|
Merkelis Petkevičius
Merkelis Petkevičius ( pl, Melchior Pietkiewicz; 1550–1608) was a Reformation (Calvinist) activist in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. He was a nobleman who worked as a court scribe in Vilnius for almost thirty years. In 1598, he published the first Lithuanian-language Protestant book printed in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (the first Lithuanian Protestant book was printed in Konigsberg in 1547 by Martynas Mažvydas). This book, a bilingual catechism in Polish and Lithuanian, was published in response to the publication of the Roman Catholic catechism of Mikalojus Daukša. However, book's heavy, artificial language with numerous loanwords make it linguistically inferior to Daukša's work. Biography Petkevičius was born to a wealthy family of Lithuanian nobles around 1550. According to the military census of 1528, his grandfather Grigas Petkevičius had to send four men to the army in case of war. Petkevičius' father Jonas had manors near Maišiagala and Salakas. Orphaned as a te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catechism By Petkevicius (1598)
A catechism (; from grc, κατηχέω, "to teach orally") is a summary or exposition of doctrine and serves as a learning introduction to the Sacraments traditionally used in catechesis, or Christian religious teaching of children and adult converts. Catechisms are doctrinal manuals – often in the form of questions followed by answers to be memorised – a format that has been used in non-religious or secular contexts as well. According to Norman DeWitt, the early Christians appropriated this practice from the Epicureans, a school whose founder Epicurus had instructed to keep summaries of the teachings for easy learning. The term '' catechumen'' refers to the designated recipient of the catechetical work or instruction. In the Catholic Church, catechumens are those who are preparing to receive the Sacrament of Baptism. Traditionally, they would be placed separately during Holy Mass from those who had been baptized, and would be dismissed from the liturgical assembly bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancery Slavonic
Ruthenian ( Belarusian: руская мова; Ukrainian: руська мова; Ruthenian: руска(ѧ) мова; also see other names) is an exonymic linguonym for a closely-related group of East Slavic linguistic varieties, particularly those spoken from the 15th to 18th centuries in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in East Slavic regions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Regional distribution of those varieties, both in their literary and vernacular forms, corresponded approximately to the territories of the modern states of Belarus and Ukraine. By the end of the 18th century, they gradually diverged into regional variants, which subsequently developed into the modern Belarusian, Ukrainian, and Rusyn languages. In the Austrian and Austro-Hungarian Empires, the same term (german: ruthenische Sprache, hu, Rutén nyelv) was employed continuously (up to 1918) as an official exonym for the entire East Slavic linguistic body within the borders of the Monarchy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksander Brückner
Aleksander Brückner (; 29 January 1856 – 24 May 1939) was a Polish scholar of Slavic languages and literatures (Slavistics), philologist, lexicographer and historian of literature. He is among the most notable Slavicists of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and the first to prepare complete monographs on the history of Polish language and culture. He published more than 1,500 titles and discovered the oldest extant prose text in Polish (the ''Holy Cross Sermons''). Life Brückner was born in Brzeżany (Berezhany) in Galicia, Austrian Empire, to an Austro-Polish family who had moved there from Stryj three generations earlier. He studied at the German Gymnasium in Lwów (Lemberg) under Omelian Ohonovsky, in Vienna under Franz Miklosich, and in Berlin under Vatroslav Jagić. Brückner first taught at Lwów (Lwów University). In 1876 he received a doctorate at the University of Vienna, and in 1878 his habilitation for a study on Slavic settlements around Magdeburg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
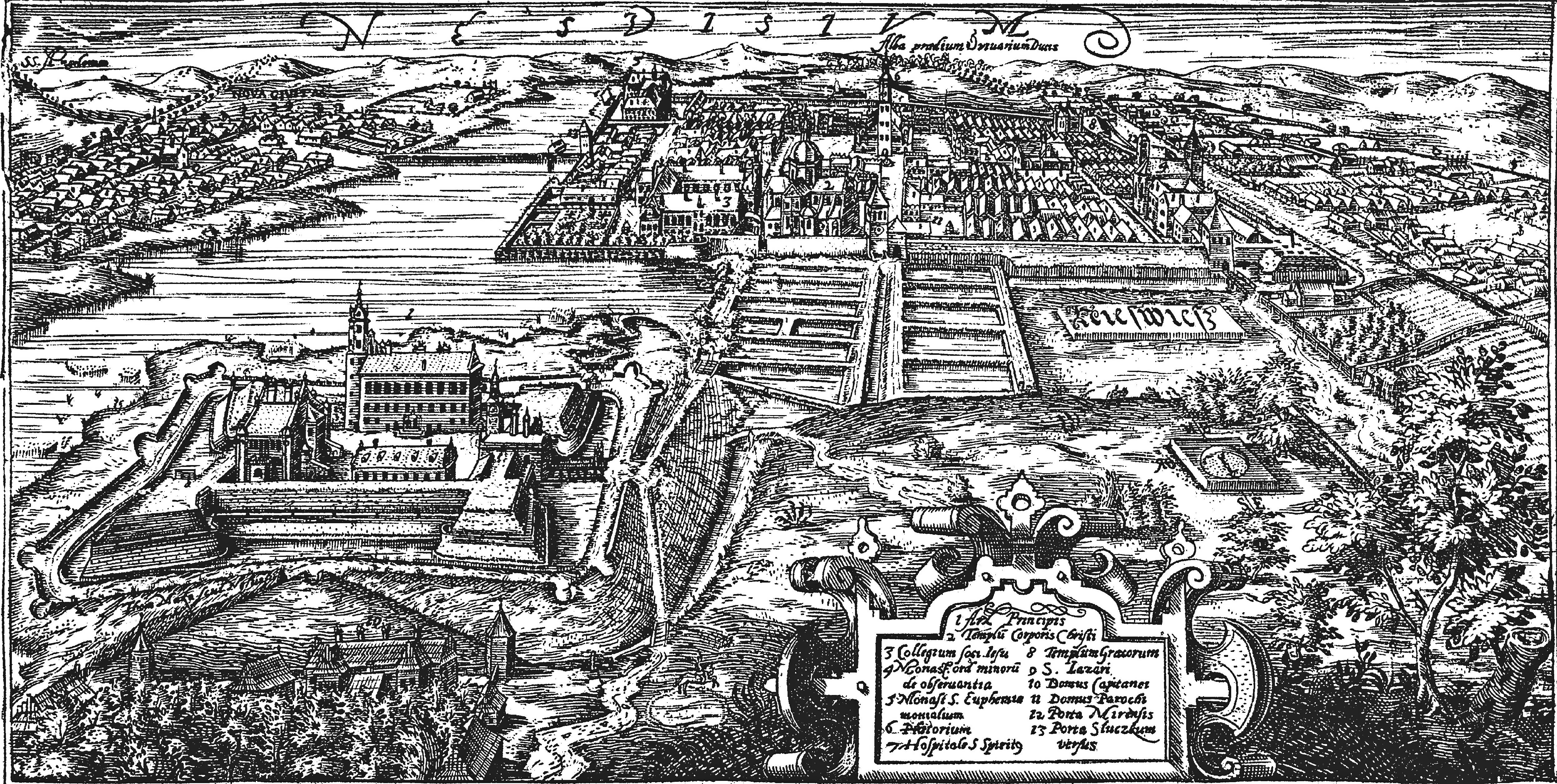
Nesvizh
Nesvizh, Niasviž ( be, Нясві́ж ; lt, Nesvyžius; pl, Nieśwież; russian: Не́свиж; yi, ניעסוויז; la, Nesvisium) is a city in Belarus. It is the administrative centre of the Nyasvizh District (''rajon'') of Minsk Region and site of Niasviž Castle, a World Heritage Site. Its 2009 population is 14,300. History Nesvizh was first documented in 1223. It was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania until 1793, but the Grand Duchy was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth since 1569. In the 15th century, while still a minor town, it belonged to the Kiszka family and later to the Radziwiłł family, and remained the family's seat until 1813. In 1561 or 1562 Maciej Kawęczyński founded the print works of the Polish Brethren. The first Belarusian language book printed in Latin script, a catechism by Symon Budny, was published in Nesvizh in 1562. The ''Nieśwież Bible'' ('' Biblia nieświeska''), one of the oldest Polish translations of the Bible, also by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikołaj "the Black" Radziwiłł
Mikołaj Krzysztof Radziwiłł (4 February 1515 – 28 May 1565), nicknamed ''The Black'' (Polish: ''Czarny''), was a Polish-Lithuanian noble who held several administrative positions within the Grand Duchy of Lithuania: Voivode of Vilnius, Grand Lithuanian Chancellor, and Grand Hetman of Lithuania. Alternate renditions of his name include lt, Mikalojus Radvila Juodasis, be, Мікалай Радзівіл Чорны, and la, Nicolaus Radvil. His first name is sometimes given in English as Nicholas. Political influence Mikołaj was able to gain much political influence thanks to the romance between his cousin Barbara Radziwiłł and the King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania Zygmunt II August.Peter Paul BajeShort history of the Radziwill Family This made him one of the most powerful royal advisers. Mikolaj became Marshal of Lithuania, Grand Chancellor of Lithuania, as well as Palatine of Vilnius, gained immense wealth and became the most powerful magnate in the Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (german: Herzogtum Preußen, pl, Księstwo Pruskie, lt, Prūsijos kunigaikštystė) or Ducal Prussia (german: Herzogliches Preußen, link=no; pl, Prusy Książęce, link=no) was a duchy in the Prussia (region), region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the State of the Teutonic Order until the Protestant Reformation in 1525. Overview The duchy became the first Protestant state when Albert, Duke of Prussia formally adopted Lutheranism in 1525. It was inhabited by a German, Polish (mainly in Masuria), and Lithuanian-speaking (mainly in Lithuania Minor) population. In 1525, during the Protestant Reformation, in accordance to the Treaty of Kraków, the Grand Masters of the Teutonic Knights, Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, Albert, secularization, secularized the order's prevailing Prussian territory (the Monastic Prussia), becoming Albert, Duke of Prussia. As the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Library Of Poland
The National Library ( pl, Biblioteka Narodowa) is the central Polish library, subject directly to the Ministry of Culture and National Heritage of the Republic of Poland. The library collects books, journals, electronic and audiovisual publications published in the territory of Poland, as well as Polonica published abroad. It is the most important humanities research library, the main archive of Polish writing and the state centre of bibliographic information about books. It also plays a significant role as a research facility and is an important methodological center for other Polish libraries. The National Library was one of the first libraries in Europe that fulfilled the tasks of a modern national library in developing collections covering the entire body of Polish literature and making available to the public. Literature and making those works accessible to the public receives a copy of every book published in Poland as legal deposit. The Jagiellonian Library is the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul The Apostle
Paul; grc, Παῦλος, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡⲁⲩⲗⲟⲥ; hbo, פאולוס השליח (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, بولس الطرسوسي; grc, Σαῦλος Ταρσεύς, Saũlos Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; la, Paulus Tarsensis AD), commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Christian apostle who spread the teachings of Jesus in the first-century world. Generally regarded as one of the most important figures of the Apostolic Age, he founded several Christian communities in Asia Minor and Europe from the mid-40s to the mid-50s AD. According to the New Testament book Acts of the Apostles, Paul was a Pharisee. He participated in the persecution of early disciples of Jesus, possibly Hellenised diaspora Jews converted to Christianity, in the area of Jerusalem, prior to his conversion. Some time after having approved of the execution of Stephen, Paul was traveling on the road to Damascus so that he might find any Christians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merkelis Giedraitis
Merkelis Giedraitis ( pl, Melchior Giedroyć; – 6 April 1609) was Bishop of Samogitia from 1576 to 1609. Educated at Protestant universities in the Duchy of Prussia and Germany, he actively combated the Reformation implementing resolutions of the Council of Trent in Samogitia. Born into the princely Giedraičiai family, he inherited a much neglected diocese that was reduced to only about 20 priests. He became known for his devotion and work to end clerical abuses, strengthen churches and schools, and increase the number of priests. Giedraitis invited the Jesuits to Kražiai where the Kražiai College was established already after his death and the Bernadines to Kretinga where they established the first monastery in Samogitia. He sponsored Mikalojus Daukša, who translated and published ''Catechism'' (1595) and ''Postil'' (1599) in the Lithuanian language—the first Lithuanian books printed within the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. He also supported Maciej Stryjkowski, author of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Königsberg
The University of Königsberg (german: Albertus-Universität Königsberg) was the university of Königsberg in East Prussia. It was founded in 1544 as the world's second Protestant academy (after the University of Marburg) by Duke Albert of Prussia, and was commonly known as the Albertina. Following World War II, the city of Königsberg was transferred to the Soviet Union according to the 1945 Potsdam Agreement, and renamed Kaliningrad in 1946. The Albertina was closed and the remaining non-Lithuanian population either executed or expelled, by the terms of the Potsdam Agreement. Today, the Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University in Kaliningrad claims to maintain the traditions of the Albertina. History Albert, former Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights and first Duke of Prussia since 1525, had purchased a piece of land behind Königsberg Cathedral on the Kneiphof island of the Pregel River from the Samland chapter, where he had an academic gymnasium (school) erected in 154 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glitiškės
Glitiškės ( pl, Glinciszki) is a village in Vilnius district Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ..., Lithuania. It is situated on the eastern bank of the Širvys Lake. According to the 2011 census, it had 549 residents. The village was the site of the massacre of several dozen Polish villagers by German collaborators in 1944. References Villages in Vilnius County Vilnius District Municipality Vilensky Uyezd {{Vilnius-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giedraičiai
left, Bell tower of Church of St. Bartholomew Giedraičiai is a town in Molėtai district municipality, Lithuania with about 700 residents. It is located some 45 km north of Vilnius, capital of Lithuania, on the banks of Lake Kiementas. It is the capital of an elderate. The town, according to a local legend founded by Duke Giedrius, is first mentioned in written sources in 1338 when Grand Duke Gediminas signed a peace treaty with the Teutonic Knights. For a long time it was the centre of Giedraitis family estate. History It is known that since 1777 the town had a parish school. A hundred years later it was reorganized to a grammar, and later to middle school. Today the high school is named after Antanas Jaroševičius, a painter who in 1912 published an album of Lithuanian crosses. The school building houses a small museum about local history. In 1410 Church of St. Bartholomew the Apostle was built. It was rebuilt in 1809 in the Classicism style by Bishop of Samogit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)