|
Matsudaira Kataoki
was the 6th ''daimyō'' of Aizu Domain in southern Mutsu Province, Japan (modern-day Fukushima Prefecture). Biography Matsudaira Kataoki was the eldest son of Matsudaira Katasada, the ninth son of Matsudaira Masakata, 3rd ''daimyō'' of Aizu Domain. In 1789, he received the courtesy titles of "Jijū" and "Wakasa-no-kami": however, the 5th ''daimyō'' of Aizu, Matsudaira Katanobu, died before formal adoption procedures were completed, and Kataoki was thus a posthumous adoption. He shows signs of continuing the fiscal reform policies of Matsudaira Katanobu, but died less than 5 months after assuming office. His wife was a daughter of Ii Naohide of Hikone Domain; however his second son and heir, Matsudaira Katahiro was the 7th ''daimyō'' of Aizu Domain in Mutsu Province, Japan (modern-day Fukushima Prefecture). His courtesy title was ''Higo-no-kami'' and ''Jijū'', and subsequently raised to '' Sakonoe-gon-shōshō'' and his Court rank was Junior Fo ..., was born t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Crest Aizu Aoi
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji era, Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominally to the Emperor of Japan, emperor and the ''kuge''. In the term, means 'large', and stands for , meaning 'private land'. From the ''shugo'' of the Muromachi period through the Sengoku period, Sengoku to the ''daimyo'' of the Edo period, the rank had a long and varied history. The backgrounds of ''daimyo'' also varied considerably; while some ''daimyo'' clans, notably the Mōri clan, Mōri, Shimazu clan, Shimazu and Hosokawa clan, Hosokawa, were cadet branches of the Imperial family or were descended from the ''kuge'', other ''daimyo'' were promoted from the ranks of the samurai, notably during the Edo period. ''Daimyo'' often hired samurai to guard their land, and they paid the samurai in land or food as relatively few could aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
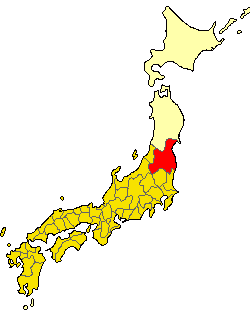
Aizu Domain
was a domain of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan during the Edo period from 1601 to 1871.Ravina, Mark. (1998) ''Land and Lordship in Early Modern Japan,'' p. 222 The Aizu Domain was based at Tsuruga Castle in Mutsu Province, the core of the modern city of Aizuwakamatsu, located in the Tōhoku region of the island of Honshu. The Aizu Domain was ruled for most of its existence by the '' shinpan'' ''daimyō'' of the Aizu-Matsudaira clan, a local cadet branch of the ruling Tokugawa clan, but was briefly ruled by the '' tozama'' ''daimyō'' of the Gamō and Katō clans. The Aizu Domain was assessed under the '' Kokudaka'' system with a peak value of 919,000 '' koku'', but this was reduced to 230,000 ''koku''. The Aizu Domain was dissolved in the abolition of the ''han'' system in 1871 by the Meiji government and its territory was absorbed into Fukushima Prefecture, covering much of the traditional region of Aizu. History Pre-Edo period The area of Kurokawa, later called "Waka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Ienari
Tokugawa Ienari ( ja, 徳川 家斉, November 18, 1773 – March 22, 1841) was the eleventh and longest-serving ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan who held office from 1787 to 1837.Hall, John Whitney ''et al.'' (1991) ''Early Modern Japan'', p. 21./ref> He was a great-grandson of the eighth shōgun Tokugawa Yoshimune through his son Munetada (1721–1764), head of the Hitotsubashi branch of the family, and his grandson Harusada (1751–1827). Ienari died in 1841 and was given the Buddhist name Bunkyouin and buried at Kan'ei-ji. Events of Ienari's ''bakufu'' * 1787 (''Tenmei 7''): Ienari becomes the 11th ''shōgun'' of the bakufu government. * 1788 (''Tenmei 7''): Riots in rice shops in Edo and Osaka. * March 6 – 11, 1788 (''Tenmei 8, 29th day of the 1st month – 4th day of the second month''): Great Fire of Kyoto. A fire in the city, which begins at 3 o'clock in the morning of March 6 burns uncontrolled until the 1st day of the second month (March 8); and embers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsudaira Katanobu
was the 5th ''daimyō'' of Aizu Domain in Mutsu Province, Japan (modern-day Fukushima Prefecture). His courtesy title was '' Sankonoe-gon-chū-shō'' and ''Jijū'', and his Court rank was Senior Fourth Rank, Upper Grade. Biography Matsudaira Katanobu was the eldest son of Matsudaira Katasada and became ''daimyō'' in 1750 on his father's death. He was presented in formal audience to Shogun Tokugawa Ieshige in 1756, and was awarded the courtesy title of ''Higo-no-kami''. In 1759, he visited Aizu for the first time, and in 1760, his courtesy title was promoted to ''Jijū'' and ''Sankonoe-gon-shō-shō'' in celebration of Tokugawa Ieshige's own promotion to the title of ''Udaijin''. He was further promoted to ''Sankonoe-gon-chū-shō'' in 1765 and his court rank to Senior Fourth Rank, Lower Grade in 1770 and Senior Fourth Rank, Upper Grade in 1778. However, these purely honorific promotions were a tremendous drain on the domain's finances, and the peasants rose in revolt over hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsudaira Katahiro
was the 7th ''daimyō'' of Aizu Domain in Mutsu Province, Japan (modern-day Fukushima Prefecture). His courtesy title was ''Higo-no-kami'' and ''Jijū'', and subsequently raised to '' Sakonoe-gon-shōshō'' and his Court rank was Junior Fourth Rank, Lower Grade. Biography Matsudaira Katahiro was the younger son of Matsudaira Kataoki and became ''daimyō'' in 1806 at the age of four on his father's death. In 1813, he was received in formal audience by Shogun Tokugawa Ienari and given the courtesy title of ''Higo-no-kami''. This was changed to ''Sakonoe-gon-shōshō'' in 1816. He was wed to Moto-hime, the 15th daughter of Tokugawa Ienari, but died in 1822 without any heir. This ended the line of direct descent from Tokugawa Hidetada begun by Hoshina Masayuki, the first ''daimyō'' of Aizu. See also *Hoshina clan The is a Japanese clan which claims descent from Emperor Seiwa, and is a branch of the Minamoto clan. They were famous for their role as retainers of the Takeda clan i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ii Naohide
II is the Roman numeral for 2. II may also refer to: Biology and medicine *Image intensifier, medical imaging equipment *Invariant chain, a polypeptide involved in the formation and transport of MHC class II protein *Optic nerve, the second cranial nerve Economics * Income inequality, or the wealth gap, in economics * Internationalization Index, used by the UN to rank nations and companies in evaluating their degree of integration with the world economy * ''Institutional Investor'' (magazine), an American finance magazine Music * Supertonic, in music * ''ii'', a 2018 song by CHVRCHES Albums * ''II'' (2 Unlimited album), 1998 * ''II'' (Aquilo album), 2018 * ''II'' (Bad Books album), 2012 * ''II'' (Boyz II Men album), 1994 * ''II'' (Capital Kings album), 2015 * ''II'' (Charade album), 2004 * ''II'' (The Common Linnets album), 2015 * ''II'' (Compact Disco album), 2011 * ''II'' (Cursed album), 2005 * ''II'' (Darna album), 2003 * ''II'' (Espers album), 2006 * ''II'' (Fuzz albu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji era, Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominally to the Emperor of Japan, emperor and the ''kuge''. In the term, means 'large', and stands for , meaning 'private land'. From the ''shugo'' of the Muromachi period through the Sengoku period, Sengoku to the ''daimyo'' of the Edo period, the rank had a long and varied history. The backgrounds of ''daimyo'' also varied considerably; while some ''daimyo'' clans, notably the Mōri clan, Mōri, Shimazu clan, Shimazu and Hosokawa clan, Hosokawa, were cadet branches of the Imperial family or were descended from the ''kuge'', other ''daimyo'' were promoted from the ranks of the samurai, notably during the Edo period. ''Daimyo'' often hired samurai to guard their land, and they paid the samurai in land or food as relatively few could aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire Tōhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagajō in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wadō 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wadō 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukushima Prefecture
Fukushima Prefecture (; ja, 福島県, Fukushima-ken, ) is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu. Fukushima Prefecture has a population of 1,810,286 () and has a geographic area of . Fukushima Prefecture borders Miyagi Prefecture and Yamagata Prefecture to the north, Niigata Prefecture to the west, Gunma Prefecture to the southwest, and Tochigi Prefecture and Ibaraki Prefecture to the south. Fukushima is the capital and Iwaki is the largest city of Fukushima Prefecture, with other major cities including Kōriyama, Aizuwakamatsu, and Sukagawa. Fukushima Prefecture is located on Japan's eastern Pacific coast at the southernmost part of the Tōhoku region, and is home to Lake Inawashiro, the fourth-largest lake in Japan. Fukushima Prefecture is the third-largest prefecture of Japan (after Hokkaido and Iwate Prefecture) and divided by mountain ranges into the three regions of Aizu, Nakadōri, and Hamadōri. History Prehistory The keyhole-shaped Ōy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsudaira Masakata
was the 3rd ''daimyō'' of Aizu Domain in Mutsu Province, Japan (modern-day Fukushima Prefecture). His courtesy title was '' Sankonoe-gon-chū-shō'' and ''Jijū'', and his Court rank was Senior Fourth Rank, Lower Grade. Biography Matsudaira Masakata was the sixth son of Hoshina Masayuki and became ''daimyō'' in 1681 on the retirement of his elder brother. His courtesy title was ''Bungo-no-kami'', which was increased to ''Sankonoe-gon-shō-shō'' in 1687. Initially, his name was Hoshina Masanobu (保科正信), but in 1696 he was permitted to change his name to Matsudaira Masakata, in recognition of the clan's status of being a cadet branch of the Tokugawa clan. His courtesy title was promoted to ''Sankonoe-gon-chū-shō'' in 1712. He was married to a daughter of Abe Masatake of Oshi Domain, and had nine sons and four daughters. He ruled to his death in 1731. See also *Hoshina clan The is a Japanese clan which claims descent from Emperor Seiwa, and is a branch of the Minam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |