|
Maude Royden
Agnes Maude Royden (23 November 1876 – 30 July 1956), later known as Maude Royden-Shaw, was an English preacher, suffragist and campaigner for the ordination of women. Early life and education Royden was born in Mossley Hill, Liverpool, the youngest daughter of shipowner Sir Thomas Bland Royden, 1st Baronet. She grew up in the family home of Frankby Hall, Wirral with her parents and seven siblings. She was educated at Cheltenham Ladies' College and Lady Margaret Hall, Oxford where she gained a degree in History. While at Oxford she started a lifelong friendship with fellow suffragist Kathleen Courtney who had the same '' alma mater''. Career After university, Royden worked for three years at the Victoria Women's Settlement in Liverpool and then in the country parish of South Luffenham, Rutland, as parish assistant to the Rector, George William Hudson Shaw. She lectured on English literature for the university extension movement and in 1909 was elected to the executive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.24 million. On the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary, Liverpool historically lay within the ancient hundred of West Derby in the county of Lancashire. It became a borough in 1207, a city in 1880, and a county borough independent of the newly-created Lancashire County Council in 1889. Its growth as a major port was paralleled by the expansion of the city throughout the Industrial Revolution. Along with general cargo, freight, and raw materials such as coal and cotton, merchants were involved in the slave trade. In the 19th century, Liverpool was a major port of departure for English and Irish emigrants to North America. It was also home to both the Cunard and White Star Lines, and was the port of registry of the ocean lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Common Cause (NUWSS Newspaper)
''The Common Cause'' was a weekly publication that supported the National Union of Women's Suffrage Societies first published on 15 April 1909 mainly financed by Margaret Ashton. Its last issue was published on Friday, 30 January 1920, in which it announced its successor The Woman's Leader. History In 1908, the Manchester councillor Margaret Ashton sold her house in Didsbury to fund the creation of a newspaper, which was eventually founded in an office in Manchester in 1912. The intention was that it would represent the policies of and publish news from the NUWSS, but for legal reasons it could not be an organ of the NUWSS . Instead The Common Cause Publishing Co. Ltd was founded with an initial capital of £2,000 to publish the new paper. Its first editor was Helena Swanwick Helena Maria Lucy Swanwick CH (née Sickert; 30 January 1864 – 16 November 1939) was a British feminist and pacifist. Her autobiography, ''I Have Been Young'' (1935), gives a remarkable account of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighth Conference Of The International Woman Suffrage Alliance
''Eighth Conference of the International Woman Suffrage Alliance'' occurred June 6–12, 1920, in Geneva, Switzerland. Conference On call of its president, Carrie Chapman Catt, the International Woman Suffrage Alliance was summoned to its eighth congress June 6–12, 1920, in Geneva, Switzerland, seven instead of the usual two years after the last one. The reason for the long gap was the outbreak of World War I in 1914. On Sunday morning, June 6, for the first time in the history of Geneva a woman spoke in the National Church, the Cathedral of St. Peter; A. Maude Royden of Great Britain preached in French and English to an audience that filled the cathedral. That morning at 9 Father Hall, sent by the Catholic ecclesiastical authorities from England for the purpose, delivered a sermon to the congress at a special mass in Notre Dame. In the afternoon, a reception was given by Emilie Gourd, president of the Swiss National Suffrage Association, in the Beau Sejour garden. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
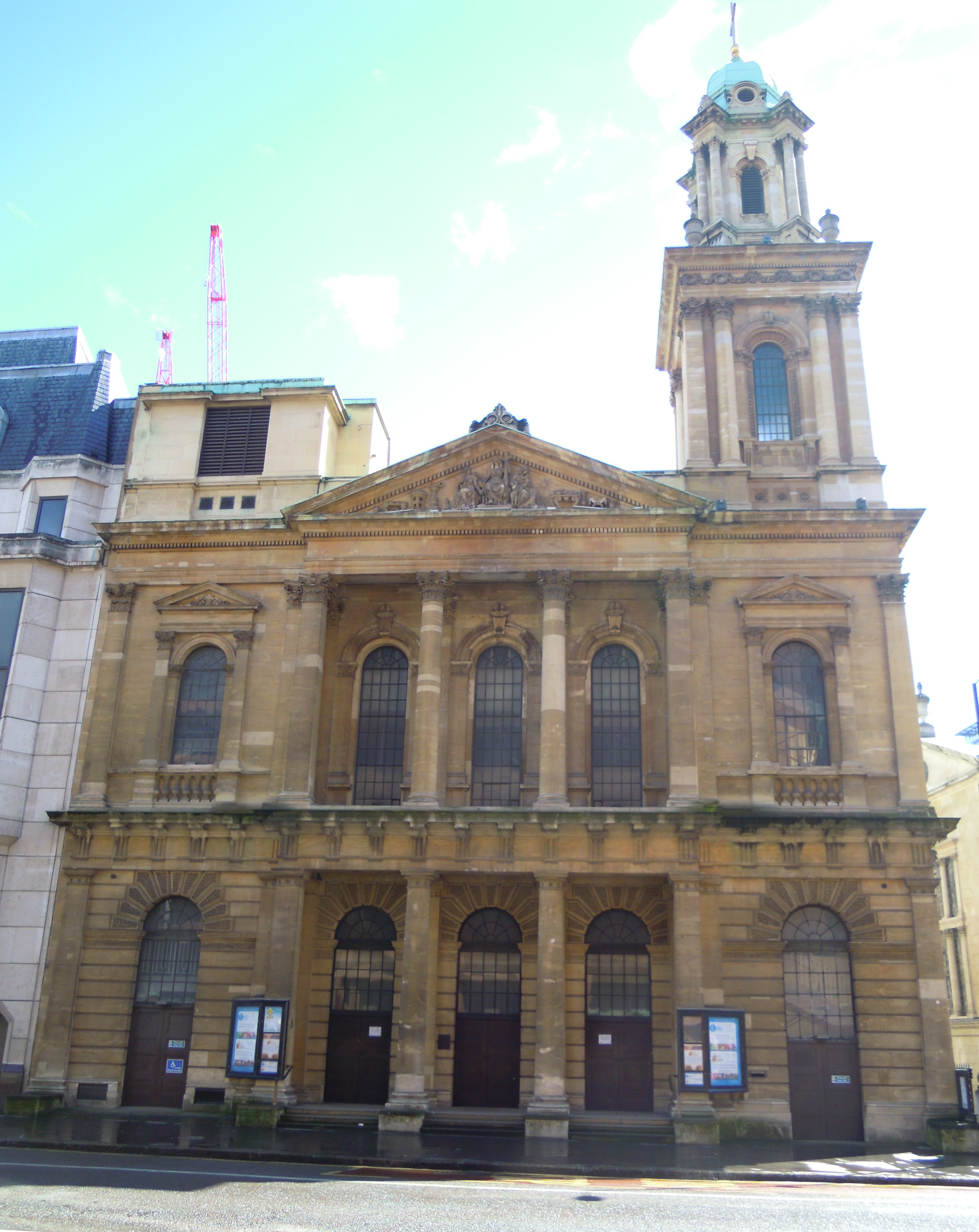
City Temple, London
The City Temple is a Nonconformist church on Holborn Viaduct in London. The current minister is Rodney Woods. The church is part of the Thames North Synod of the United Reformed Church and is a member of the Evangelical Alliance. The City Temple is most famous as the preaching place of the 20th century liberal theologian Leslie Weatherhead. Other notable preachers have included R. J. Campbell, Joseph Fort Newton, Thomas Goodwin and Joseph Parker. The first church building on the present site was built in 1874. The congregation was founded much earlier; the traditional date is 1640 but some evidence suggests it was founded as early as the 1560s by Puritans. Destroyed by bombing during the Second World War, it was rebuilt and reopened in 1958. Early history The City Temple is widely believed to have been founded by Thomas Goodwin. The exact date of its foundation is unknown, but it is believed to have been around 1640. It is the oldest Nonconformist congregation in the City ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain by the 3rd century and to the 6th-century Gregorian mission to Kent led by Augustine of Canterbury. The English church renounced papal authority in 1534 when Henry VIII failed to secure a papal annulment of his marriage to Catherine of Aragon. The English Reformation accelerated under Edward VI's regents, before a brief restoration of papal authority under Queen Mary I and King Philip. The Act of Supremacy 1558 renewed the breach, and the Elizabethan Settlement charted a course enabling the English church to describe itself as both Reformed and Catholic. In the earlier phase of the English Reformation there were both Roman Catholic martyrs and radical Protestant martyrs. The later phases saw the Penal Laws punis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservative Party (UK)
The Conservative Party, officially the Conservative and Unionist Party and also known colloquially as the Tories, is one of the two main political parties in the United Kingdom, along with the Labour Party. It is the current governing party, having won the 2019 general election. It has been the primary governing party in Britain since 2010. The party is on the centre-right of the political spectrum, and encompasses various ideological factions including one-nation conservatives, Thatcherites, and traditionalist conservatives. The party currently has 356 Members of Parliament, 264 members of the House of Lords, 9 members of the London Assembly, 31 members of the Scottish Parliament, 16 members of the Welsh Parliament, 2 directly elected mayors, 30 police and crime commissioners, and around 6,683 local councillors. It holds the annual Conservative Party Conference. The Conservative Party was founded in 1834 from the Tory Party and was one of two dominant political pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
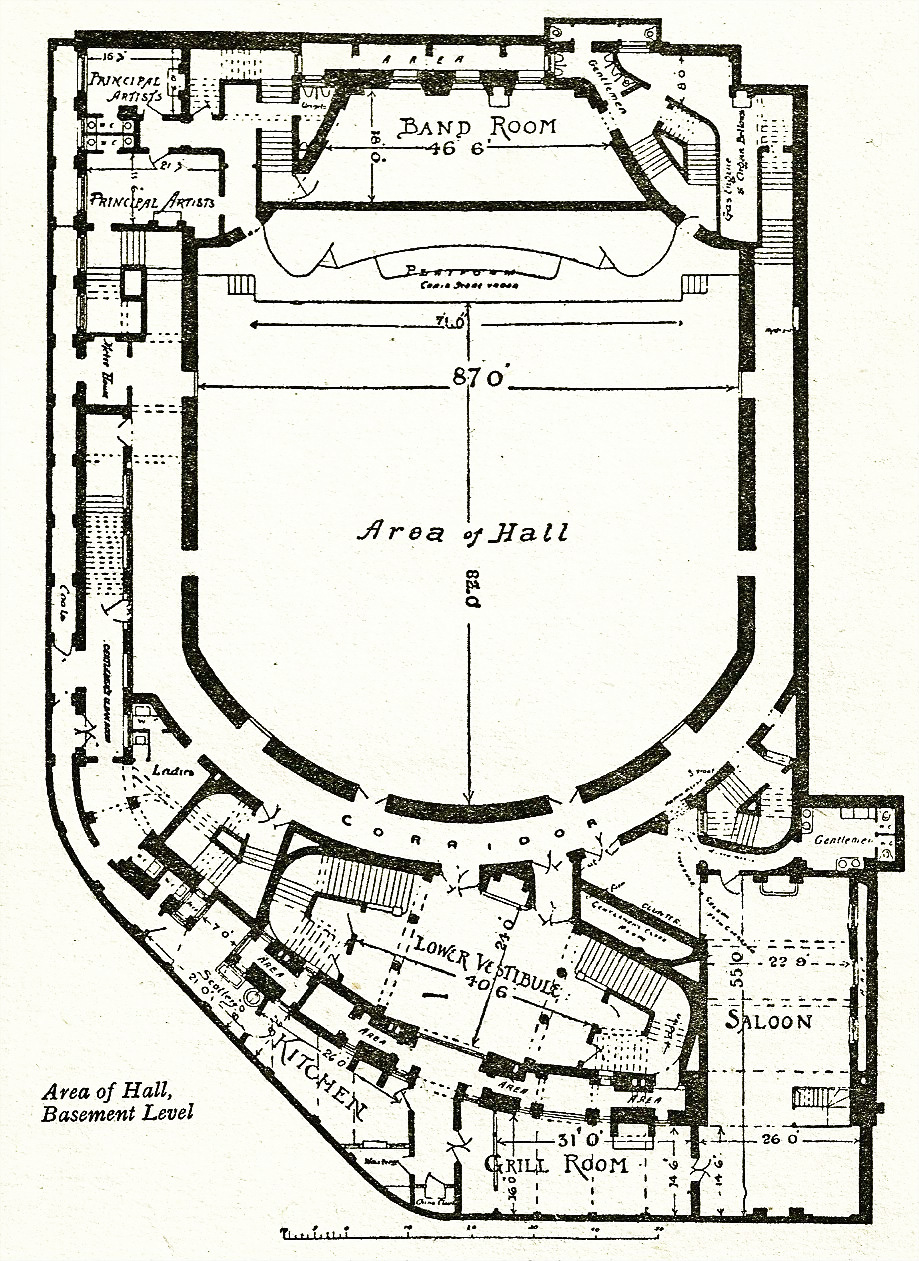
Queen's Hall
The Queen's Hall was a concert hall in Langham Place, London, Langham Place, London, opened in 1893. Designed by the architect Thomas Knightley, it had room for an audience of about 2,500 people. It became London's principal concert venue. From 1895 until 1941, it was the home of the The Proms, promenade concerts ("The Proms") founded by Robert Newman (impresario), Robert Newman together with Henry Wood. The hall had drab decor and cramped seating but superb acoustics. It became known as the "musical centre of the [British] British Empire, Empire", and several of the leading musicians and composers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries performed there, including Claude Debussy, Edward Elgar, Maurice Ravel and Richard Strauss. In the 1930s, the hall became the main London base of two new orchestras, the BBC Symphony Orchestra and the London Philharmonic Orchestra. These two ensembles raised the standards of orchestral playing in London to new heights, and the hall's resident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's International League For Peace And Freedom
The Women's International League for Peace and Freedom (WILPF) is a non-profit non-governmental organization working "to bring together women of different political views and philosophical and religious backgrounds determined to study and make known the causes of war and work for a permanent peace" and to unite women worldwide who oppose oppression and exploitation. WILPF has national sections in 37 countries. The WILPF is headquartered in Geneva and maintains a United Nations office in New York City. Organizational history WILPF developed out of the International Women's Congress against World War I that took place in The Hague, Netherlands, in 1915 and the formation of the International Women's Committee of Permanent Peace;Paull, John (2018The Women Who Tried to Stop the Great War: The International Congress of Women at The Hague 1915 In A. H. Campbell (Ed.), Global Leadership Initiatives for Conflict Resolution and Peacebuilding (pp. 249-266). (Ch.12) Hershey, PA: IGI Globa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women At The Hague
Women at the Hague was an International Congress of Women conference held at The Hague, Netherlands in April 1915. It had over 1,100 delegates and it established an International Committee of Women for Permanent Peace (ICWPP) with Jane Addams as president. It led to the creation of the Women's International League for Peace and Freedom (WILPF).Paull, John (2018The Women Who Tried to Stop the Great War: The International Congress of Women at The Hague 1915 In A. H. Campbell (Ed.), Global Leadership Initiatives for Conflict Resolution and Peacebuilding (pp. 249-266). (Chapter 12) Hershey, PA: IGI Global. Preparations The 1915 International Congress of Women was organized by the German feminist Anita Augspurg, Germany's first female jurist, and Lida Gustava Heymann (1868–1943) at the invitation of the Dutch pacifist, feminist and suffragist Aletta Jacobs to protest the war then raging in Europe, and to suggest ways to prevent war in the future. The scheme of an International Congr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Pacifism
Christian pacifism is the theological and ethical position according to which pacifism and non-violence have both a scriptural and rational basis for Christians, and affirms that any form of violence is incompatible with the Christian faith. Christian pacifists state that Jesus himself was a pacifist who taught and practiced pacifism and that his followers must do likewise. Notable Christian pacifists include Martin Luther King Jr., Leo Tolstoy, Adin Ballou and Ammon Hennacy. Ballou and Hennacy believed that adherence to Christianity required not just pacifism but, because governments inevitably threatened or used force to resolve conflicts, anarchism. However, most Christian pacifists, including the peace churches, Christian Peacemaker Teams, and individuals such as John Howard Yoder, make no claim to be anarchists. History Old Testament Roots of Christian pacifism can be found in the scriptures of the Old Testament according to Baylor University professor of religion, Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellowship Of Reconciliation
The Fellowship of Reconciliation (FoR or FOR) is the name used by a number of religious nonviolent organizations, particularly in English-speaking countries. They are linked by affiliation to the International Fellowship of Reconciliation (IFOR). In the United Kingdom, the acronym "FoR" is normally typeset with a lower-case "o"; elsewhere, it is usually typeset in all capital letters, as "FOR", such as in "IFOR". The FoR in the United Kingdom The first body to use the name "Fellowship of Reconciliation" was formed as a result of a pact made in August 1914 at the outbreak of the First World War by two Christians, Henry Hodgkin (an English Quaker) and Friedrich Siegmund-Schultze (a German Lutheran), who were participating in a Christian pacifist conference in Konstanz in southern Germany. On the platform of the railway station at Cologne, they pledged to each other that, "We are one in Christ and can never be at war." There were a number of people involved in the creation of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Christmas Letter
The Open Christmas Letter was a public message for peace addressed "To the Women of Germany and Austria",Oldfield, 2003, p. 46. signed by a group of 101 British suffragists at the end of 1914 as the first Christmas of the First World War approached. The Open Christmas Letter was written in acknowledgment of the mounting horror of modern war and as a direct response to letters written to American feminist Carrie Chapman Catt, the president of the International Woman Suffrage Alliance (IWSA), by a small group of German women's rights activists. Published in January 1915 in '' Jus Suffragii'', the journal of the IWSA, the Open Christmas Letter was answered two months later by a group of 155 prominent German and Austrian women who were pacifists. The exchange of letters between women of nations at war helped promote the aims of peace, and helped prevent the fracturing of the unity which lay in the common goal they shared, suffrage for women. Reaction to war The decision by some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)

