|
Mataghis
Madagiz ( hy, Մատաղիս, Mataghis) or Sugovushan (, ), is a village in the Tartar District of Azerbaijan, in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh. The village had an ethnic Armenian-majority population prior to the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. Madagiz was part of the Martakert Province of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh between 10 April 1994 and 3 October 2020. History In 1943, during the Soviet period, Madagiz was given the status of an urban-type settlement within the Mardakert District of the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast. In 1949, Madagiz was home to an industrial complex, including a furniture factory and a lime production workshop. In 1953, a secondary school was opened. The Madagiz hydroelectric power station was built nearby on the banks of the Tartar River. During the First Nagorno-Karabakh War, Azerbaijani forces launched an offensive into the Mardakert District in the summer of 1992, capturing most of the district. However, as the result of a count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2016 Nagorno-Karabakh Skirmishes
The 2016 Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, also known as the Four-Day War,, IPA: ʰɑroɾjɑ pɑtɛɾɑzm az, Dördgünlük müharibə April War,; or April clashes, began along the Nagorno-Karabakh line of contact on 1 April 2016 with the Artsakh Defence Army, backed by the Armenian Armed Forces on one side and the Azerbaijani Armed Forces on the other. The clashes occurred in a region that is disputed between the self-proclaimed Republic of Artsakh and the Republic of Azerbaijan. The region includes the former Soviet Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast and surrounding areas, which are integral part of the Republic of Artsakh according to its Constitution. Azerbaijan claimed to prevent purported continuous Armenian shelling of civilian areas in Azerbaijan and started a military operation for this purpose. However, there was no evidence of Armenian shelling. Until the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war, the clashes were the worst since the 1994 ceasefire agreement signed by Artsakh, Azerba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
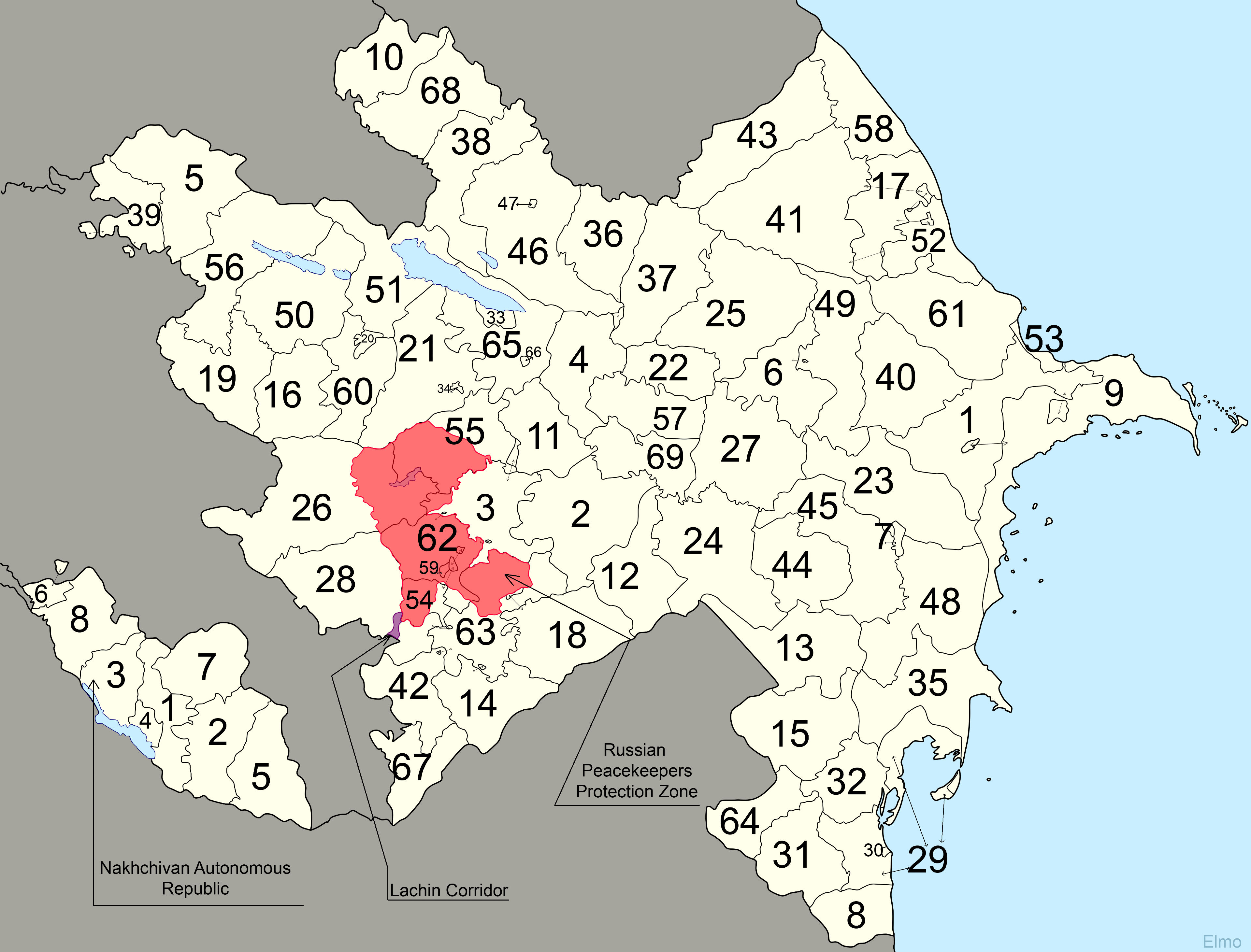
Administrative Divisions Of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 66 districts () and 11 cities () that are subordinate to the Republic. Out of these, 7 districts and 1 city is located within the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The districts are further divided into municipalities (). Additionally, the districts of Azerbaijan are grouped into 14 Economic Regions (). On July 7, 2021, the President of Azerbaijan Ilham Aliyev signed Decree "On the new division of economic regions in the Republic of Azerbaijan". Administrative divisions Contiguous Azerbaijan The territory of former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast presently consists of the districts of Khojavend, Shusha, Khojaly, the eastern portion of Kalbajar and the western portion of Tartar. The Autonomous Oblast was abolished on 26 November 1991, by the Supreme Soviet of the Azerbaijan SSR. Since then, the territory of the autonomous oblast has been administratively split between the aforementioned districts. As a result of the First N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tartar (river)
The Tartar ( az, Tərtərçay, hy, Թարթառ) is one of the tributaries of the Kura located in Azerbaijan. It passes through the districts of Kalbajar, Barda and Tartar. Parts of the river flows through the self-proclaimed Republic of Artsakh's Martakert Province. Overview Tartar is the left tributary of Kura, the largest river in the Caucasus. The river originates in the area where Qonqur, Alaköz and Mıxtökən mountain ranges meet on Karabakh Plateau in the vicinity of hot springs village of Istisu located de jure in Kalbajar Rayon of Azerbaijan and de facto in the Martakert Province of the Republic of Artsakh. The altitude where the river originates from mountain springs is above sea level. The river flows eastward through the whole Kalbajar rayon (de facto Martakert Province) passing through Kalbajar city, Tartar and Barda raions passing through Tartar and Barda cities before discharging into Kura. The river has two left tributaries: Levçay () and Ağdabançay (), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Power Stations In Azerbaijan ...
The following page lists all power stations in Azerbaijan. Renewable energy Hydroelectric power stations in Azerbaijan Photovoltaic power stations Non-renewable energy Thermal power stations See also * Energy law * List of power stations in Asia * List of power stations in Europe * List of largest power stations in the world References External links Area.gov.az- Official website of the State Agency for Alternative and Renewable Energy Sources Mie.gov.az- Official website of the Ministry of Energy of Azerbaijan Azerenerji.gov.az- Official website of Azerenerji JSC {{Power stations Azerbaijan * Power stations A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid. Many po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. Husbandry has a long history, starting with the Neolithic Revolution when animals were first domesticated, from around 13,000 BC onwards, predating farming of the first crops. By the time of early civilisations such as ancient Egypt, cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs were being raised on farms. Major changes took place in the Columbian exchange, when Old World livestock were brought to the New World, and then in the British Agricultural Revolution of the 18th century, when livestock breeds like the Dishley Longhorn cattle and Lincoln Longwool sheep were rapidly improved by agriculturalists, such as Robert Bakewell, to yield more meat, milk, and wool. A wide range of other species, such as horse, water buffalo, llama, rabbit, and guinea pig, are used as livestock in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture. The major agricultural products can be broadly grouped into foods, fibers, fuels, and raw materials (such as rubber). Food classes include cereals (grains), vegetables, fruits, cooking oils, meat, milk, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevlakh District
Yevlakh District ( az, Yevlax rayonu) is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the centre of the country and belongs to the Central Aran Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Qakh, Shaki, Agdash, Barda, Tartar, Goranboy, and Samukh. Its capital and largest city is Yevlakh. As of 2020, the district had a population of 129,700. History Yevlakh was called as a Yevlakh village of Elisabethpol Governorate on official documents belonging to the beginning of the 19th century, was called as Dzhevanshirsky Uyezd during the years between 1920 and 1935. The Yevlakh region was created on February 20, 1935, by the decision of the Central Executive Committee of the Azerbaijan SSR. Yevlakh became a city on February 1, 1939, according to the decision of the Supreme Soviet of the Azerbaijan SSR Azerbaijan ( az, Азәрбајҹан, Azərbaycan, italics=no), officially the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic (Azerbaijan SSR; az, Азәрбајҹан С ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goranboy District
Goranboy District ( az, Goranboy rayonu) is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the west of the country and belongs to the Ganja-Dashkasan Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Kalbajar, Tartar, Yevlakh, Samukh, and Goygol. Its capital and largest city is Goranboy. As of 2020, the district had a population of 105,000. During the Soviet era, the region was best known for the oil-cure sanatorium resort of Naftalan, though administratively Naftalan counts as an independent city. Naftalan is now starting to operate again following several years of virtual inaction when the resorts were filled with refugees from the First Nagorno-Karabakh War. Geography The relief of the region in the northeast is lowland, and in the southwest it is mountainous, crossed by gorges. The terrain allows oil (including medical oil), limestone and clay to be extracted from minerals. The subtropical dry, mild climate is common in this area. The average temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vachagan III
Vachagan III the Pious () or Vachagan II (according to some authors) was the last Arsacid king of Caucasian Albania, ruling approximately from 485 to 523. Background His lineage is uncertain. Murtazali Gadjiev considers him a son (or nephew) of the King of Kings () Yazdegerd II () and brother (or nephew) of Vache II. However, Aleksan Hakobyan refers to 5th century Armenian historian Elishe's mention of Vache as "a son inherited families", concluding that Vache was not heir but a second son. Hence, according to him, Vachagan was the son of elder but deceased son of Aswagen, thus a nephew of Vache II. Reign Vache II previously ruled Caucasian Albania as a Sasanian vassal, but had been forced to abdicate after his revolt was crushed by Yazdegerd II's son and successor Peroz I () in 462. Albania would remain kingless until 485, when Vachagan III was installed on the throne by Peroz's brother and successor Balash (). This happened around the time of the signing of the Treaty of Nv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeghishe Arakyal Monastery
Yeghishe Arakyal Monastery ( hy, Եղիշե առաքյալի վանք, Yeghishe Arakyali Vank) or Monastery of Yeghishe the Apostle ( az, Müqəddəs Yelisey monastırı) is an Armenian Apostolic Church in Nagorno-Karabakh, located close to the village of Madagiz, on the bank of the Tartar River. The complex comprises the church, seven chapels, a cemetery, and ruins of other buildings. History Yeghishe Arakyal Monastery was built sometime in the 5th century and expanded in the 13th century. One of the seven chapels surrounding the minster is the tomb of Vachagan III, King of Caucasian Albania, also known as Vachagan the Pious (487–510). Gallery General plan of the Yeghish Arakyal monastery complex.jpg, Plan of the monastery Yeghishe_Arakyal_Monastery_-_Եղիշե_առաքյալի_վանք_17.JPG, Armenian khachkars in the wall in the monastery of St. Yeghishe. Yeghishe Arakyal102.jpg Yeghishe Arakyal103.jpg Yeghishe Arakyal104.jpg Yeghishe Arakyal106.jpg Yeghishe Araky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khachkar
A ''khachkar'', also known as a ''khatchkar'' or Armenian cross-stone ( hy, խաչքար, , խաչ xačʿ "cross" + քար kʿar "stone") is a carved, memorial stele bearing a cross, and often with additional motifs such as rosettes, interlaces, and botanical motifs. ''Khachkars'' are characteristic of medieval Christian Armenian art.The Grove Encyclopedia of Medieval Art and Architecture. — Oxford University Press, 2012. — Vol. 2. — P. 222.''"'Khatck'ar' rmen.:'cross-stone'Typical Armenian stone monument, comprising an upright slab (h. c. 1—3 m) carved with a cross design, usually set on a plinth or rectangular base. "'' Since 2010, khachkars, their symbolism and craftsmanship are inscribed in the UNESCO list of Intangible Cultural Heritage. Description The most common ''khachkar'' feature is a cross surmounting a rosette or a solar disc. The remainder of the stone face is typically filled with elaborate patterns of leaves, grapes, pomegranates, and bands o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Goranboy
Operation Goranboy was a large-scale military offensive by Azerbaijan in the summer of 1992. Its aims were to take complete control of the entire territory of Nagorno-Karabakh and put a decisive end to the secessionist Nagorno-Karabakh Republic (NKR). This offensive is regarded as a successful breakthrough by the Azerbaijani Army and marked the peak of Azerbaijani success throughout the entire six years of the First Nagorno-Karabakh War. After Azerbaijan's initial military successes, re-grouped Armenian forces repelled the attack, re-capturing most of the seized regions. The offensive On 12 June 1992, just five days after Abulfaz Elchibey of the Popular Front of Azerbaijan was elected the President of Azerbaijan, the Azerbaijani military first launched a large scale diversionary attack from the east, in the direction of the Askeran region at the center of Nagorno-Karabakh. The Azerbaijani troops attacked positions to the north and south of Askeran. As a result of fierce fightin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |