|
Melanin-concentrating Hormone Receptor 1
Melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1, also known as MCH1, is one of the melanin-concentrating hormone receptors found in all mammals. The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family 1, is an integral plasma membrane protein which binds melanin-concentrating hormone. The encoded protein can inhibit cAMP accumulation and stimulate intracellular calcium flux, and is probably involved in the neuronal regulation of food consumption. Although structurally similar to somatostatin receptors, this protein does not seem to bind somatostatin. Function MCH1 is thought to have a number of functions including in the regulation of appetite, and in stress, anxiety and depression. Selective ligands Agonists * Melanin concentrating hormone (MCH) * S-36057 - modified MCH 6-13 fragment substituted with 3-iodotyrosine at N-terminus via dioxyoctanoyl linker, used as 125I radioligand for mapping MCH1 ''in vivo''. * LK-184 (Procter & Gamble The Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanin-concentrating Hormone Receptor
Two Melanin-concentrating hormone receptors (MCHR) have recently been characterized: MCH-R1 and MCH-R2. These two receptors share approximately 38% homology. * MCH-R1 is expressed in all mammals. * MCH-R2 is only found in some primates and carnivores including dogs, ferrets and humans. Clinical significance Antagonists might be useful in the treatment of obesity and anxiety and depression. An agonist might have possible utility as a treatment for osteoporosis and insomnia Research is ongoing for antagonists affecting MCH receptors R1 and R2. See also * Melanin concentrating hormone * Melanin Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ... References External links * * * * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanin Concentrating Hormone
Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), also known as pro-melanin stimulating hormone (PMCH), is a cyclic 19-amino acid orexigenic hypothalamic peptide Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A ... originally isolated from the pituitary gland of teleost fish, where it controls skin pigmentation. In mammals it is involved in the regulation of feeding behavior, mood, sleep-wake cycle and energy balance. Structure MCH is a cyclic 19-amino acid neuropeptide, as it is a polypeptide chain that is able to act as a neurotransmitter. MCH neurons are mainly concentrated in the lateral hypothalamic area, zona incerta, and the incerto-hypothalamic area, but they are also located, in much smaller amounts, in the paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF), medial preoptic area, laterodors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
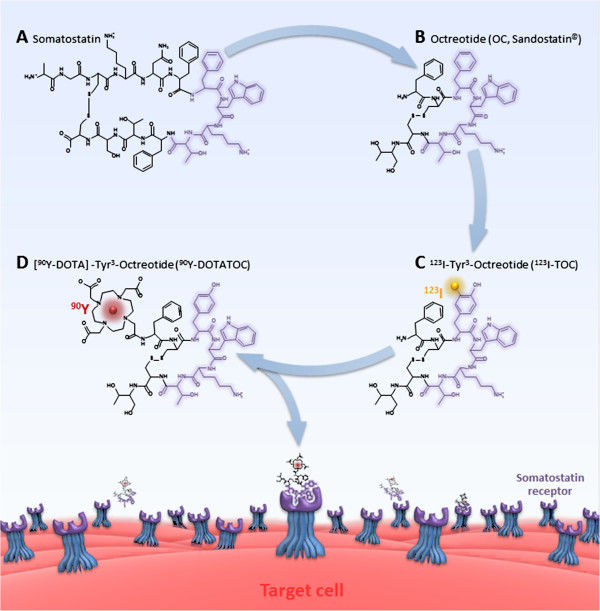
Somatostatin Receptor
Somatostatin receptors are receptors for the ligand somatostatin, a small neuropeptide associated with neural signaling, particularly in the post-synaptic response to NMDA receptor co-stimulation/activation. Somatostatin is encoded by a CRE and is very susceptible to gene promoter region activation by transcription factor CREB. There are five known somatostatin receptors: * SST1 () * SST2 () * SST3 () * SST4 () * SST5 () All are G protein-coupled seven transmembrane receptor G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of protein family, evolution ...s. References External links * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatostatin
Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion. Somatostatin has two active forms produced by the alternative cleavage of a single preproprotein: one consisting of 14 amino acids (shown in infobox to right), the other consisting of 28 amino acids. Among the vertebrates, there exist six different somatostatin genes that have been named ''SS1, SS2, SS3, SS4, SS5'' and ''SS6''. Zebrafish have all six. The six different genes, along with the five different somatostatin receptors, allow somatostatin to possess a large range of functions. Humans have only one somatostatin gene, ''SST''. Nomenclature Synonyms of "somatostatin" include: * growth hormone� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopic Labeling
Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope (an atom with a detectable variation in neutron count) through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling. In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procter & Gamble
The Procter & Gamble Company (P&G) is an American multinational consumer goods corporation headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio, founded in 1837 by William Procter and James Gamble. It specializes in a wide range of personal health/consumer health, personal care and hygiene products; these products are organized into several segments including beauty; grooming; health care; fabric & home care; and baby, feminine, & family care. Before the sale of Pringles to Kellogg's, its product portfolio also included food, snacks, and beverages. P&G is incorporated in Ohio. In 2014, P&G recorded $83.1 billion in sales. On August 1, 2014, P&G announced it was streamlining the company, dropping and selling off around 100 brands from its product portfolio in order to focus on the remaining 65 brands, which produced 95% of the company's profits. A.G. Lafley, the company's chairman and CEO until October 2015, said the future P&G would be "a much simpler, much less complex company of leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATC-0175
ATC-0175 is a drug used in scientific research, which is a selective, non-peptide antagonist at the melanin concentrating hormone receptor MCH1. In animal studies it has been shown to produce both anxiolytic and antidepressant actions, but without sedative or ataxic Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements. Ataxia is a clinical manifestation indicating dysfunction of ... side effects. References Antidepressants Anxiolytics Quinazolines Benzamides Fluoroarenes {{Anxiolytic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GW-803,430
GW-803430 (GW-3430) is a drug used in scientific research and is a selective non-peptide antagonist at the melanin concentrating hormone receptor MCH1. In animal studies it has anxiolytic, antidepressant Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, hea ... and anorectic effects. References Experimental antidepressants Anxiolytics Anorectics 1-Pyrrolidinyl compounds Phenol ethers Lactams Chloroarenes {{Anxiolytic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGD-4715
NGD-4715 is a drug developed by Neurogen, which acts as a selective, non-peptide antagonist at the melanin concentrating hormone receptor MCH1. In animal models it has anxiolytic, antidepressant, and anorectic effects, and it has successfully passed Phase I clinical trials in humans. Neurogen was acquired by Ligand Pharmaceuticals Ligand Pharmaceuticals is a biopharmaceutical company located in San Diego, California. Founded in 1987 as Progenix Inc., the company went public in 1992. Initially focused on developing its own drugs, a period of turbulence in the early 2000s cul ... in August, 2009, and NGD-4715 was not listed among its key assets. All four laboratories were closed and sold, and no employees were retained. The structure of NGD-4715 has been confused with for example 1-(5-bromo-6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-4-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)piperazine. References Antidepressants Anxiolytics Anorectics Pyridines Phenol ethers Abandoned drugs {{anxiolytic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNAP-7941
SNAP-7941 is a drug used in scientific research, which is a selective, non-peptide antagonist at the melanin concentrating hormone receptor MCH1. In initial animal studies it had promising anxiolytic, antidepressant and anorectic effects, but subsequent trial results were disappointing, and the main significance of SNAP-7941 is as the lead compound A lead compound (, i.e. a "leading" compound, not to be confused with various compounds of the metallic element lead) in drug discovery is a chemical compound that has pharmacology, pharmacological or biological activity likely to be therapeutical ... from which more potent and selective antagonists such as SNAP-94847 were developed, although it continues to be used for research into the function of the MCH1 receptor. References Experimental antidepressants Anxiolytics Ethers Fluoroarenes Anilides Pyrimidones Methyl esters {{Pharma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNAP-94847
SNAP-94847 is a drug used in scientific research, which is a selective, non-peptide antagonist at the melanin concentrating hormone receptor MCH1. In animal studies it has been shown to produce both anxiolytic and antidepressant effects, and also reduces food consumption suggesting a possible anorectic An anorectic or anorexic is a drug which reduces appetite, resulting in lower food consumption, leading to weight loss. By contrast, an appetite stimulant is referred to as orexigenic. The term is (from the Greek ''ἀν-'' (an-) = "without" a ... effect. References 4-Phenylpiperidines Experimental antidepressants Anxiolytics Anorectics Fluoroarenes Phenol ethers Carboxamides Anilides {{Anxiolytic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |