|
Mental Development
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The field of neural development draws on both neuroscience and developmental biology to describe and provide insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which complex nervous systems develop, from nematodes and Drosophila melanogaster, fruit flies to mammals. Defects in neural development can lead to malformations such as holoprosencephaly, and a wide variety of neurological disorders including paresis, limb paresis and paralysis, balance and vision disorders, and seizures, and in humans other disorders such as Rett syndrome, Down syndrome and intellectual disability. Overview of vertebrate brain development The vertebrate central nervous system (CNS) is derived from the ectoderm—the outermost germ layer of the embryo. A part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nervous System
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 million years ago. In vertebrates it consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor nerves or '' efferent'' nerves, while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves or '' afferent''. Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that serve both fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * jawed vertebrates, which include: ** cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays, and ratfish) ** bony vertebrates, which include: *** ray-fins (the majority of living bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described animal species; the rest are invertebrates, which lack vertebral columns. The vertebrates traditionally include the hagfish, which do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
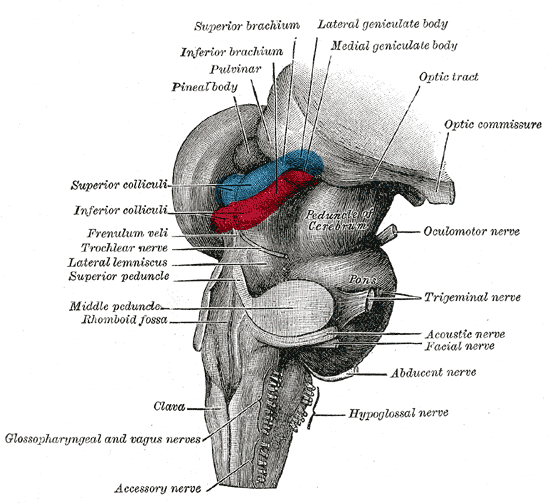
Hindbrain
The hindbrain or rhombencephalon or lower brain is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes. Metencephalon Rhombomeres Rh3-Rh1 form the metencephalon. The metencephalon is composed of the pons and the cerebellum; it contains: * a portion of the fourth (IV) ventricle, * the trigeminal nerve (CN V), * abducens nerve (CN VI), * facial nerve (CN VII), * and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). Myelencephalon Rhombomeres Rh8-Rh4 form the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon forms the medulla oblongata in the adult brain; it contains: * a portion of the fourth ventricle, * the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), * vagus nerve (CN X), * accessory nerve (CN XI), * hypoglossal nerve (CN XII), * and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). Evolution The hindbrain is homologous to a part of the arthropod brain known as the sub- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesencephalon
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while caudally it adjoins the hindbrain (pons, medulla and cerebellum). In the rostral direction, the midbrain noticeably splays laterally. Sectioning of the midbrain is usually performed axially, at one of two levels – that of the superior colliculi, or that of the inferior colliculi. One common technique for remembering the structures of the midbrain involves visualizing these cross-sections (especially at the level of the superior colliculi) as the upside-down face of a bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while caudally it adjoins the hindbrain (pons, medulla and cerebellum). In the rostral direction, the midbrain noticeably splays laterally. Sectioning of the midbrain is usually performed axially, at one of two levels – that of the superior colliculi, or that of the inferior colliculi. One common technique for remembering the structures of the midbrain involves visualizing these cross-sections (especially at the level of the superior colliculi) as the upside-down face of a be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosencephalon
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the Anatomical terms of location#Directional terms, rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three Brain vesicle, primary brain vesicles during the early development of the nervous system. The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions. At the five-vesicle stage, the forebrain separates into the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, and epithalamus) and the telencephalon which develops into the cerebrum. The cerebrum consists of the cerebral cortex, underlying white matter, and the basal ganglia. In humans, by 5 weeks in utero it is visible as a single portion toward the front of the fetus. At 8 weeks in utero, the forebrain splits into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. When the embryonic forebrain fails to divide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the Anatomical terms of location#Directional terms, rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three Brain vesicle, primary brain vesicles during the early development of the nervous system. The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions. At the five-vesicle stage, the forebrain separates into the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, and epithalamus) and the telencephalon which develops into the cerebrum. The cerebrum consists of the cerebral cortex, underlying white matter, and the basal ganglia. In humans, by 5 weeks in utero it is visible as a single portion toward the front of the fetus. At 8 weeks in utero, the forebrain splits into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. When the embryonic forebrain fails to divide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |