|
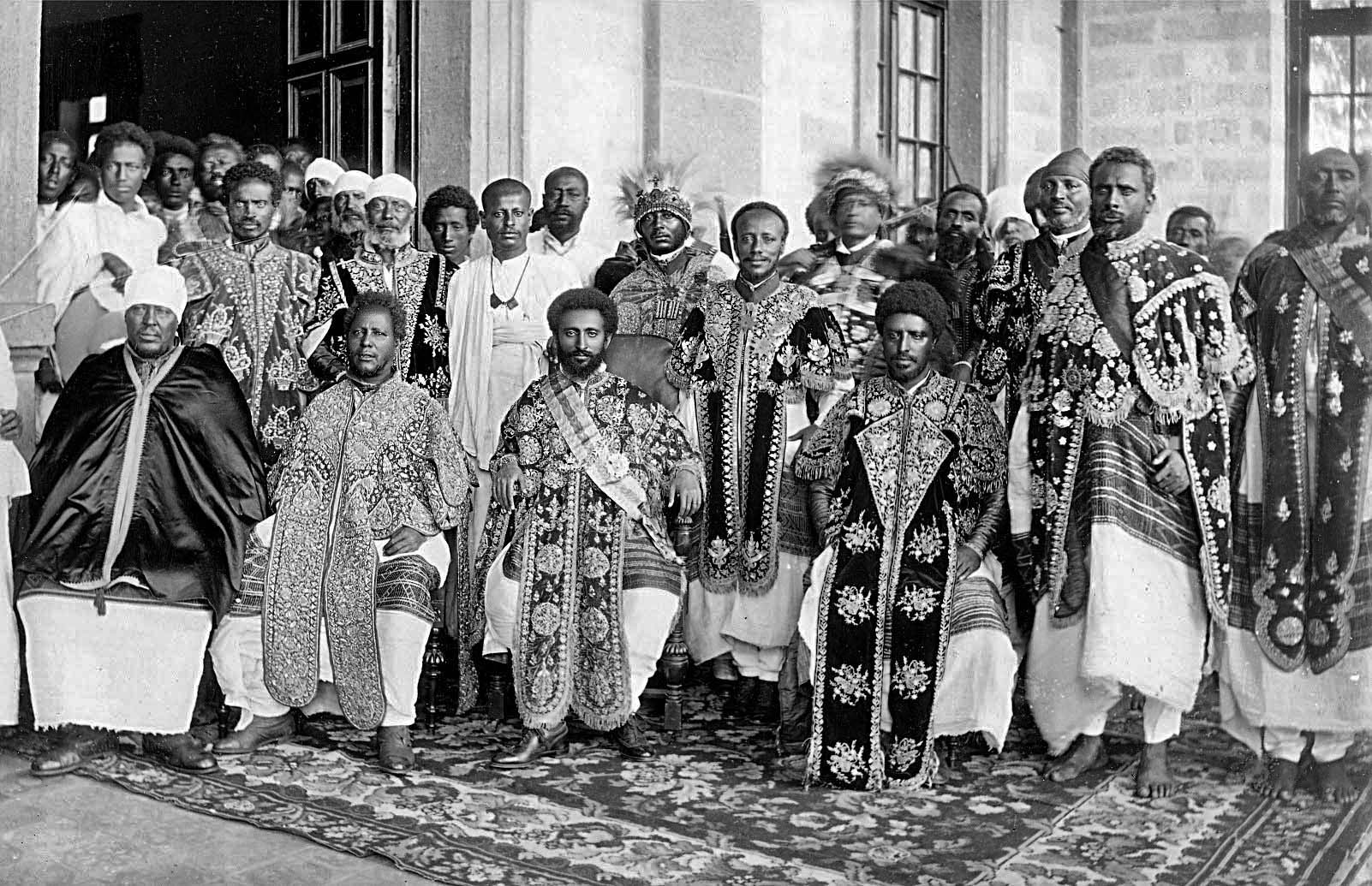
Menelek II Of Ethiopia
, spoken = ; ''djānhoi'', lit. ''"O steemedroyal"'' , alternative = ; ''getochu'', lit. ''"Our master"'' (pl.) Menelik II ( gez, ዳግማዊ ምኒልክ ; horse name Abba Dagnew (Amharic: አባ ዳኘው ''abba daññäw''); 17 August 1844 – 12 December 1913), baptised as Sahle Maryam (ሣህለ ማርያም ''sahlä maryam'') was King of Shewa from 1866 to 1889 and Emperor of Ethiopia from 1889 to his death in 1913. At the height of his internal power and external prestige, the process of territorial expansion and creation of the modern empire-state was completed by 1898.Zewde, Bahru. A history of Ethiopia: 1855–1991. 2nd ed. Eastern African studies. 2001 The Ethiopian Empire was transformed under Emperor Menelik: the major signposts of modernisation were put in place, with the assistance of key ministerial advisors. Externally, Menelik led Ethiopian troops against Italian invaders in the First Italo-Ethiopian War; following a decisive victory at the Battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Aristocratic And Court Titles
Until the end of the Ethiopian monarchy in 1974, there were two categories of nobility in Ethiopia and Eritrea. The Mesafint ( gez, መሳፍንት , modern , singular መስፍን , modern , "prince"), the hereditary nobility, formed the upper echelon of the ruling class. The Mekwanint ( gez, መኳንንት , modern , singular መኰንን , modern or am, መኮንን , "officer") were the appointed nobles, often of humble birth, who formed the bulk of the aristocracy. Until the 20th century, the most powerful people at court were generally members of the ''Mekwanint'' appointed by the monarch, while regionally, the ''Mesafint'' enjoyed greater influence and power. Emperor Haile Selassie greatly curtailed the power of the ''Mesafint'' to the benefit of the ''Mekwanint'', who by then were essentially coterminous with the Ethiopian government. The ''Mekwanint'' were officials who had been granted specific offices in the Abyssinian government or court. Higher ranks from the titl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menelik II Seal (born 1988), British player of American football
{{disambiguation ...
Menelek or Menelik may refer to: *Menelik I, first Emperor of Ethiopia *Menelik II (1844–1913), Emperor of Ethiopia *Menelek XIV, fictional Emperor of Abyssinia in the novel ''Beyond Thirty'' by Edgar Rice Burroughs *Ménélik (born 1970), French singer *Menelik Watson Menelik Watson (born 22 December 1988) is an English former professional American football offensive tackle. He was drafted by the Oakland Raiders in the second round of the 2013 NFL Draft. He played college football at Florida State. Early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zewditu
, spoken = ; ''djānhoi'', lit. ''"O steemedroyal"'' , alternative = ; ''getochu'', lit. ''"Our master"'' (pl.) Zewditu ( gez, ዘውዲቱ, born Askala Maryam; 29 April 1876 – 2 April 1930) was Empress of Ethiopia from 1916 to 1930. The first female head of an internationally recognized country in Africa in the 19th and 20th centuries, and the first and only empress regnant of the Ethiopian Empire, her reign was noted for the reforms of her Regent and designated heir ''Ras'' Tafari Makonnen (who succeeded her as Emperor Haile Selassie I), about which she was at best ambivalent and often stridently opposed, due to her staunch conservatism and strong religious devotion. She is the most recent empress regnant, as well as the last female Ethiopian head of state until the 2018 election of Sahle-Work Zewde as president. Early life Baptised as Askala Maryam ("Askal of Mary", a type of flower), but using the given name ''Zewditu'', the future Empress was the eldest daught ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welayta People
The Welayta, Wolayta or Wolaitta ( Ge'ez: ወላይታ ''Wolaytta'') are an ethnic group and its former kingdom, located in southern Ethiopia. According to the most recent estimate (2017), the people of Wolayta numbered 5.83 million in Welayta Zone. The language of the Wolayta people, similarly called Wolaytta, belongs to the Omotic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family. Despite their small population, Wolayta people have widely influenced national music, dance and cuisine in Ethiopia. History The people of Wolayta had their own kingdom for hundreds of years with kings (called "Kawo") and a monarchical administration. The earlier name of the kingdom was allegedly " Damot" - this was said to include the south, south-east, south-west and part of the central region of present Ethiopia. The ruler was King (Kawo) Motolomi who is mentioned in the religious book ''Gedle Teklehaimanot'', as an invader of the north and the king to whom was surrendered the mother of the Ethiopian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidamo Province
Sidamo Province (Amharic: ሲዳሞ) was a province in the southern part of Ethiopia, with its capital city at Irgalem, and after 1978 at Awasa. It was named after an ethnic group native to Ethiopia, called the Sidama, who are located in the south-central part of the country. According to the old political division, Sidamo was bordered on the west by Gamu-Gofa, on the north by Shewa, on the north and east by Bale, a small portion on the southeast by Somalia, and on the south by Kenya. History With its extensive coffee plantations, Sidamo was a province with abundant revenues and assigned to its rule were nobles loyal to the Emperor, such as Dejazmach Balcha Safo, who governed it at different times before the Italian occupation. Its largest settlement was Hawassa (Awasa). Following the liberation of Ethiopia from Italy in 1942, the provinces of Borana and Welayta, created from conquered states of that name, were merged into Sidamo. Sidamo was the scene of a revolt of the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Kaffa
The Kingdom of Kaffa was a kingdom located in what is now Ethiopia from 1390 to 1897, with its first capital at Bonga. The Gojeb River formed its northern border, beyond which lay the Gibe kingdoms; to the east the territory of the Konta and Kullo peoples lay between Kaffa and the Omo River; to the south numerous subgroups of the Gimira people, and to the west lay the Majangir people. The native language, also known as Kaffa, is one of the Omotic group of languages. Kaffa was divided into four sub-groups, who spoke a common language Kefficho, one of the Gonga/Kefoid group of Omotic languages; a number of groups of foreigners, Ethiopian Muslim traders and members of the Ethiopian Church, also lived in the kingdom. There were a number of groups of people, "but with the status of submerged status", who also lived in the kingdom; these included the ''Manjo'', or hunters; the ''Manne'', or leatherworkers; and the ''Qemmo'', or blacksmiths. The ''Manjo'' even had their own king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oromo People
The Oromo (pron. Oromo language, Oromo: ''Oromoo'') are a Cushitic people, Cushitic ethnic group native to the Oromia region of Ethiopia and parts of Northern Kenya, who speak the Oromo language (also called ''Afaan Oromoo'' or ''Oromiffa''), which is part of the Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are the largest List of ethnic groups in Ethiopia, ethnic group in Ethiopia and represent a large portion of Ethiopia's population. The Oromo people traditionally used the ''gadaa'' system as the primary form of governance.Harold G. MarcuA History of Ethiopia University of California Press (1994) pp. 55 Google Books A leader is elected by the ''gadaa'' system and their term lasts eight years, with an election taking place at the end of those eight years. Although most modern Oromos are Muslims and Christians, about 3% practice Waaqeffanna, the native ancient monotheistic religion of Oromos. Origins and nomenclature The Oromo people are one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menelik's Expansions
Menelik's Expansions, also known as the Agar Maqnat (Amharic: 'Cultivation' of land), was a series of wars and conquests carried out by Menelik II of Shewa to expand the Ethiopian Empire. In 1866 Menelik II became the king of Shewa and in 1878 began a series of wars to conquer land for the Ethiopian Empire and to increase Shewan supremacy within Ethiopia. Menelik II sought to build a "greater Ethiopia" and to incorporate lands from the era of Amda Seyon I, prior to the Ethiopian–Adal War and Oromo migrations. He is viewed as the founder of modern Ethiopia.Richard PankhursThe Ethiopian Borderlands: Essays in Regional History from Ancient Times to the End of the 18th Century – Google Books" 1997. p. 284. Gurageland In the late 1870s Menelik led a campaign to incorporate the lands of Gurage into Shewa. In 1878, the Soddo Gurage living in Northern and Eastern Gurageland peacefully submitted to Menelik and their lands were left untouched by his armies, likely due to their share ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Adwa
The Battle of Adwa (; ti, ውግእ ዓድዋ; , also spelled ''Adowa'') was the climactic battle of the First Italo-Ethiopian War. The Ethiopian forces defeated the Italian invading force on Sunday 1 March 1896, near the town of Adwa. The decisive victory thwarted the campaign of the Kingdom of Italy to expand its colonial empire in the Horn of Africa. By the end of the 19th century, European powers had carved up almost all of Africa after the Berlin Conference; only Ethiopia and Liberia still maintained their independence. Adwa became a pre-eminent symbol of pan-Africanism and secured Ethiopian sovereignty until the Second Italo-Ethiopian War forty years later. Background In 1889, the Italians signed the Treaty of Wuchale with the then King Menelik of Shewa. The treaty, signed after the Italian occupation of Eritrea, recognized Italy's claim over the coastal colony. In it, Italy also promised to provide financial assistance and military supplies. A dispute later arose ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Italo-Ethiopian War
The First Italo-Ethiopian War, lit. ''Abyssinian War'' was fought between Italy and Ethiopia from 1895 to 1896. It originated from the disputed Treaty of Wuchale, which the Italians claimed turned Ethiopia into an Italian protectorate. Full-scale war broke out in 1895, with Italian troops from Italian Eritrea achieving initial successes against Tigrayan warlords at the battle of Coatit and the battle of Senafe until they were reinforced by a large Ethiopian army led by Emperor Menelik II. Italian defeat came about after the Battle of Adwa, where the Ethiopian army dealt the heavily outnumbered Italian soldiers and Eritrean askaris a decisive blow and forced their retreat back into Eritrea. The war concluded with the Treaty of Addis Ababa. Because this was one of the first decisive victories by African forces over a European colonial power, this war became a preeminent symbol of pan-Africanism and secured Ethiopia's sovereignty until 1936. Background The Khedive of Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an 1946 Italian institutional referendum, institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and form the modern Italy, Italian Republic. The state resulted from a decades-long process, the ''Italian unification, Risorgimento'', of consolidating the different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single state. That process was influenced by the House of Savoy, Savoy-led Kingdom of Sardinia, which can be considered Italy's legal Succession of states, predecessor state. Italy Third Italian War of Independence, declared war on Austrian Empire, Austria in alliance with Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia in 1866 and received the region of Veneto following their victory. Italian troops Capture of Rome, entered Rome in 1870, ending Papal States, more tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modernisation
Modernization theory is used to explain the process of modernization within societies. The "classical" theories of modernization of the 1950s and 1960s drew on sociological analyses of Karl Marx, Emile Durkheim and a partial reading of Max Weber, and were strongly influenced by the writings of Harvard sociologist Talcott Parsons. Modernization theory was a dominant paradigm in the social sciences in the 1950s and 1960s, then went into a deep eclipse. It made a comeback after 1991, when Francis Fukuyama wrote about the end of the Cold War as confirmation on modernization theory and more generally of universal history. But the theory remains a controversial model. Modernization refers to a model of a progressive transition from a "pre-modern" or "traditional" to a "modern" society. Modernization theory suggests that traditional societies will develop as they adopt more modern practices. Proponents of modernization theory claim that modern states are wealthier and more powerful and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |