|
Mastigina
''Mastigamoeba'' is a genus of peolobionts, and treated by some as members of the Archamoebae group of protists. ''Mastigamoeba ''are characterized as anaerobic, amitochondriate organisms that are polymorphic. Their dominant life cycle stage is as an amoeboid flagellate. Species are typically free living, though endobiotic species have been described. The genus is relatively understudied, and under contention regarding the composition of the genus. While dozens of species have been described (some in other genera such as ''Phreatamoeba'', ''Dinamoeba'', and ''Mastigina''), the well described species are ''Mastigamoeba aspera'' Schulze, 1875; ''Mastigamoeba simplex'' Kent, 1880; ''Mastigamoeba chlamys'' Frenzel, 1897 Lemmermann, 1914; ''Mastigamoeba viridis'' Prowazek, 1900; ''Mastigamoeba trichophora'' Lauterborn, 1901; ''Mastigamoeba balamuthi'' (Chàvez et al., 1986) Simpson et al., 1997; ''Mastigamoeba schizophrenia'' Simpson et al., 1997; and ''Mastigamoeba punctachora'' B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigamoeba Simplex
''Mastigamoeba'' is a genus of peolobionts, and treated by some as members of the Archamoebae group of protists. ''Mastigamoeba ''are characterized as anaerobic, amitochondriate organisms that are polymorphic. Their dominant life cycle stage is as an amoeboid flagellate. Species are typically free living, though endobiotic species have been described. The genus is relatively understudied, and under contention regarding the composition of the genus. While dozens of species have been described (some in other genera such as ''Phreatamoeba'', ''Dinamoeba'', and ''Mastigina''), the well described species are ''Mastigamoeba aspera'' Schulze, 1875; ''Mastigamoeba simplex'' Kent, 1880; ''Mastigamoeba chlamys'' Frenzel, 1897 Lemmermann, 1914; ''Mastigamoeba viridis'' Prowazek, 1900; ''Mastigamoeba trichophora'' Lauterborn, 1901; ''Mastigamoeba balamuthi'' (Chàvez et al., 1986) Simpson et al., 1997; ''Mastigamoeba schizophrenia'' Simpson et al., 1997; and ''Mastigamoeba punctachora'' B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigamoeba Balamuthi
''Mastigamoeba'' is a genus of peolobionts, and treated by some as members of the Archamoebae group of protists. ''Mastigamoeba ''are characterized as anaerobic, amitochondriate organisms that are polymorphic. Their dominant life cycle stage is as an amoeboid flagellate. Species are typically free living, though endobiotic species have been described. The genus is relatively understudied, and under contention regarding the composition of the genus. While dozens of species have been described (some in other genera such as ''Phreatamoeba'', ''Dinamoeba'', and ''Mastigina''), the well described species are ''Mastigamoeba aspera'' Schulze, 1875; ''Mastigamoeba simplex'' Kent, 1880; ''Mastigamoeba chlamys'' Frenzel, 1897 Lemmermann, 1914; ''Mastigamoeba viridis'' Prowazek, 1900; ''Mastigamoeba trichophora'' Lauterborn, 1901; ''Mastigamoeba balamuthi'' (Chàvez et al., 1986) Simpson et al., 1997; ''Mastigamoeba schizophrenia'' Simpson et al., 1997; and ''Mastigamoeba punctachora'' B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigamoeba Hylae
''Mastigamoeba'' is a genus of peolobionts, and treated by some as members of the Archamoebae group of protists. ''Mastigamoeba ''are characterized as anaerobic, amitochondriate organisms that are polymorphic. Their dominant life cycle stage is as an amoeboid flagellate. Species are typically free living, though endobiotic species have been described. The genus is relatively understudied, and under contention regarding the composition of the genus. While dozens of species have been described (some in other genera such as ''Phreatamoeba'', ''Dinamoeba'', and ''Mastigina''), the well described species are ''Mastigamoeba aspera'' Schulze, 1875; ''Mastigamoeba simplex'' Kent, 1880; ''Mastigamoeba chlamys'' Frenzel, 1897 Lemmermann, 1914; ''Mastigamoeba viridis'' Prowazek, 1900; ''Mastigamoeba trichophora'' Lauterborn, 1901; ''Mastigamoeba balamuthi'' (Chàvez et al., 1986) Simpson et al., 1997; ''Mastigamoeba schizophrenia'' Simpson et al., 1997; and ''Mastigamoeba punctachora'' B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigamoeba Longfilum
''Mastigamoeba'' is a genus of peolobionts, and treated by some as members of the Archamoebae group of protists. ''Mastigamoeba ''are characterized as anaerobic, amitochondriate organisms that are polymorphic. Their dominant life cycle stage is as an amoeboid flagellate. Species are typically free living, though endobiotic species have been described. The genus is relatively understudied, and under contention regarding the composition of the genus. While dozens of species have been described (some in other genera such as ''Phreatamoeba'', ''Dinamoeba'', and ''Mastigina''), the well described species are ''Mastigamoeba aspera'' Schulze, 1875; ''Mastigamoeba simplex'' Kent, 1880; ''Mastigamoeba chlamys'' Frenzel, 1897 Lemmermann, 1914; ''Mastigamoeba viridis'' Prowazek, 1900; ''Mastigamoeba trichophora'' Lauterborn, 1901; ''Mastigamoeba balamuthi'' (Chàvez et al., 1986) Simpson et al., 1997; ''Mastigamoeba schizophrenia'' Simpson et al., 1997; and ''Mastigamoeba punctachora'' B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigamoeba Punctachora
''Mastigamoeba'' is a genus of peolobionts, and treated by some as members of the Archamoebae group of protists. ''Mastigamoeba ''are characterized as anaerobic, amitochondriate organisms that are polymorphic. Their dominant life cycle stage is as an amoeboid flagellate. Species are typically free living, though endobiotic species have been described. The genus is relatively understudied, and under contention regarding the composition of the genus. While dozens of species have been described (some in other genera such as ''Phreatamoeba'', ''Dinamoeba'', and ''Mastigina''), the well described species are ''Mastigamoeba aspera'' Schulze, 1875; ''Mastigamoeba simplex'' Kent, 1880; ''Mastigamoeba chlamys'' Frenzel, 1897 Lemmermann, 1914; ''Mastigamoeba viridis'' Prowazek, 1900; ''Mastigamoeba trichophora'' Lauterborn, 1901; ''Mastigamoeba balamuthi'' (Chàvez et al., 1986) Simpson et al., 1997; ''Mastigamoeba schizophrenia'' Simpson et al., 1997; and ''Mastigamoeba punctachora'' B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigamoeba Schizophrenia
''Mastigamoeba'' is a genus of peolobionts, and treated by some as members of the Archamoebae group of protists. ''Mastigamoeba ''are characterized as anaerobic, amitochondriate organisms that are polymorphic. Their dominant life cycle stage is as an amoeboid flagellate. Species are typically free living, though endobiotic species have been described. The genus is relatively understudied, and under contention regarding the composition of the genus. While dozens of species have been described (some in other genera such as ''Phreatamoeba'', ''Dinamoeba'', and ''Mastigina''), the well described species are ''Mastigamoeba aspera'' Schulze, 1875; ''Mastigamoeba simplex'' Kent, 1880; ''Mastigamoeba chlamys'' Frenzel, 1897 Lemmermann, 1914; ''Mastigamoeba viridis'' Prowazek, 1900; ''Mastigamoeba trichophora'' Lauterborn, 1901; ''Mastigamoeba balamuthi'' (Chàvez et al., 1986) Simpson et al., 1997; ''Mastigamoeba schizophrenia'' Simpson et al., 1997; and ''Mastigamoeba punctachora'' B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigamoeba Setosa
''Mastigamoeba'' is a genus of peolobionts, and treated by some as members of the Archamoebae group of protists. ''Mastigamoeba ''are characterized as anaerobic, amitochondriate organisms that are polymorphic. Their dominant life cycle stage is as an amoeboid flagellate. Species are typically free living, though endobiotic species have been described. The genus is relatively understudied, and under contention regarding the composition of the genus. While dozens of species have been described (some in other genera such as ''Phreatamoeba'', ''Dinamoeba'', and ''Mastigina''), the well described species are ''Mastigamoeba aspera'' Schulze, 1875; ''Mastigamoeba simplex'' Kent, 1880; ''Mastigamoeba chlamys'' Frenzel, 1897 Lemmermann, 1914; ''Mastigamoeba viridis'' Prowazek, 1900; ''Mastigamoeba trichophora'' Lauterborn, 1901; ''Mastigamoeba balamuthi'' (Chàvez et al., 1986) Simpson et al., 1997; ''Mastigamoeba schizophrenia'' Simpson et al., 1997; and ''Mastigamoeba punctachora'' B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archamoebae
The Archamoebae are a group of protists originally thought to have evolved before the acquisition of mitochondria by eukaryotes. They include genera that are internal parasites or commensals of animals (''Entamoeba'' and ''Endolimax''). A few species are human pathogens, causing diseases such as amoebic dysentery. The other genera of archamoebae live in freshwater habitats and are unusual among amoebae in possessing flagella. Most have a single nucleus and flagellum, but the giant amoeba '' Pelomyxa'' has many of each. Description Archamoebae are a diverse group of amoebae. Many have flagella for motility, while others do not. They grow in the absence of oxygen, though some can tolerate small amounts. Most described species of Archamoebae either lack mitochondria or are described to have reduced mitosomes. Habitat They thrive and live in soil, freshwater, and marine habitats. History The group Archamoebae was proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 1998 as part of the Archezoa, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigamoebidae
The Archamoebae are a group of protists originally thought to have evolved before the acquisition of mitochondria by eukaryotes. They include genera that are internal parasites or commensals of animals (''Entamoeba'' and '' Endolimax''). A few species are human pathogens, causing diseases such as amoebic dysentery. The other genera of archamoebae live in freshwater habitats and are unusual among amoebae in possessing flagella. Most have a single nucleus and flagellum, but the giant amoeba '' Pelomyxa'' has many of each. Description Archamoebae are a diverse group of amoebae. Many have flagella for motility, while others do not. They grow in the absence of oxygen, though some can tolerate small amounts. Most described species of Archamoebae either lack mitochondria or are described to have reduced mitosomes. Habitat They thrive and live in soil, freshwater, and marine habitats. History The group Archamoebae was proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 1998 as part of the Archez ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endobiotic
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosome
A mitosome is an organelle found in some unicellular eukaryotic organisms, like in members of the supergroup Excavata. The mitosome was found and named in 1999, and its function has not yet been well characterized. It was termed a ''crypton'' by one group, but that name is no longer in use. The mitosome has been detected only in anaerobic or microaerophilic organisms that do not have mitochondria. These organisms do not have the capability of gaining energy from oxidative phosphorylation, which is normally performed by mitochondria. The mitosome was first described in ''Entamoeba histolytica,'' an intestinal parasite of humans. Mitosomes have also been identified in several species of Microsporidia and in '' Giardia intestinalis''. Origin and function Mitosomes are almost certainly derived from mitochondria. Like mitochondria, they have a double membrane and most proteins are delivered to them by a targeting sequence of amino acids. The targeting sequence is similar to that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
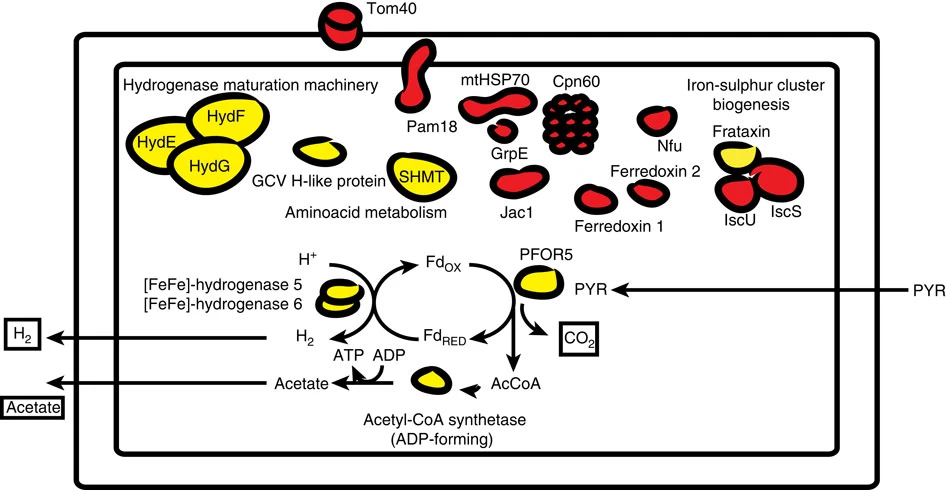
Hydrogenosome
A hydrogenosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in some anaerobic ciliates, flagellates, and fungi. Hydrogenosomes are highly variable organelles that have presumably evolved from protomitochondria to produce molecular hydrogen and ATP in anaerobic conditions. Hydrogenosomes were discovered in 1973 by D. G. Lindmark and M. Müller. Because hydrogenosomes hold evolutionary lineage significance for organisms living in anaerobic or oxygen-stressed environments, many research institutions have since documented their findings on how the organelle differs in various sources. History Hydrogenosomes were isolated, purified, biochemically characterized and named in the early 1970s by Lindmark and Müller at Rockefeller University. In addition to this seminal study on hydrogenosomes, they also demonstrated for the first time the presence of pyruvate:ferredoxin oxido-reductase and hydrogenase in eukaryotes. Further studies were subsequently conducted on the biochemical cytolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |