|
Meltdown (Clearfield And Tilcsik Book)
''Meltdown: Why Our Systems Fail and What We Can Do About It'' is a non-fiction book by Chris Clearfield and András Tilcsik, published in March 2018 by Penguin Press. It explores how complexity causes problems in modern systems and how individuals, organizations, and societies can prevent or mitigate the resulting failures. ''Meltdown'' was named a best book of the year by the ''Financial Times'' and won Canada's National Business Book Award in 2019. Background The book is the result of a collaboration between Chris Clearfield, a former derivatives trader, and András Tilcsik, a professor at the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management. Clearfield and Tilcsik took top honors in the 2015 competition for ''The Financial Times'' and McKinsey Bracken Bower Prize with their proposal for a book about how to understand systemic risk and prevent catastrophic failures in business and beyond. The following year, they signed with Penguin Press to publish ''Meltdown''. Synopsis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failure
Failure is the state or condition of not meeting a desirable or intended objective (goal), objective, and may be viewed as the opposite of Success (concept), success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. One person might consider a failure what another person considers a success, particularly in cases of direct competition or a Zero sum, zero-sum game. Similarly, the degree of success or failure in a situation may be differently viewed by distinct observers or participants, such that a situation that one considers to be a failure, another might consider to be a success, a qualified success or a neutral situation. It may also be difficult or impossible to ascertain whether a situation meets criteria for failure or success due to ambiguous or ill-defined definition of those criteria. Finding useful and effective criteria, or heuristics, to judge the success or failure of a situation may itself be a significan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tight Coupling
In computing and systems design, a loosely coupled system is one # in which components are weakly associated (have breakable relationships) with each other, and thus changes in one component least affect existence or performance of another component. # in which each of its components has, or makes use of, little or no knowledge of the definitions of other separate components. Subareas include the coupling of classes, interfaces, data, and services. Loose coupling is the opposite of tight coupling. Advantages and disadvantages Components in a loosely coupled system can be replaced with alternative implementations that provide the same services. Components in a loosely coupled system are less constrained to the same platform, language, operating system, or build environment. If systems are decoupled in time, it is difficult to also provide transactional integrity; additional coordination protocols are required. Data replication across different systems provides loose coupling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
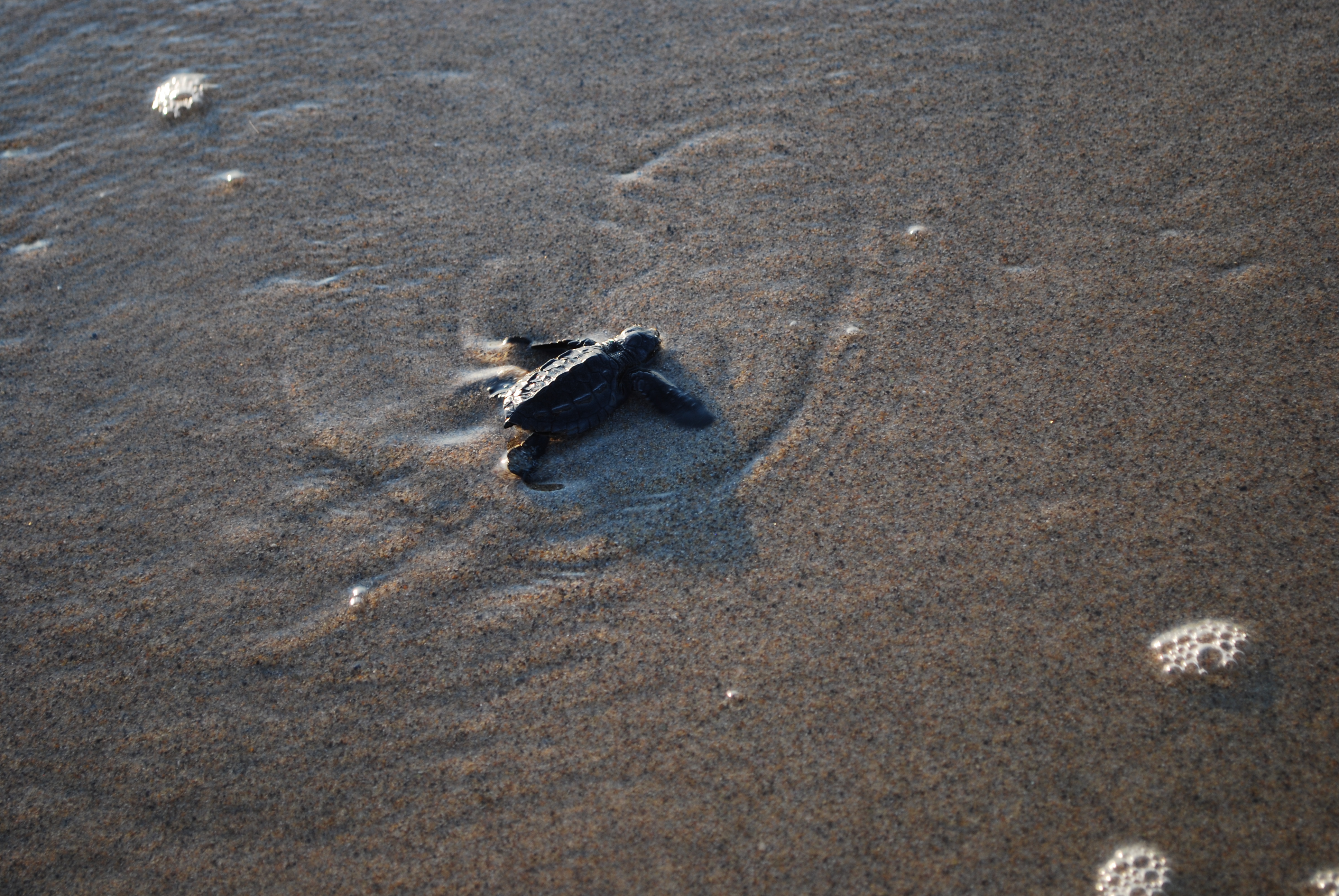
Instinct
Instinct is the inherent inclination of a living organism towards a particular complex behaviour, containing both innate (inborn) and learned elements. The simplest example of an instinctive behaviour is a fixed action pattern (FAP), in which a very short to medium length sequence of actions, without variation, are carried out in response to a corresponding clearly defined stimulus. Any behaviour is instinctive if it is performed without being based upon prior experience (that is, in the absence of learning), and is therefore an expression of innate biological factors. Sea turtles, newly hatched on a beach, will instinctively move toward the ocean. A marsupial climbs into its mother's pouch upon being born. Other examples include animal fighting, animal courtship behaviour, internal escape functions, and the building of nests. Though an instinct is defined by its invariant innate characteristics, details of its performance can be changed by experience; for example, a dog can imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Age (metaphor)
A golden age is a period considered the apotheosis in the history of a country or people, a time period when the greatness, greatest achievements were made. The term originated from early ancient Greece, Greek and ancient Rome, Roman poets, who used it to refer to a time when mankind lived in a better time and was pure (see Golden Age). The ancient Greek philosopher Hesiod introduced the term in his ''Works and Days'', when referring to the period when the "Golden Race" of man lived. This was part of fivefold division of Ages of Man, starting with the Golden age, then the Silver Age, the Bronze Age, the Greek Heroic Age, Age of Heroes (including the Trojan War), and finally, the current Iron Age. The concept was further refined by Ovid, in his ''Metamorphoses'', into the four "metal ages" (golden, silver, bronze, and iron). The Golden age in Classic literature The Golden age as described by Hesiod was an age where all humans were created directly by the Olympian gods. They d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilogue
An epilogue or epilog (from Greek ἐπίλογος ''epílogos'', "conclusion" from ἐπί ''epi'', "in addition" and λόγος ''logos'', "word") is a piece of writing at the end of a work of literature, usually used to bring closure to the work. It is presented from the perspective of within the story. When the author steps in and speaks directly to the reader, that is more properly considered an afterword. The opposite is a prologue—a piece of writing at the ''beginning'' of a work of literature or drama, usually used to open the story and capture interest. Some genres, for example television programs and video games, call the epilogue an "outro" patterned on the use of "intro" for "introduction". Epilogues are usually set in the future, after the main story is completed. Within some genres it can be used to hint at the next installment in a series of work. It is also used to satisfy the reader's curiosity and to cover any loose ends of the story. History of the term T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Management
Crisis management is the process by which an organization deals with a disruptive and unexpected event that threatens to harm the organization or its stakeholders. The study of crisis management originated with large-scale industrial and environmental disasters in the 1980s.ASIS International, "Organizational Resilience: Security, Preparedness, and Continuity Management Systems-Requirements with Guidance for Use, ASIS SPC.1-2009, American National Standard", 2009 It is considered to be the most important process in public relations. Three elements are common to a crisis: (a) a threat to the organization, (b) the element of surprise, and (c) a short decision time. Venette argues that "crisis is a process of transformation where the old system can no longer be maintained". Therefore, the fourth defining quality is the need for change. If change is not needed, the event could more accurately be described as a failure or incident. In contrast to risk management, which involves a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Stranger (sociology)
"The Stranger" is an essay by Georg Simmel, originally written as an excursus to a chapter dealing with the sociology of space in his book ''Soziologie''. In this essay, Simmel introduced the notion of "the stranger" as a unique sociological category. He differentiates the stranger both from the "outsider" who has no specific relation to a group and from the "wanderer" who comes today and leaves tomorrow. The stranger, he says, comes today and stays tomorrow. The stranger is a member of the group in which he lives and participates and yet remains distant from other – "native" – members of the group. In comparison to other forms of social distance and difference (such as class, gender, and even ethnicity) the distance of the stranger has to do with his "origins". The stranger is perceived as extraneous to the group and even though he is in constant relation to other group members; his "distance" is more emphasized than his "nearness". As one subsequent interpreter of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diversity (politics)
Diversity as seen in sociology and political studies is the degree of differences in identifying features among the members of a purposefully defined group, such as any group differences in racial or ethnic classifications, age, gender, religion, philosophy, physical abilities, socioeconomic background, sexual orientation, gender identity, intelligence, mental health, physical health, genetic attributes, personality, behavior or attractiveness. When measuring human diversity, a diversity index exemplifies the likelihood that two randomly selected residents have different ethnicities. If all residents are of the same ethnic group it is zero by definition. If half are from one group and half from another, it is 50. The diversity index does not take into account the willingness of individuals to cooperate with those of other ethnicities. International human rights The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities affirms to "respect difference and acceptance of person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skepticism
Skepticism, also spelled scepticism, is a questioning attitude or doubt toward knowledge claims that are seen as mere belief or dogma. For example, if a person is skeptical about claims made by their government about an ongoing war then the person doubts that these claims are accurate. In such cases, skeptics normally recommend not disbelief but suspension of belief, i.e. maintaining a neutral attitude that neither affirms nor denies the claim. This attitude is often motivated by the impression that the available evidence is insufficient to support the claim. Formally, skepticism is a topic of interest in philosophy, particularly epistemology. More informally, skepticism as an expression of questioning or doubt can be applied to any topic, such as politics, religion, or pseudoscience. It is often applied within restricted domains, such as morality ( moral skepticism), atheism (skepticism about the existence of God), or the supernatural. Some theorists distinguish "good" or moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissent
Dissent is an opinion, philosophy or sentiment of non-agreement or opposition to a prevailing idea or policy enforced under the authority of a government, political party or other entity or individual. A dissenting person may be referred to as a ''dissenter''. The term's antonyms include ''agreement'', '' consensus'' (when all or nearly all parties agree on something) and ''consent'' (when one party agrees to a proposition made by another). Philosophical In philosophical skepticism, particularly that of Pyrrhonism, the existence of dissent is a rationale for suspending judgment regarding the issue associated with the dissent. Dissent in this respect appears as one of the tropes in the Five Modes of Agrippa, pointing to the uncertainty demonstrated by the differences of opinions among philosophers and people in general. Political Political dissent is a dissatisfaction with or opposition to the policies of a governing body. Expressions of dissent may take forms from voca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near Miss (safety)
A near miss, near hit or close call is an unplanned event that has the potential to cause, but does not actually result in human injury, environmental or equipment damage, or an interruption to normal operation. OSHA defines a near miss as an incident in which no property was damaged and no personal injury was sustained, but where, given a slight shift in time or position, damage or injury easily could have occurred. Near misses also may be referred to as near accidents, accident precursors, injury-free events and, in the case of moving objects, near collisions. A near miss is often an error, with harm prevented by other considerations and circumstances. Causes There are factors for a near miss related to the operator, and factors related to the context. Fatigue is an example for the former. The risk of a car crash after a more than 24h shift for physicians has been observed to increase by 168%, and the risk of near miss by 460%. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Tool
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either rational or irrational. The decision-making process is a reasoning process based on assumptions of values, preferences and beliefs of the decision-maker. Every decision-making process produces a final choice, which may or may not prompt action. Research about decision-making is also published under the label problem solving, particularly in European psychological research. Overview Decision-making can be regarded as a problem-solving activity yielding a solution deemed to be optimal, or at least satisfactory. It is therefore a process which can be more or less rational or irrational and can be based on explicit or tacit knowledge and beliefs. Tacit knowledge is often used to fill the gaps in complex decision-making processes. Usually, both of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |