|
Meatpacking
The meat-packing industry (also spelled meatpacking industry or meat packing industry) handles the slaughtering, processing, packaging, and distribution of meat from animals such as cattle, pigs, sheep and other livestock. Poultry is generally not included. This greater part of the entire meat industry is primarily focused on producing meat for human consumption, but it also yields a variety of by-products including hides, dried blood, protein meals such as meat & bone meal, and, through the process of rendering, fats (such as tallow). In the United States and some other countries, the facility where the meat packing is done is called a ''slaughterhouse'', ''packinghouse'' or a ''meat-packing plant''; in New Zealand, where most of the products are exported, it is called a ''freezing works''. An abattoir is a place where animals are slaughtered for food. The meat-packing industry grew with the construction of the railroads and methods of refrigeration for meat preservation. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meat Industry
The meat industry are the people and companies engaged in modern industrialized livestock agriculture for the production, packing, preservation and marketing of meat (in contrast to dairy products, wool, etc.). In economics, the meat industry is a fusion of primary (agriculture) and secondary (industry) activity and hard to characterize strictly in terms of either one alone. The greater part of the meat industry is the meat packing industry – the segment that handles the slaughtering, processing, packaging, and distribution of animals such as poultry, cattle, pigs, sheep and other livestock. A great portion of the ever-growing meat branch in the food industry involves intensive animal farming in which livestock are kept almost entirely indoors or in restricted outdoor settings like pens. Many aspects of the raising of animals for meat have become industrialized, even many practices more associated with smaller family farms, e.g. gourmet foods such as foie gras. The production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slaughter (livestock)
Animal slaughter is the killing of animals, usually referring to killing domestic livestock. It is estimated that each year 80 billion land animals are slaughtered for food. Most animals are slaughtered for food; however, they may also be slaughtered for other reasons such as for harvesting of pelts, being diseased and unsuitable for consumption, or being surplus for maintaining a breeding stock. Slaughter typically involves some initial cutting, opening the major body cavities to remove the entrails and offal but usually leaving the carcass in one piece. Such dressing can be done by hunters in the field (field dressing of game) or in a slaughterhouse. Later, the carcass is usually butchered into smaller cuts. The animals most commonly slaughtered for food are cattle and water buffalo, sheep, goats, pigs, deers, horses, poultry (mainly chickens, turkeys, ducks and geese), insects (a commercial species is the house cricket), and increasingly, fish in the aquaculture indust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abattoir
A slaughterhouse, also called abattoir (), is a facility where animals are slaughtered to provide food. Slaughterhouses supply meat, which then becomes the responsibility of a packaging facility. Slaughterhouses that produce meat that is not intended for human consumption are sometimes referred to as ''knacker's yards'' or ''knackeries''. This is where animals are slaughtered that are not fit for human consumption or that can no longer work on a farm, such as retired work horses. Slaughtering animals on a large scale poses significant issues in terms of logistics, animal welfare, and the environment, and the process must meet public health requirements. Due to public aversion in different cultures, determining where to build slaughterhouses is also a matter of some consideration. Frequently, animal rights groups raise concerns about the methods of transport to and from slaughterhouses, preparation prior to slaughter, animal herding, and the killing itself. History Until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slaughterhouse
A slaughterhouse, also called abattoir (), is a facility where animals are slaughtered to provide food. Slaughterhouses supply meat, which then becomes the responsibility of a packaging facility. Slaughterhouses that produce meat that is not intended for human consumption are sometimes referred to as ''knacker's yards'' or ''knackeries''. This is where animals are slaughtered that are not fit for human consumption or that can no longer work on a farm, such as retired work horses. Slaughtering animals on a large scale poses significant issues in terms of logistics, animal welfare, and the environment, and the process must meet public health requirements. Due to public aversion in different cultures, determining where to build slaughterhouses is also a matter of some consideration. Frequently, animal rights groups raise concerns about the methods of transport to and from slaughterhouses, preparation prior to slaughter, animal herding, and the killing itself. History Unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Meat Inspection Act
The Federal Meat Inspection Act of 1906 (FMIA) is an American law that makes it illegal to adulterate or misbrand meat and meat products being sold as food, and ensures that meat and meat products are slaughtered and processed under strictly regulated sanitary conditions. These requirements also apply to imported meat products, which must be inspected under equivalent foreign standards. United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) inspection of poultry was added by the Poultry Products Inspection Act of 1957 (PPIA). The Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act authorizes the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to provide inspection services for all livestock and poultry species not listed in the FMIA or PPIA, including venison and buffalo. The Agricultural Marketing Act authorizes the USDA to offer voluntary, fee-for-service inspection services for these same species. Historical motivation for enactment The original 1906 Act authorized the Secretary of Agriculture to inspect and cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pure Food And Drug Act Of 1906
The Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906, also known as Dr. Wiley's Law, was the first of a series of significant consumer protection laws which was enacted by Congress in the 20th century and led to the creation of the Food and Drug Administration. Its main purpose was to ban foreign and interstate traffic in adulterated or mislabeled food and drug products, and it directed the U.S. Bureau of Chemistry to inspect products and refer offenders to prosecutors. It required that active ingredients be placed on the label of a drug's packaging and that drugs could not fall below purity levels established by the United States Pharmacopeia or the National Formulary. In the late 1800s, the quality of food in the United States decreased significantly as populations moved to cities and the time from farm to market increased. Many food producers turned to using dangerous preservatives, even formaldehyde, to keep food fresh. Simultaneously, the quality of medicine was abysmal. Quack medicine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
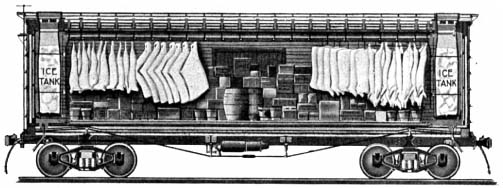
Gustavus Franklin Swift
Gustavus Franklin Swift, Sr. (June 24, 1839 – March 29, 1903) was an American business executive. He founded a meat-packing empire in the Midwest during the late 19th century, over which he presided until his death. He is credited with the development of the first practical ice-cooled railroad car, which allowed his company to ship dressed meats to all parts of the country and abroad, ushering in the "era of cheap beef." Swift pioneered the use of animal by-products for the manufacture of soap, glue, fertilizer, various types of sundries, and even medical products. Swift donated large sums of money to such institutions as the University of Chicago, the Methodist Episcopal Church, and YMCA. He established Northwestern University's "School of Oratory" in memory of his daughter, Annie May Swift, who died while a student there. When he died in 1903, his company was valued at between US$125 million and $135 million, and had a workforce of more than 21,000. "The House of Swift" s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Armour
Philip Danforth Armour Sr. (16 May 1832 – 6 January 1901) was an American meatpacking industrialist who founded the Chicago-based firm of Armour & Company. Born on an upstate New York farm, he made $8,000 in the California gold rush, 1852–56. He opened a wholesale soap business in Cincinnati, then moved it to Milwaukee. He made millions selling meat to the United States Army during the Civil War. In 1875, he moved his base to Chicago. Armour's innovations including bringing live hogs to the metropolis for slaughter, inventing an assembly line system for the dis-assembly of hogs, canning the product, economy of scale and efficiency in detail. He systematically utilized waste products, boasting that he made use of "everything but the squeal". The introduction of refrigerated rail cars opened a national market for him and competitors such as Gustavus Swift. Armour expanded into banking and speculation on the futures market for pork and wheat by 1900, his plants employed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus''). In prehistoric times, humankind hunted aurochs and later domesticated them. Since that time, numerous breeds of cattle have been bred specifically for the quality or quantity of their meat. Today, beef is the third most widely consumed meat in the world, after pork and poultry. As of 2018, the United States, Brazil, and China were the largest producers of beef. Beef can be prepared in various ways; cuts are often used for steak, which can be cooked to varying degrees of doneness, while trimmings are often ground or minced, as found in most hamburgers. Beef contains protein, iron, and vitamin B12. Along with other kinds of red meat, high consumption is associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer and coronary heart disease, especially when processed. Beef has a high environmental impact, being a primary driver of deforestation with the highest greenhouse gas emissions of any agricultural product. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
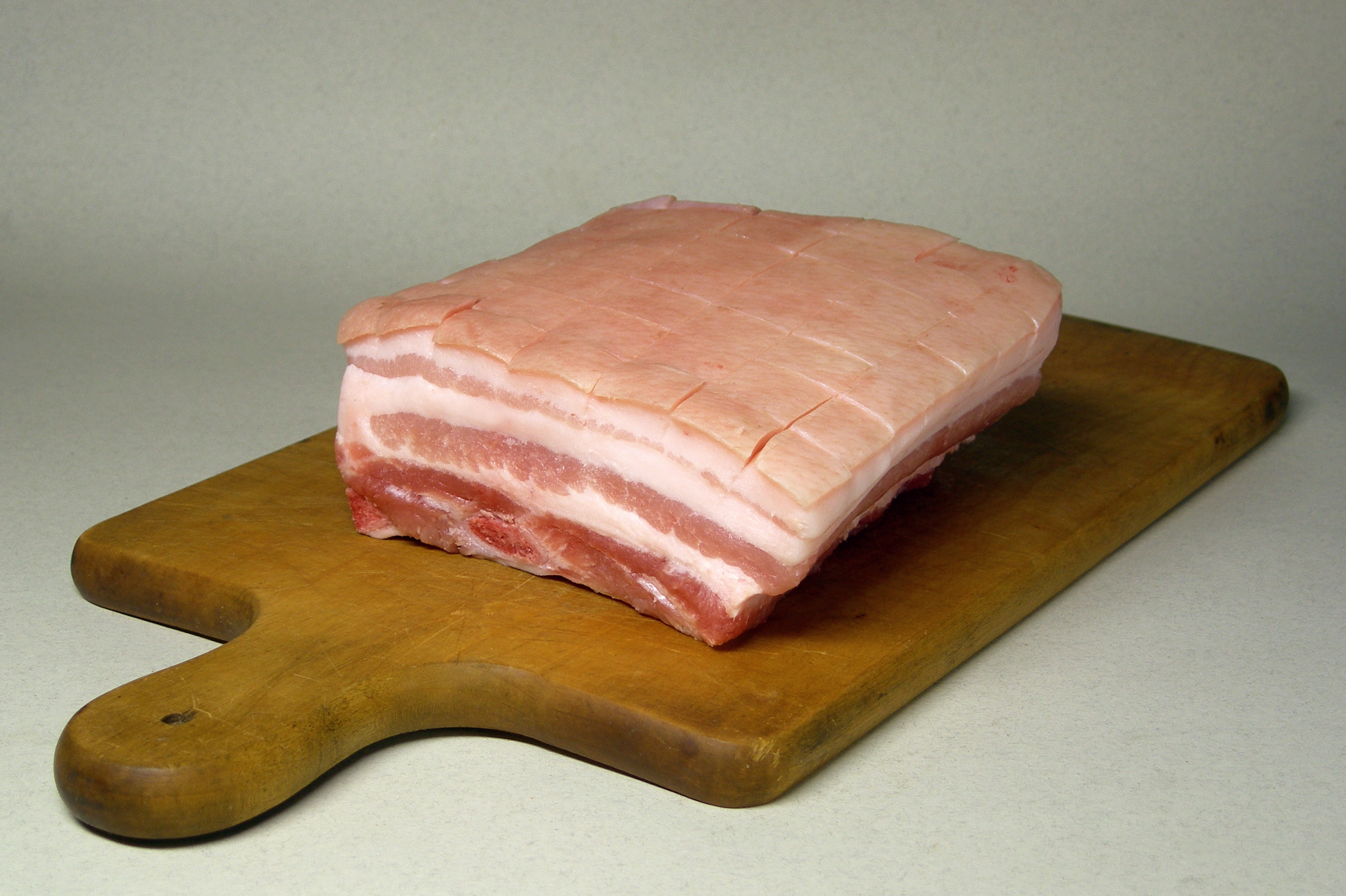
Pork Dressing (20107657)
Pork is the culinary name for the meat of the domestic pig (''Sus domesticus''). It is the most commonly consumed meat worldwide, with evidence of pig husbandry dating back to 5000 BCE. Pork is eaten both freshly cooked and preserved; curing extends the shelf life of pork products. Ham, gammon, bacon, and sausage are examples of preserved pork. Charcuterie is the branch of cooking devoted to prepared meat products, many from pork. Pork is the most popular meat in the Western world, particularly in Central Europe. It is also very popular in East and Southeast Asia (Mainland Southeast Asia, Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor). The meat is highly prized in Asian cuisines, especially in Mainland China, for its fat content and texture. Some religions and cultures prohibit pork consumption, notably Islam and Judaism. History Pigs were domesticated in Mesopotamia around 13,000 BC. Charcuterie is the branch of cooking devoted to prepared meat products such as bacon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(14776552555).jpg)
.jpg)