|
Matir Moina
''Matir Moina'' ( bn, মাটির ময়না; also known in English as ''The Clay Bird'') is a 2002 Bengali War-drama film was written and directed by Tareque Masud. It was his debut feature film. Based on Tareque's story the screenplay was co-written by Tareque and Catherine Masud. In the film, Tareque's childhood experience is revealed against the backdrop of 1969 Mass uprising in East Pakistan on the eve of Bangladesh Liberation War. The film stars Nurul Islam Bablu, Russell Farazi, Jayanta Chattopadhyay, Rokeya Prachy, Soaeb Islam and Lameesa R. Reemjheem in the lead role. The film deals with its historical references during the independence of Bangladesh. It portrays the experiences of a young protagonist, his family, his teachers and his life at the madrasah. Production began with initial funding from the French government. The film was officially screened on 15 May 2002 at the 55th Cannes Film Festival. Produced by Catherine Masud, the film grossed about at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tareque Masud
Tareque Masud (6 December 1956 – 13 August 2011) was a Cinema of Bangladesh, Bangladeshi independent film director, film producer, screenwriter and lyricist. He first found success with the films ''Muktir Gaan'' (1995) and ''Matir Moina'' (2002), for which he won three international awards, including the International Critics' FIPRESCI Prize, in the Directors' Fortnight at 2002 Cannes Film Festival. The film became List of Bangladeshi submissions for the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film, Bangladesh's first film to compete for the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film. Masud died in a road accident on 13 August 2011 while returning to Dhaka from Manikganj on the Dhaka-Aricha highway after visiting a filming location. Masud was working on ''Kagojer Phool'' (The Paper Flower). In 2012, he posthumously received Ekushey Padak, the second highest civilian award of Bangladesh. In 2013, New York University Asian/Pacific/American Institute, and South Asia Solidarity Ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Film Awards (Bangladesh)
The National Film Awards ( bn, জাতীয় চলচ্চিত্র পুরস্কার) is an annual awards ceremony held annually in Dhaka, Bangladesh. It is considered to be the most prominent film award ceremony in Bangladesh. The National Film Awards were established in 1975 by the government of Bangladesh. Every year, a national panel appointed by the government selects the winning entries. History The National Film Awards were first presented in 1975. The government of Bangladesh offers the National Film Awards to the films and individuals for notable contributions to the art of cinema. Beginning in 1975, The National Film Awards is an event that takes place annually that includes colorful programs, dance, and music. The awards are the only film awards awarded by the government of Bangladesh. No awards were given in 1981 because the panel determined that no film was competent enough to receive an award. Juries and rules The juries are appointed by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
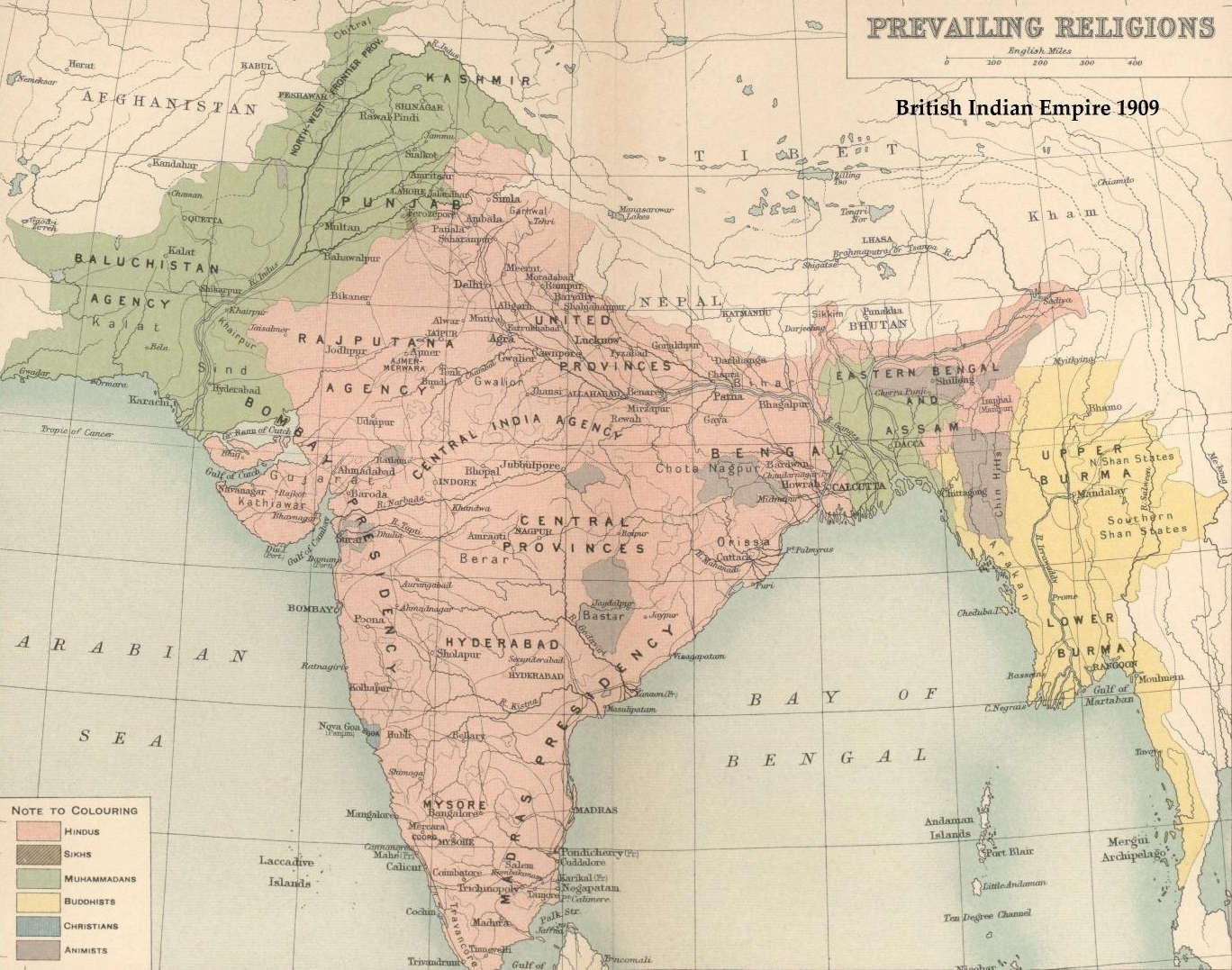
Hindu Festivals
Across the globe, Hindus celebrate a diverse number of festivals and celebrations, typically marking events from ancient India and often coinciding with seasonal changes. These celebrations take place either on a fixed annual date on the solar calendar, or on a specific day of the lunisolar calendar. There is some regional variation with the observance of the festivals, and numerous festivals that are primarily celebrated by specific sects or in certain regions of the Indian subcontinent. Terminology Utsava ''Utsava'' is the Sanskrit word for festivals. The Sanskrit word ''Utsava'' comes from the word "''ut''" meaning "removal" and "''sava''" which means "worldly sorrows" or "grief". Observance periods (''tithi'') Hindu calendar dates are usually prescribed according to a lunisolar calendar. In Vedic timekeeping, a ''māsa'' is a lunar month, a ''pakṣa'' is a lunar fortnight and a ''tithi'' is a lunar day. Two definitions of the lunar month prevail: amānta and pūrṇi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left-wing Politics
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in society whom its adherents perceive as disadvantaged relative to others as well as a belief that there are unjustified inequalities that need to be reduced or abolished. Left-wing politics are also associated with popular or state control of major political and economic institutions. According to emeritus professor of economics Barry Clark, left-wing supporters "claim that human development flourishes when individuals engage in cooperative, mutually respectful relations that can thrive only when excessive differences in status, power, and wealth are eliminated." Within the left–right political spectrum, ''Left'' and '' Right'' were coined during the French Revolution, referring to the seating arrangement in the French Estates General. Thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan Army
The Pakistan Army (, ) is the land service branch of the Pakistan Armed Forces. The roots of its modern existence trace back to the British Indian Army that ceased to exist following the Partition of British India, which occurred as a result of the 1947 Indian Independence Act of the United Kingdom. According to statistics provided by the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) in 2021, the Pakistan Army has approximately 560,000 active-duty personnel, supported by the Army Reserve and National Guard. Pakistani citizens can enlist for voluntary military service upon reaching 16 years of age, but cannot be deployed for combat until the age of 18 in accordance with the Constitution of Pakistan. The primary objective and constitutional mission of the Pakistan Army is to ensure the national security and national unity of Pakistan by defending it against any form of external aggression or the threat of war. It can also be requisitioned by the Pakistani federal go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeopathy
Homeopathy or homoeopathy is a pseudoscientific system of alternative medicine. It was conceived in 1796 by the German physician Samuel Hahnemann. Its practitioners, called homeopaths, believe that a substance that causes symptoms of a disease in healthy people can cure similar symptoms in sick people; this doctrine is called '' similia similibus curentur'', or "like cures like". Homeopathic preparations are termed ''remedies'' and are made using homeopathic dilution. In this process, the selected substance is repeatedly diluted until the final product is chemically indistinguishable from the diluent. Often not even a single molecule of the original substance can be expected to remain in the product. Between each dilution homeopaths may hit and/or shake the product, claiming this makes the diluent remember the original substance after its removal. Practitioners claim that such preparations, upon oral intake, can treat or cure disease. All relevant scientific knowledge a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the Muhammad in Islam, main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad (''sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (''hadith''). With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Islam in Africa, Africa, 25% of Islam in Asia, Asia and Islam in Oceania, Oceania (collectively), 6% of Islam in Europe, Europe, and 1% of the Islam in the Americas, Americas. Addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamentalist
Fundamentalism is a tendency among certain groups and individuals that is characterized by the application of a strict literal interpretation to scriptures, dogmas, or ideologies, along with a strong belief in the importance of distinguishing one's ingroup and outgroup,Kunst, J., Thomsen, L., Sam, D. (2014). Late Abrahamic reunion? Religious fundamentalism negatively predicts dual Abrahamic group categorization among Muslims and Christians. ''European Journal of Social Psychology'' https://www.academia.edu/6436421/Late_Abrahamic_reunion_Religious_fundamentalism_negatively_predicts_dual_Abrahamic_group_categorization_among_Muslims_and_Christians which leads to an emphasis on some conception of "purity", and a desire to return to a previous ideal from which advocates believe members have strayed. The term is usually used in the context of religion to indicate an unwavering attachment to a set of irreducible beliefs (the "fundamentals"). The term "fundamentalism" is generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangladesh War Of Liberation
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in East Pakistan, which resulted in the independence of Bangladesh. The war began when the Pakistani military junta based in West Pakistan—under the orders of Yahya Khan—launched Operation Searchlight against the people of East Pakistan on the night of 25 March 1971, initiating the Bangladesh genocide. In response to the violence, members of the Mukti Bahini—a guerrilla resistance movement formed by Bengali military, paramilitary and civilians—launched a mass guerrilla war against the Pakistani military, liberating numerous towns and cities in the initial months of the conflict. At first, the Pakistan Army regained momentum during the monsoon, but Bengali guerrillas counterattacked by car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Myanmar, with a coastline on the Bay of Bengal. East Pakistanis were popularly known as "Pakistani Bengalis"; to distinguish this region from India's state West Bengal (which is also known as "Indian Bengal"), East Pakistan was known as "Pakistani Bengal". In 1971, East Pakistan became the newly independent state Bangladesh, which means "country of Bengal" in Bengali. East Pakistan was renamed from East Bengal by the One Unit Scheme of Pakistani Prime Minister Mohammad Ali of Bogra. The Constitution of Pakistan of 1956 replaced the Pakistani monarchy with an Islamic republic. Bengali politician H. S. Suhrawardy served as the Prime Minister of Pakistan between 1956 and 1957 and a Bengali bureaucrat Iskander Mirza became the first President of Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
75th Academy Awards
The 75th Academy Awards ceremony, presented by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS) took place on March 23, 2003, at the Kodak Theatre in Hollywood, Los Angeles. During the ceremony, AMPAS presented Academy Awards (commonly referred to as Oscars) in 24 categories honoring films released in 2002. The ceremony, televised in the United States by ABC, was produced by Gil Cates and was directed by Louis J. Horvitz. Actor Steve Martin hosted for the second time, having previously presided over the 73rd ceremony held in 2001. Three weeks earlier in a ceremony at Regent Beverly Wilshire Hotel in Beverly Hills, California held on March 1, the Academy Awards for Technical Achievement were presented by host Kate Hudson. ''Chicago'' won six awards, including Best Picture. Other winners included '' The Pianist'' with three awards, ''Frida'' and '' The Lord of the Rings: The Two Towers'' with two, and '' 8 Mile'', ''Adaptation'', ''Bowling for Columbine'', '' The C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Award For Best International Feature Film
The Academy Award for Best International Feature Film (known as Best Foreign Language Film prior to 2020) is one of the Academy Awards handed out annually by the U.S.-based Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS). It is given to a feature-length motion picture produced outside the United States with a predominantly non-English dialogue track.80th Academy Awards – Special Rules for the Best Foreign Language Film Award . . Retrieved November 2, 2007. When the first Academy Awards ceremony was held on May 16, 1929, to honor fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |