|
Merge (linguistics)
Merge (usually capitalized) is one of the basic operations in the Minimalist Program, a leading approach to generative syntax, when two syntactic objects are combined to form a new syntactic unit (a set). Merge also has the property of recursion in that it may apply to its own output: the objects combined by Merge are either lexical items or sets that were themselves formed by Merge. This recursive property of Merge has been claimed to be a fundamental characteristic that distinguishes language from other cognitive faculties. As Noam Chomsky (1999) puts it, Merge is "an indispensable operation of a recursive system ... which takes two syntactic objects A and B and forms the new object G=" (p. 2). Mechanisms of Merge Within the Minimalist Program, syntax is derivational, and Merge is the structure-building operation. Merge is assumed to have certain formal properties constraining syntactic structure, and is implemented with specific mechanisms. In terms of a merge-base theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonological Change
In historical linguistics, phonological change is any sound change that alters the distribution of phonemes in a language. In other words, a language develops a new system of oppositions among its phonemes. Old contrasts may disappear, new ones may emerge, or they may simply be rearranged. Sound change may be an impetus for changes in the phonological structures of a language (and likewise, phonological change may sway the process of sound change). One process of phonological change is ''rephonemicization'', in which the distribution of phonemes changes by either addition of new phonemes or a reorganization of existing phonemes. Mergers and splits are types of rephonemicization and are discussed further below. Types In a typological scheme first systematized by Henry M. Hoenigswald in 1965, a historical sound law can only affect a phonological system in one of three ways: * Conditioned merger (which Hoenigswald calls "primary split"), in which some instances of phoneme A becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Projection Principle
The extended projection principle (EPP) is a linguistic hypothesis about subjects. It was proposed by Noam Chomsky as an addendum to the projection principle. The basic idea of the EPP is that clauses must contain a noun phrase or determiner phrase in the subject position (i.e. in the specifier of a tense phrase or inflectional phrase or in the specifier of a verb phrase in languages in which subjects don't raise to TP/IP, e.g. Welsh). Details Most verbs require meaningful subjects—for example, "kick" in "Tom kicked the ball" takes the subject "Tom". However, other verbs do not require (and in fact, do not permit) meaningful subjects—for example, one can say "it rains" but not "the sky rains". The EPP states that regardless of whether the main predicate assigns a meaningful theta role to a subject, a subject must be present syntactically. As a result, verbs that do not assign external theta roles will appear with subjects that are either dummy pronouns (e.g. expletive "it, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Item
In lexicography, a lexical item is a single word, a part of a word, or a chain of words ( catena) that forms the basic elements of a language's lexicon (≈ vocabulary). Examples are ''cat'', ''traffic light'', ''take care of'', ''by the way'', and ''it's raining cats and dogs''. Lexical items can be generally understood to convey a single meaning, much as a lexeme, but are not limited to single words. Lexical items are like semes in that they are "natural units" translating between languages, or in learning a new language. In this last sense, it is sometimes said that language consists of grammaticalized lexis, and not lexicalized grammar. The entire store of lexical items in a language is called its lexis. Lexical items composed of more than one word are also sometimes called ''lexical chunks'', ''gambits'', ''lexical phrases'', ''lexicalized stems'', or ''speech formulae''. The term ''polyword listemes'' is also sometimes used. Types Common types of lexical items/chunks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parse Tree
A parse tree or parsing tree or derivation tree or concrete syntax tree is an ordered, rooted tree that represents the syntactic structure of a string according to some context-free grammar. The term ''parse tree'' itself is used primarily in computational linguistics; in theoretical syntax, the term ''syntax tree'' is more common. Concrete syntax trees reflect the syntax of the input language, making them distinct from the abstract syntax trees used in computer programming. Unlike Reed-Kellogg sentence diagrams used for teaching grammar, parse trees do not use distinct symbol shapes for different types of constituents. Parse trees are usually constructed based on either the constituency relation of constituency grammars (phrase structure grammars) or the dependency relation of dependency grammars. Parse trees may be generated for sentences in natural languages (see natural language processing), as well as during processing of computer languages, such as programming languages. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
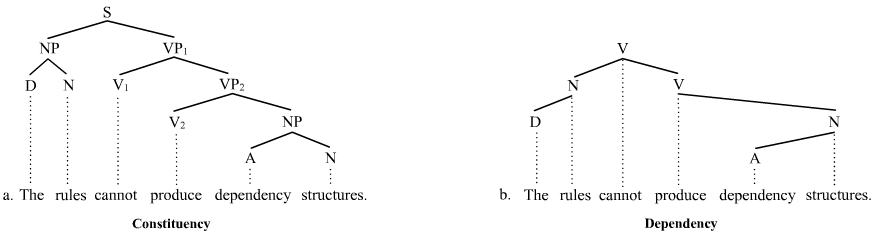
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue (Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining trait of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation associated with dependency grammars; hence, phrase structure grammars are also known as constituency grammars. Any of several related theories for the parsing of natural language qualify as constituency grammars, and most of them have been develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb phrase constituent, and they are thus well suited for the analysis of languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Rules
Phrase structure rules are a type of rewrite rule used to describe a given language's syntax and are closely associated with the early stages of transformational grammar, proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1957. They are used to break down a natural language sentence into its constituent parts, also known as syntactic categories, including both lexical categories (parts of speech) and phrasal categories. A grammar that uses phrase structure rules is a type of phrase structure grammar. Phrase structure rules as they are commonly employed operate according to the constituency relation, and a grammar that employs phrase structure rules is therefore a ''constituency grammar''; as such, it stands in contrast to ''dependency grammars'', which are based on the dependency relation. Definition and examples Phrase structure rules are usually of the following form: :A \to B \quad C meaning that the constituent A is separated into the two subconstituents B and C. Some examples for English are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
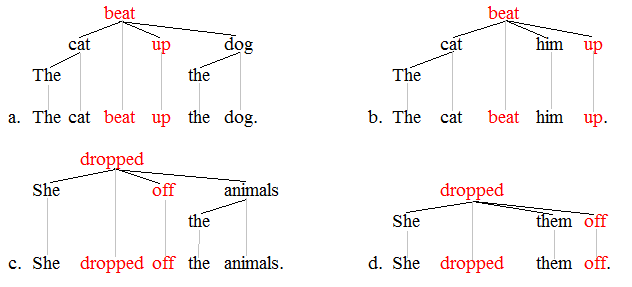
Subcategorization
In linguistics, subcategorization denotes the ability/necessity for lexical items (usually verbs) to require/allow the presence and types of the syntactic arguments with which they co-occur. The notion of subcategorization is similar to the notion of valency, although the two concepts (subcategorization and valency) stem from different traditions in the study of syntax and grammar. Argument structure Argument structure is the list of selected arguments associated with a lexical category, such as a verb (SKS, 2015). When every predicate, otherwise known as a verb, is used, it selects a specific set of arguments that need to be fulfilled to create a well-formed sentence (Kroger, 2005). These are arguments such as AGENT, PATIENT, EXPERIENCER, THEME, RECIPIENT, and STIMULUS. To illustrate this, the sentence ''The adults asked if the cats would pee on the sofa'', has been broken down into its semantic roles and argument selections below. It is necessary to understand the fundame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labelling Demonstration
Labelling or using a label is describing someone or something in a word or short phrase. For example, the Label (sociology), label "criminal" may be used to describe someone who has broken a law. Labeling theory, Labelling theory is a theory in sociology which ascribes labelling of people to control and identification of deviant behaviour. It has been argued that labelling is necessary for communication. However, the use of the term is often intended to highlight the fact that the ''label'' is a description applied from the outside, rather than something intrinsic to the labelled thing. This can be done for several reasons: * To provoke a discussion about what the best description is * To reject a particular label * To reject the whole idea that the labelled thing can be described in a short phrase. This last usage can be seen as an accusation that such a short description is overly-Reduction (philosophy), reductive. Giving something a label can be seen as positive, but the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntactic Category
A syntactic category is a syntactic unit that theories of syntax assume. Word classes, largely corresponding to traditional parts of speech (e.g. noun, verb, preposition, etc.), are syntactic categories. In phrase structure grammars, the ''phrasal categories'' (e.g. noun phrase, verb phrase, prepositional phrase, etc.) are also syntactic categories. Dependency grammars, however, do not acknowledge phrasal categories (at least not in the traditional sense). Word classes considered as syntactic categories may be called ''lexical categories'', as distinct from phrasal categories. The terminology is somewhat inconsistent between the theoretical models of different linguists. However, many grammars also draw a distinction between ''lexical categories'' (which tend to consist of content words, or phrases headed by them) and ''functional categories'' (which tend to consist of function words or abstract functional elements, or phrases headed by them). The term ''lexical category'' therefore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labelling Example
Labelling or using a label is describing someone or something in a word or short phrase. For example, the label "criminal" may be used to describe someone who has broken a law. Labelling theory is a theory in sociology which ascribes labelling of people to control and identification of deviant behaviour. It has been argued that labelling is necessary for communication. However, the use of the term is often intended to highlight the fact that the ''label'' is a description applied from the outside, rather than something intrinsic to the labelled thing. This can be done for several reasons: * To provoke a discussion about what the best description is * To reject a particular label * To reject the whole idea that the labelled thing can be described in a short phrase. This last usage can be seen as an accusation that such a short description is overly- reductive. Giving something a label can be seen as positive, but the term ''label'' is not usually used in this case. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-command
In generative grammar and related frameworks, a node in a parse tree c-commands its sister node and all of its sister's descendants. In these frameworks, c-command plays a central role in defining and constraining operations such as syntactic movement, binding, and scope. Tanya Reinhart introduced c-command in 1976 as a key component of her theory of anaphora. The term is short for "constituent command". Definition and examples Standard Definition Common terms to represent the relationships between nodes are below (refer to the tree on the right): *M is a parent or mother to A and B. *A and B are children or daughters of M. *A and B are sisters. *M is a grandparent to C and D. The standard definition of c-command is based partly on the relationship of dominance: ''Node N1 dominates node N2 if N1 is above N2 in the tree and one can trace a path from N1 to N2 moving only downwards in the tree (never upwards)''; that is, if N1 is a parent, grandparent, etc. of N2. For a node ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
.jpg)