|
Mediastinal
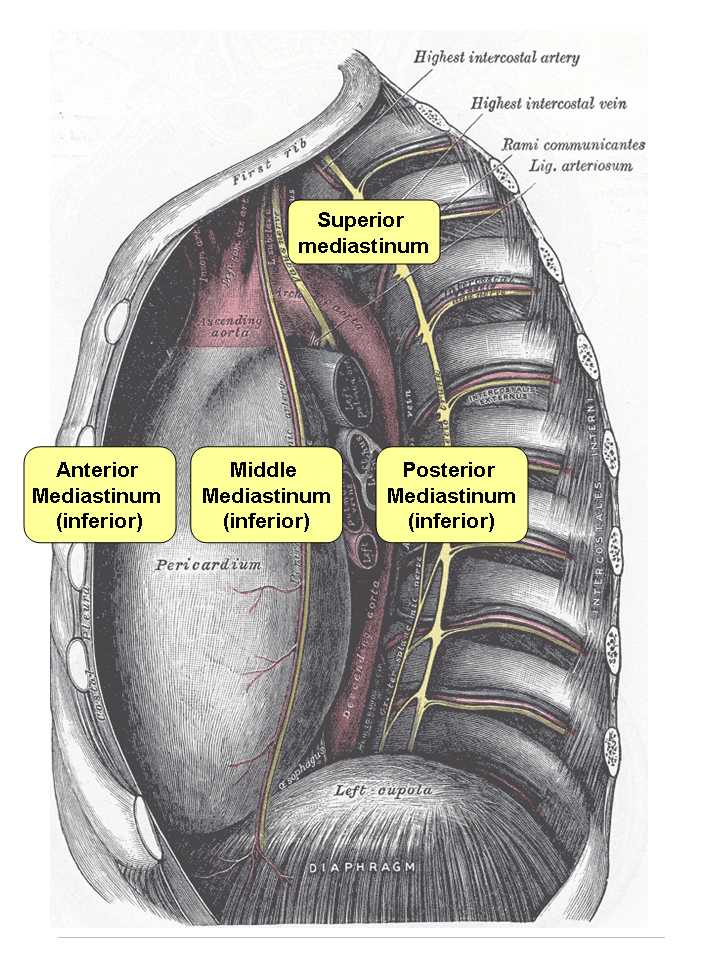
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest. Anatomy The mediastinum lies within the thorax and is enclosed on the right and left by pleurae. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lungs to the sides and the spine at the back. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck. The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part: * The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends at the thoracic plane. * The inferior mediastinum from this level to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Plane
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest. Anatomy The mediastinum lies within the thorax and is enclosed on the right and left by pleurae. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lungs to the sides and the spine at the back. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck. The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part: * The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends at the thoracic plane. * The inferior mediastinum from this level to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic nerve, phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest. Anatomy The mediastinum lies within the thorax and is enclosed on the right and left by pulmonary pleurae, pleurae. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lungs to the sides and the Spine (anatomy), spine at the back. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck. The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part: * The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends at the #Thoracic plane, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Pleurae
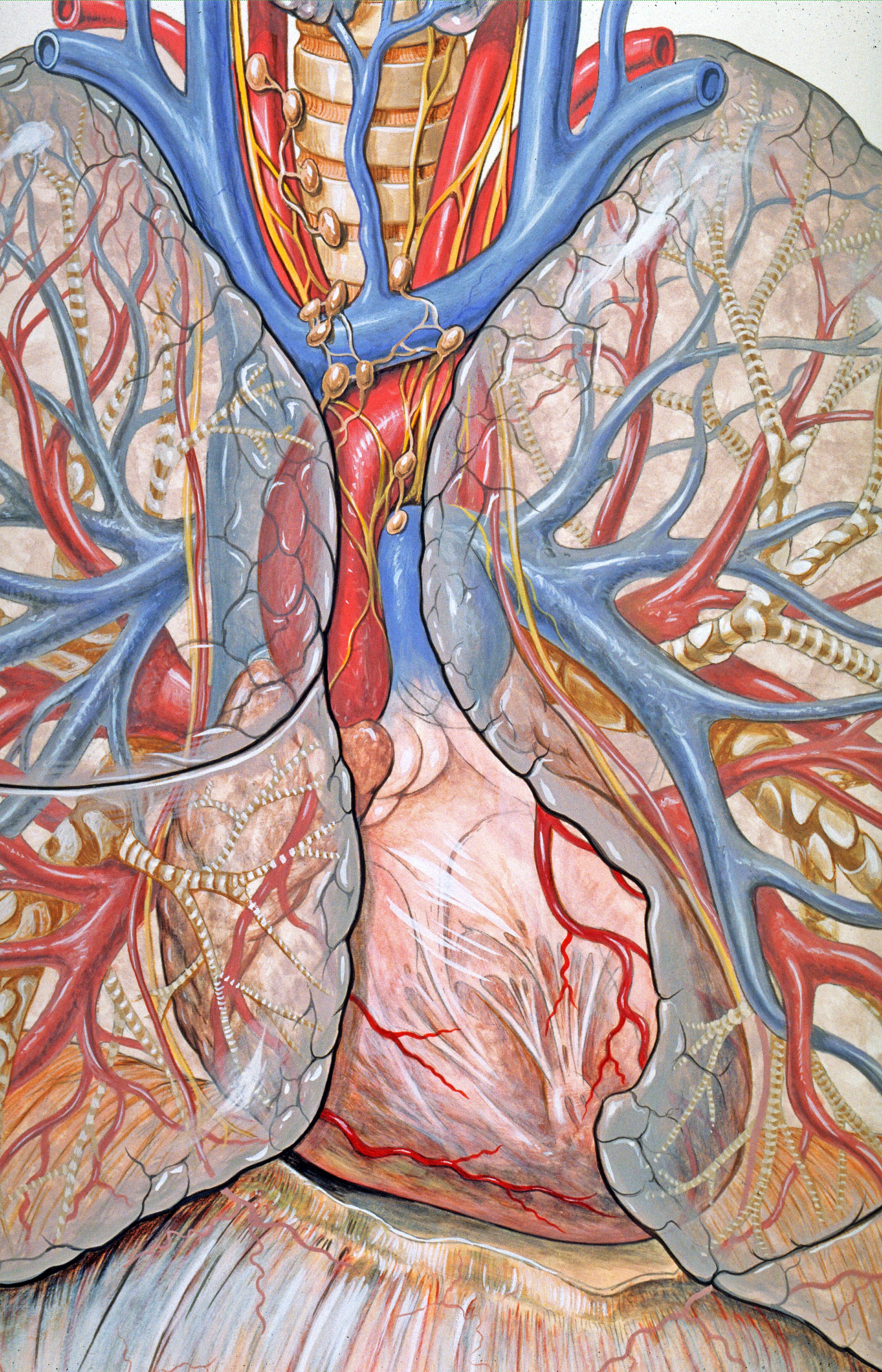
The pulmonary pleurae (''sing.'' pleura) are the two opposing layers of serous membrane overlying the lungs and the inside of the surrounding chest walls. The inner pleura, called the visceral pleura, covers the surface of each lung and dips between the lobes of the lung as ''fissures'', and is formed by the invagination of lung buds into each coelomic cavity, thoracic sac during embryonic development. The outer layer, called the parietal pleura, lines the inner surfaces of the thoracic cavity on each side of the mediastinum, and can be subdivided into ''mediastinal'' (covering the side surfaces of the fibrous pericardium, oesophagus and thoracic aorta), ''diaphragmatic'' (covering the upper surface of the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm), ''costal'' (covering the inside of rib cage) and cervical (covering the underside of the suprapleural membrane) pleurae. The visceral and the mediastinal parietal pleurae are connected at the root of the lung ("hilum") through a smooth fold kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible. Humans have two lungs, one on the left and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve is a mixed motor/sensory nerve which originates from the C3-C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, the right and left phrenic nerves are primarily supplied by the C4 spinal nerve, but there is also contribution from the C3 and C5 spinal nerves. From its origin in the neck, the nerve travels downward into the chest to pass between the heart and lungs towards the diaphragm. In addition to motor fibers, the phrenic nerve contains sensory fibers, which receive input from the central tendon of the diaphragm and the mediastinal pleura, as well as some sympathetic nerve fibers. Although the nerve receives contributions from nerves roots of the cervical plexus and the brachial plexus, it is usually considered separate from either plexus. The name of the nerve comes from Ancient Greek ''phren'' 'diaphragm'. Structure The phrenic n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule. The thymus is made up of immature T cells called thymocytes, as well as lining cells called epithelial cells which help the thymocytes develop. T cells that successfully develop react appropriately with MHC immune receptors of the body (called ''positive selection'') and not against proteins of the body (called ''negative selection''). The thymus is largest and most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens, the thymus begins to decrease in size and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There are two openings of the thoracic cavity, a superior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic inlet and a lower inferior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic outlet. The thoracic cavity includes the tendons as well as the cardiovascular system which could be damaged from injury to the back, spine or the neck. Structure Structures within the thoracic cavity include: * structures of the cardiovascular system, including the heart and great vessels, which include the thoracic aorta, the pulmonary artery and all its branches, the superior and inferior vena cava, the pulmonary veins, and the azygos vein * structures of the respiratory system, including the diaphragm, trachea, bronchi and lungs * structures of the digestive system, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loose Connective Tissue
Loose connective tissue, sometimes called areolar tissue, is a cellular connective tissue with thin and relatively sparse collagen fibers. Its ground substance occupies more volume than the fibers do. It has a viscous to gel-like consistency and plays an important role in the diffusion of oxygen and nutrients from the capillaries that course through this connective tissue as well as in the diffusion of carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes back to the vessels. Moreover, loose connective tissue is primarily located beneath the epithelia that cover the body surfaces and line the internal surfaces of the body. It is also associated with the epithelium of glands and surrounds the smallest blood vessels. This tissue is thus the initial site where pathogenic agents, such as bacteria that have breached an epithelial surface, are challenged and destroyed by cells of the immune system. In the past, the designations areolar tissue, adipose tissue, and reticular tissue have been listed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about long in adults, that travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word ''oesophagus'' is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω (phérō, “I carry”) + ἔφαγον (éphagon, “I ate”). The wall of the esophagus from the lumen outwards consists of mucosa, submucosa (connective tissue), layers of muscle fibers between layers of fibrous tissue, and an outer layer of connective tissue. The mucosa is a stratified squamous epithel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying annular ligaments of trachea, ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing. The trachea begins to form in the second month of embryo development, becoming longer and more fixed in its position over time. It is epithelium lined with columnar epithelium, column-shaped cells that have hair-like extensions called cilia, with scattered goblet cells that produce protective mucins. The trachea can be affected by inflammation or infection, us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gladiolus) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of serous membrane (serous pericardium). It encloses the pericardial cavity, which contains pericardial fluid, and defines the middle mediastinum. It separates the heart from interference of other structures, protects it against infection and blunt trauma, and lubricates the heart's movements. The English name originates from the Ancient Greek prefix "''peri-''" (περί; "around") and the suffix "''-cardion''" (κάρδιον; "heart"). Anatomy The pericardium is a tough fibroelastic sac which covers the heart from all sides except at the cardiac root (where the great vessels join the heart) and the bottom (where only the serous pericardium exists to cover the upper surface of the central tendon of diaphragm). The fibrous pericardiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |