|
Matteo Albertone
Matteo Francesco Albertone (29 March 1840 – 13 February 1919) was an Italian general, mostly known for his role during the First Italo-Ethiopian War. He led the Native Brigade during the battle of Adwa and was taken prisoner by the Ethiopians. Early life Born in Alessandria when the town was still in Sardinia-Piedmont, he graduated from the Military Academy in Turin shortly after the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy in 1861. Appointed sub-lieutenant in the Bersaglieri, he fought in the 1866 Austro-Italian War and in the capture of Rome in 1870. In the following years he was appointed captain in the Army Staff and started teaching logistics at the School of War. In 1888 he was assigned to the Special Operation Corps of Alessandro Asinari di San Marzano in Eritrea and took command of the 1st Cacciatori d'Africa Regiment. When the Corps was disbanded, he was reassigned to garrison duties in Massawa until 1890. First Italo-Ethiopian War Albertone returned in Eritrea in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alessandria
Alessandria (; pms, Lissandria ) is a city and ''comune'' in Piedmont, Italy, and the capital of the Province of Alessandria. The city is sited on the alluvial plain between the Tanaro and the Bormida rivers, about east of Turin. Alessandria is also a major railway hub. History Alessandria was founded in 1168 with a charter as a free comune; it was sited upon a preexisting urban nucleus, to serve as a stronghold for the Lombard League, defending the traditional liberties of the communes of northern Italy against the Imperial forces of Frederick Barbarossa. Alessandria stood in the territories of the marchese of Montferrat, a staunch ally of the Emperor, with a name assumed in 1168 to honour the Emperor's opponent, Pope Alexander III. In 1174–1175 the fortress was sorely tested by the Imperial siege and stood fast. A legend (related in Umberto Eco's book ''Baudolino'', and which recalls one concerning Bishop Herculanus’ successful defence of Perugia several centuries ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, etc. In militaries, the captain is typically at the level of an officer commanding a company or battalion of infantry, a ship, or a battery of artillery, or another distinct unit. The term also may be used as an informal or honorary title for persons in similar commanding roles. Etymology The term "captain" derives from (, , or 'the topmost'), which was used as title for a senior Byzantine military rank and office. The word was Latinized as capetanus/catepan, and its meaning seems to have merged with that of the late Latin "capitaneus" (which derives from the classical Latin word "caput", meaning head). This hybridized term gave rise to the English language term captain and its equivalents in other languages (, , , , , , , , , kapitány, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menelik II
, spoken = ; ''djānhoi'', lit. ''"O steemedroyal"'' , alternative = ; ''getochu'', lit. ''"Our master"'' (pl.) Menelik II ( gez, ዳግማዊ ምኒልክ ; horse name Abba Dagnew (Amharic: አባ ዳኘው ''abba daññäw''); 17 August 1844 – 12 December 1913), baptised as Sahle Maryam (ሣህለ ማርያም ''sahlä maryam'') was King of Shewa from 1866 to 1889 and Emperor of Ethiopia from 1889 to his death in 1913. At the height of his internal power and external prestige, the process of territorial expansion and creation of the modern empire-state was completed by 1898.Zewde, Bahru. A history of Ethiopia: 1855–1991. 2nd ed. Eastern African studies. 2001 The Ethiopian Empire was transformed under Emperor Menelik: the major signposts of modernisation were put in place, with the assistance of key ministerial advisors. Externally, Menelik led Ethiopian troops against Italian invaders in the First Italo-Ethiopian War; following a decisive victory at the Battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigray Province
Tigray Province (Amharic and ), also known as Tigre ( tigrē), was a historical province of northern Ethiopia that overlayed the present day Afar and Tigray regions. Akele Guzai borders with the Tigray province It was one It encompassed most of the territories of Tigrinya-speakers (and a few minority groups) in Ethiopia. Tigray was separated from the northern Tigrinya speaking territories by the Mareb River, now serving as the state border to Eritrea (formerly Eritrea Province), with the Tekezé River separating it from the Amhara dominated south. The great majority of inhabitants were Orthodox Christians (95.5% in 1994), with the exception of a small, but important Muslim subgroup ( Jeberti) and a few Catholics (mainly Irob). Protestantism is only a very recent urban phenomenon. Despite a general impression of ethnic and cultural homogeneity, there were a few ethnic minorities, especially at the borders of Tigray, belonging to a non-Tigrinya groups, such as the Saho-speakin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
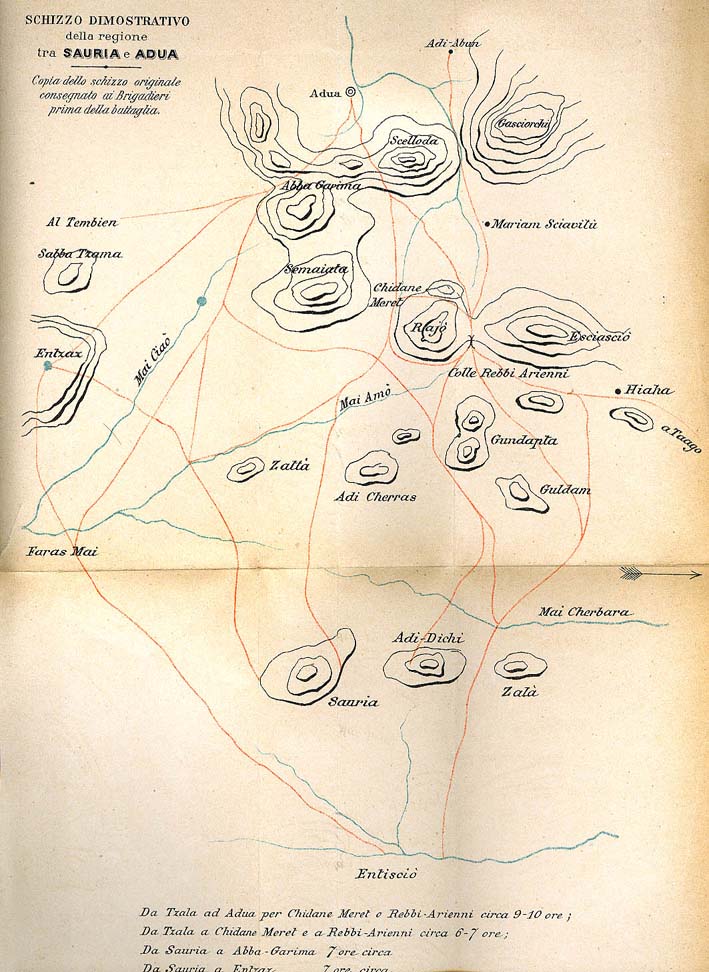
Battle Of Coatit
The Battle of Coatit was fought on 13 January 1895 between Italy and Ethiopian proxies led by Tigrayan warlord Ras Mengesha Yohannes in what is now Eritrea. It was the opening battle of the First Italo–Ethiopian War, and was a significant victory for the Italians, as they rebuffed an invasion force. Prelude By 1894, the relationship between the Italian colonialists and the Ethiopians had become strained. Ethiopian emperor Menelik had repudiated the Treaty of Wuchale, and was consolidating his power with plans to oust the Italians. Former Italian allies, the Tigrian warlords Ras Mengesha Yohannes, Ras Alula, Bahta Hagos and Wolde Mikael traveled to Addis Ababa to seek forgiveness from the Negus for their dealings with the colonial governor, General Oreste Baratieri. Menelik forgave them and offered Mengesha the crown of Tigray in exchange for his loyalty and help in evicting the Italians. In December 1894, Bahta Hagos led a rebellion in Akkele Guzay, which set the stage for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giuseppe Arimondi
Giuseppe Edoardo Arimondi, OSML, OMS, OCI (26 April 1846 – 1 March 1896) was an Italian general, mostly known for his role during the First Italo-Ethiopian War. He was one of the few European commanders who gained a victory over the Mahdists before Kitchener's Expedition, soundly defeating them at Agordat in 1893. After a long and successful colonial service, he died in combat at Adwa, and was posthumously awarded the Gold Medal of Military Valor. Early life Born in Savigliano on 26 April 1846, Arimondi attended the Royal Military Academy in Modena. After graduating in 1865, he was appointed sub-lieutenant in the Bersaglieri, and fought in the 1866 Italo-Austrian War. Upon reaching the rank of captain he served as a military observer during the Franco-Prussian War. He then attended the School of War and in 1874 was promoted major in the Army Staff. Colonial service in Eritrea In 1887, Arimondi was assigned as a staff officer to the expeditionary corps of General Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eritrean Ascari
The Royal Corps Of Eritrean Colonial Troops were indigenous soldiers from Eritrea, who were enrolled as askaris in the Royal Corps of Colonial Troops (''Regio Corpo di Truppe Coloniali'') of the Royal Italian Army (''Regio Esercito'') during the period 1889–1941. Characteristics These regular troops played an important role in the initial conquest of the various colonial possessions of the Kingdom of Italy. They subsequently acted as garrison and internal security forces in the Italian Empire, and finally served in large numbers during the Italian conquest of British Somaliland and the East African campaign of 1940-41 . History ''Except for the German parachute division in Italy and the Japanese in Burma no enemy with whom the British and Indian troops were matched put up a finer fight than those Savoia battalions at Keren (Eritrea). Moreover, the Colonial troops, until they cracked at the very end, fought with valour and resolution, and their staunchness was a testimony to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mek'ele
Mekelle ( ti, መቐለ, am, መቀሌ, mäqälle, mek’elē) or Mekele is a special zone and capital of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Mekelle was formerly the capital of Enderta awraja in Tigray. It is located around north of the Ethiopian capital Addis Ababa, with an elevation of above sea level. Administratively, Mekelle is considered a Special Zone, which is divided into seven sub-cities. It is the economic, cultural, and political hub of northern Ethiopia. Mekelle has grown rapidly since 1991 with a population of 61,000 in 1984, 97,000 inhabitants in 1994 (96.5% being Tigrinya-speakers), and 170,000 in 2006 (i.e. 4% of the population of Tigray). Mekelle is the second-largest city in Ethiopia after Addis Ababa, with a population of around 545,000. It is 2.6 times larger than Adigrat, the second-largest regional center. The majority of the population of Mekelle depends on government employment, commerce, and small-scale enterprises. In 2007, Mekelle had new engineering, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adigrat
Adigrat (, ''ʿaddigrat'', also called ʿAddi Grat) is a city and separate woreda in Tigray Region of Ethiopia. It is located in the Misraqawi Zone at longitude and latitude , with an elevation of above sea level and below a high ridge to the west. Adigrat is a strategically important gateway to Eritrea and the Red Sea. Adigrat was part of Ganta Afeshum woreda before a separate woreda was created for the city. Currently, Adigrat serves as the capital of the Eastern Tigray zone. Adigrat is one of the most important cities of Tigray, which evolved from earlier political centers and camps of regional governors. Antalo, Aläqot and Adigrat were a few of them. The decline of Antalo was followed by the rise of Adigrat as another prominent, yet short-lived, capital of Tigray. It used to serve as the capital of Agame. History Origins Tradition attributes the origin of the name Adigrat, which means "the country of farmland", to the then popular Tigrayan chief Akhadom. Adigrat seems t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that historically spanned the geographical area of present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea from the establishment of the Solomonic dynasty by Yekuno Amlak approximately in 1270 until the 1974 coup d'etat of Emperor Haile Selassie by the Derg. By 1896, the Empire incorporated other regions such as Hararghe, Gurage and Wolayita, and saw its largest expansion with the federation of Eritrea in 1952. Throughout much of its existence, it was surrounded by hostile forces in the African Horn; however, it managed to develop and preserve a kingdom based on its ancient form of Christianity. Founded in 1270 by the Solomonic Dynasty nobleman Yekuno Amlak, who claimed to descend from the last Aksumite king and ultimately the Biblical Menelik I and the Queen of Sheba, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Wuchale
The Treaty of Wuchale (also spelled Treaty of Ucciale; it, Trattato di Uccialli, am, የውጫሌ ውል) was a treaty signed between the Ethiopian Empire and the Kingdom of Italy. The signing parties were King Menelik II of Shewa, acting as Emperor of Ethiopia, and Count representing Italy, on 2 May 1889, established the treaty after the Italian occupation of Eritrea. It was signed in the small Ethiopian town of Wuchale, from which the treaty got its name. The purpose of the treaty was to promote friendship and trade among the two countries. It was a treaty to maintain a positive long lasting relationship between the two empires. The treaty has twenty articles written in two languages, Amharic and Italian, however, there were marked differences in the Italian and the Amharic versions of the treaty which created miscommunications between the two countries. Specifically, Article 17 of the treaty was translated and interpreted differently by Ethiopia and Italy. Italy claimed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massawa
Massawa ( ; ti, ምጽዋዕ, məṣṣəwaʿ; gez, ምጽዋ; ar, مصوع; it, Massaua; pt, Maçuá) is a port city in the Northern Red Sea region of Eritrea, located on the Red Sea at the northern end of the Gulf of Zula beside the Dahlak Archipelago.Matt Phillips, Jean-Bernard Carillet, ''Lonely Planet Ethiopia and Eritrea'', (Lonely Planet: 2006), p.340. It has been a historically important port for many centuries. Massawa was the capital of the Italian Colony of Eritrea until the seat of the colonial government was moved to Asmara in 1897. Massawa has an average temperature of nearly , which is one of the highest experienced in the world, and is "one of the hottest marine coastal areas in the world." History Massawa was originally a small seaside village, lying in lands coextensive with the Kingdom of Axum—also known as Kingdom of Zula in antiquity—and overshadowed by the nearby port of Adulis about to the south. Massawa has been ruled or occupied by a successi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)