up a rotation of fresh grass after burning with two years of rest. Conservation grazing proposes to use grazing animals to improve the biodiversity of a site, but studies show that the greatest benefit to biodiversity comes from removing grazing animals from the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Radiation
In evolutionary biology, adaptive radiation is a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available, alters biotic interactions or opens new environmental niches. Starting with a single ancestor, this process results in the speciation and phenotypic adaptation of an array of species exhibiting different morphological and physiological traits. The prototypical example of adaptive radiation is finch speciation on the Galapagos ("Darwin's finches"), but examples are known from around the world. Characteristics Four features can be used to identify an adaptive radiation: #A common ancestry of component species: specifically a ''recent'' ancestry. Note that this is not the same as a monophyly in which ''all'' descendants of a common ancestor are included. #A phenotype-environment correlation: a ''significant'' association between environments and the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus '' Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hipparion
''Hipparion'' (Greek, "pony") is an extinct genus of horse that lived in North America, Asia, Europe, and Africa during the Miocene through Pleistocene ~23 Mya—781,000 years ago. It lived in non-forested, grassy plains, shortgrass prairie or steppes. Morphology ''Hipparion'' resembled the modern horse, but still had two vestigial outer toes (in addition to its hoof The hoof (plural: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits, yet the rumin ...). In some species, these outer toes were functional. ''Hipparion'' was about tall at the shoulder. Species References {{Taxonbar, from=Q971275 Cenozoic mammals of Asia Cenozoic mammals of North America Miocene horses Pliocene horses Pleistocene horses Miocene genus first appearances Pleistocene genus extinctions Cenozoic mammals of Europe Cenozoic m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |