|
Mbuti People
The Mbuti people, or Bambuti, are one of several indigenous pygmy groups in the Congo region of Africa. Their languages are Central Sudanic languages and Bantu languages. Subgroups Bambuti are pygmy hunter-gatherers, and are one of the oldest indigenous people of the Congo region of Africa. The Bambuti are composed of bands which are relatively small in size, ranging from 15 to 60 people. The Bambuti population totals about 30,000 to 40,000 people. Many Batwa in various parts of the DRC call themselves Bambuti as well. There are three distinct subgroups: * The Sua (also Kango, or Mbuti), who speak a dialect (or perhaps two) of the language of a neighboring Bantu people, Bila. They are located centrally and are eponymous of the larger group. * The Efé, who speak the language of the neighboring Central Sudanic Lese. * The Asua, speakers of the Mangbetu (Central Sudanic) Asua language. Environment The Mbuti population live in the Ituri, a tropical rainforest covering a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osa Johnson
Martin Elmer Johnson (October 9, 1884 – January 13, 1937) and Osa Helen Johnson (née Leighty, March 14, 1894 – January 7, 1953) were married American adventurers and documentary filmmakers. In the first half of the 20th century the couple captured the public's imagination through their films and books of adventure in exotic, faraway lands. Photographers, explorers, marketers, naturalists and authors, Martin and Osa studied the wildlife and peoples of East and Central Africa, the South Pacific Islands and British North Borneo. They explored then-unknown lands and brought back film footage and photographs, offering many Americans their first understanding of these distant lands. Early Lives Martin Elmer Johnson was born on October 9, 1884. Osa Leighty was born March 14, 1894, and raised in Chanute, Kansas. Although born in Rockford, Illinois, Martin Johnson grew up in the Kansas towns of Lincoln and Independence. His father worked as a jeweler and would bring home crates la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Trypanosomiasis
African trypanosomiasis, also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals. It is caused by the species ''Trypanosoma brucei''. Humans are infected by two types, ''Trypanosoma brucei gambiense'' (TbG) and '' Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense'' (TbR). TbG causes over 98% of reported cases. Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas. Initially, the first stage of the disease is characterized by fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains, beginning one to three weeks after the bite. Weeks to months later, the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness, and trouble sleeping. Diagnosis is by finding the parasite in a blood smear or in the fluid of a lymph node. A lumbar puncture is often needed to tell the difference between first- and second-stage disease. If the disease is not treated quickly it can lead to death. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsetse Flies
Tsetse ( , or ) (sometimes spelled tzetze; also known as tik-tik flies), are large, biting flies that inhabit much of tropical Africa. Tsetse flies include all the species in the genus ''Glossina'', which are placed in their own family, Glossinidae. The tsetse are obligate parasites, which live by feeding on the blood of vertebrate animals. Tsetse have been extensively studied, because of their role in transmitting disease. They have a prominent economic impact in sub-Saharan Africa, as the biological vectors of trypanosomes, causing human and animal trypanosomiasis. Tsetse are multivoltine and long-lived, typically producing about four broods per year, with up to 31 broods over their lifespans. Tsetse can be distinguished from other large flies by two easily-observed features: Primarily, tsetse fold their wings over their abdomens completely when they are resting (so that one wing rests directly on top of the other); Secondly, tsetse also have a long proboscis, extending d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, dysfunction, distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injuries, disabilities, disorders, syndromes, infections, isolated symptoms, deviant behaviors, and atypical variations of structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The temperate counterpart to the tropical dry season is summer or winter. Rain belt The tropical rain belt lies in the southern hemisphere roughly from October to March; during that time the northern tropics have a dry season with sparser precipitation, and days are typically sunny throughout. From April to September, the rain belt lies in the northern hemisphere, and the southern tropics have their dry season. Under the Köppen climate classification, for tropical climates, a dry season month is defined as a month when average precipitation is below . The rain belt reaches roughly as far north as the Tropic of Cancer and as far south as the Tropic of Capricorn. Near these latitudes, there is one wet season and one dry season annually. At the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Republic Of The Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in Central Africa. It is bordered to the northwest by the Republic of the Congo, to the north by the Central African Republic, to the northeast by South Sudan, to the east by Uganda, Rwanda, and Burundi, and by Tanzania (across Lake Tanganyika), to the south and southeast by Zambia, to the southwest by Angola, and to the west by the South Atlantic Ocean and the Cabinda exclave of Angola. By area, it is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 108 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous officially Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the nation's economic center. Centered on the Cong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainforest, but other types have been described. Estimates vary from 40% to 75% of all biotic species being indigenous to the rainforests. There may be many millions of species of plants, insects and microorganisms still undiscovered in tropical rainforests. Tropical rainforests have been called the "jewels of the Earth" and the " world's largest pharmacy", because over one quarter of natural medicines have been discovered there. Rainforests as well as endemic rainforest species are rapidly disappearing due to deforestation, the resulting habitat loss and pollution of the atmosphere. Definition Rainforest are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, high humidity, the presence of moisture-dependent vegetation, a moist layer of lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ituri Rainforest
The Ituri Rainforest is a rainforest located in the Ituri Province of northeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. The forest's name derives from the nearby Ituri River which flows through the rainforest, connecting firstly to the Aruwimi River and finally into the Congo. Geography The Ituri Rainforest is about in area, and is located between 0° and 3°N and 27° and 30° E. Elevation in the Ituri ranges from about . The climate is warm and humid, as exemplified by the nearby city of Bunia, which however is at a slightly higher elevation. About one-fifth of the rainforest is made up of the Okapi Wildlife Reserve, a World Heritage Site. It is also the home of the Mbuti pygmies, one of the hunter-gatherer peoples living in equatorial rainforests characterised by their short height (below , on average). They have been the subject of research by a variety of outsiders, including Patrick and Anne Eisner Putnam, who lived on the banks of the at the edge of the Ituri. They were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
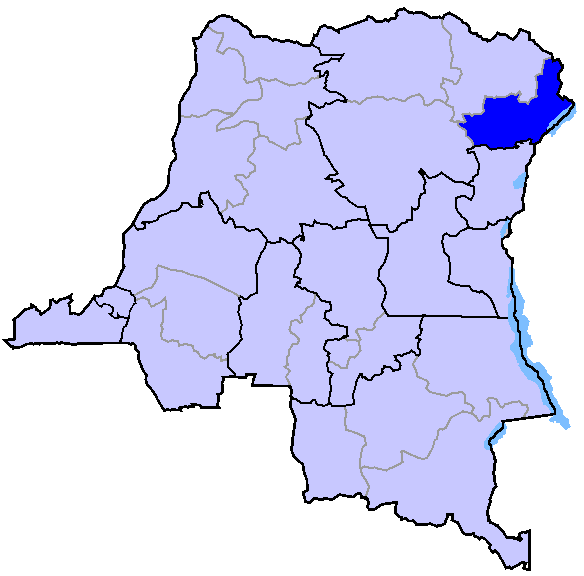
Région Ituri République Démocratique Du Congo
France is divided into eighteen administrative regions (french: régions, singular ), of which thirteen are located in metropolitan France (in Europe), while the other five are overseas regions (not to be confused with the overseas collectivities, which have a semi-autonomous status). All of the thirteen metropolitan administrative regions (including Corsica ) are further subdivided into two to thirteen administrative departments, with the prefect of each region's administrative centre's department also acting as the regional prefect. The overseas regions administratively consist of only one department each and hence also have the status of overseas departments. Most administrative regions also have the status of regional territorial collectivities, which comes with a local government, with departmental and communal collectivities below the region level. The exceptions are Corsica, French Guiana, Mayotte and Martinique, where region and department functions are managed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asua Language
Asoa, also known as ''Asua, Asuae, Asuati,'' or ''Aka,'' is a Central Sudanic language spoken by the Mbuti Pygmies known as the Asua. It is closely related to the Mangbetu language, and the Asua live in association with the Mangbetu people, among others. It is the only distinctive Pygmy language in the east. Asua is spoken in the forests to the north of the Aruwimi River, between the Nepoko River and the headwaters of the Rubi River The Rubi River (french: Rivière Rubi) is a left tributary of the Itimbiri River, which forms where the Rubi joins the Likati River. Course The Rubi River originates in the southeast of the Bas-Uélé province, then flows west until it meets the L ....Demolin, Didier. 1992. ''Le Mangbetu: etude phonétique et phonologique'', 2 vols. Brussels: Faculté de Philosophie et Lettres, Université libre de Bruxelles dissertation. References Central Sudanic languages African Pygmies Languages of the Democratic Republic of the Congo {{Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |