|
Massif Central (geology)
The Massif Central is one of the two large basement massifs in France, the other being the Armorican Massif. The Massif Central's geological evolution started in the late Neoproterozoic and continues to this day. It has been shaped mainly by the Caledonian orogeny and the Variscan orogeny. The Alpine orogeny has also left its imprints, probably causing the important Cenozoic volcanism. The Massif Central has a very long geological history, underlined by zircon ages dating back into the Archaean 3billion years ago. Structurally it consists mainly of stacked metamorphic basement nappes. Introduction The basement outcrops of the Massif Central have roughly the outline of a triangle standing on its tip. Because of its size – 500 kilometers long and 340 kilometers wide – the Massif Central partakes in several tectono-metamorphic zones formed during the Variscan orogeny. The bulk of the massif belongs to the Ligero-Arvernian Zone, sometimes also called the microcontinent Ligeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massif Central
The (; oc, Massís Central, ; literally ''"Central Massif"'') is a highland region in south-central France, consisting of mountains and plateaus. It covers about 15% of mainland France. Subject to volcanism that has subsided in the last 10,000 years, these central mountains are separated from the Alps by a deep north–south cleft created by the Rhône river and known in French as the ' (literally "Rhône furrow"). The region was a barrier to transport within France until the opening of the A75 motorway, which not only made north–south travel easier, but also opened access to the massif itself. Geography and geology The is an old massif, formed during the Variscan orogeny, consisting mostly of granitic and metamorphic rocks. It was powerfully raised and made to look geologically younger in the eastern section by the uplift of the Alps during the Paleogene period and in the southern section by the uplift of the Pyrenees. The massif thus presents a strongly asymmet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morvan
The Morvan (historically Morvand from the Latin ''Murvinnum'' 590)Pierre-Henri Billy, ''Dictionnaire des noms de lieux de la France'', éditions Errance, 640 pages, 2011 , is a mountainous massif lying just to the west of the Côte d'Or escarpment in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region, central-east France. It is a northerly extension of the Massif Central and is of Variscan age. It is composed of granites and basalts and formed a promontory extending northwards into the Jurassic sea. It is the smallest mountain area in France in terms of landmass covered, as well as the lowest, with a maximum altitude of 901 metres (2,956 feet) at Haut-Folin. Geography The Morvan is located across the Côte-d'Or, Nièvre, Saône-et-Loire and Yonne departments in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in central-east France. At its heart nowadays is the protected area of Morvan Regional Natural Park (French: ''Parc naturel régional du Morvan''). Its main town is Château-Chinon, Nièvre on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a single geomorphological unit and low mountain range of around in area. It runs in a north-northeast direction from the Burgundian Gate (the Belfort–Ronchamp– Lure line) to the Börrstadt Basin (the Winnweiler– Börrstadt–Göllheim line), and forms the western boundary of the Upper Rhine Plain. The Grand Ballon is the highest peak at , followed by the Storkenkopf (), and the Hohneck ().IGN maps available oGéoportail/ref> Geography Geographically, the Vosges Mountains are wholly in France, far above the Col de Saverne separating them from the Palatinate Forest in Germany. The latter area logically continues the same Vosges geologic structure but traditionally receives this different name for historical and political reasons. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tournaisian
The Tournaisian is in the ICS geologic timescale the lowest stage or oldest age of the Mississippian, the oldest subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Tournaisian age lasted from Ma to Ma. It is preceded by the Famennian (the uppermost stage of the Devonian) and is followed by the Viséan. Name and regional alternatives The Tournaisian was named after the Belgian city of Tournai. It was introduced in scientific literature by Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1832. Like many Devonian and lower Carboniferous stages, the Tournaisian is a unit from West European regional stratigraphy that is now used in the official international time scale. The Tournaisian correlates with the regional North American Kinderhookian and lower Osagean stages and the Chinese Tangbagouan regional stage. In British stratigraphy, the Tournaisian contains three substages: the Hastarian, Ivorian and lower part of the Chadian (the upper part falls in the Viséan). Stratigraphy The base of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frasnian
The Frasnian is one of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian Period. It lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Givetian Stage and followed by the Famennian Stage. Major reef-building was under way during the Frasnian Stage, particularly in western Canada and Australia. On land, the first forests were taking shape. In North America, the Antler orogeny peaked, which were contemporary with the Bretonic phase of the Variscan orogeny in Europe. The Frasnian coincides with the second half of the "charcoal gap" in the fossil record, a time when atmospheric oxygen levels were below 13 percent, the minimum necessary to sustain wildfires. North American subdivisions of the Frasnian include * West Falls Group * Sonyea Group * Genesee Group Name and definition The Frasnian Stage was proposed in 1879 by French geologist Jules Gosselet Jules-Auguste Gosselet (19 April 1832 – 20 March 1916) was a French geologist born in Cambrai, France. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armorican Terrane
The Armorican terrane, Armorican terrane assemblage, or simply Armorica, was a microcontinent or group of continental fragments that rifted away from Gondwana towards the end of the Silurian and collided with Laurussia towards the end of the Carboniferous during the Variscan orogeny. The name is taken from Armorica, the Gaulish name for a large part of northwestern France that includes Brittany, as this matches closely to the present location of the rock units that form the main part of this terrane. Extent The main exposures of the Armorican terrane are found throughout Brittany, the Channel Islands, parts of Upper Normandy, forming the Armorican Massif. Other fragments thought to have originally formed part of the Armorican terrane assemblage include rock units exposed in the Vosges, Black Forest, Bohemian Massif and most of the Iberian peninsula. History All of the fragments that make up the Armorican terrane are thought to have originally formed part of the northern margin of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America (forming the Drake Passage) and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name (see ), it is also commonly called Gondwanaland. Gondwana was formed by the accretion of several cratons. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of about , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. During the Carboniferous Period, it merged with Laurasia to form a larger supercontinent called Pangaea. Gondwana (and Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods (myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) became fully terrestrialized. A significant evolutionary milestone during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
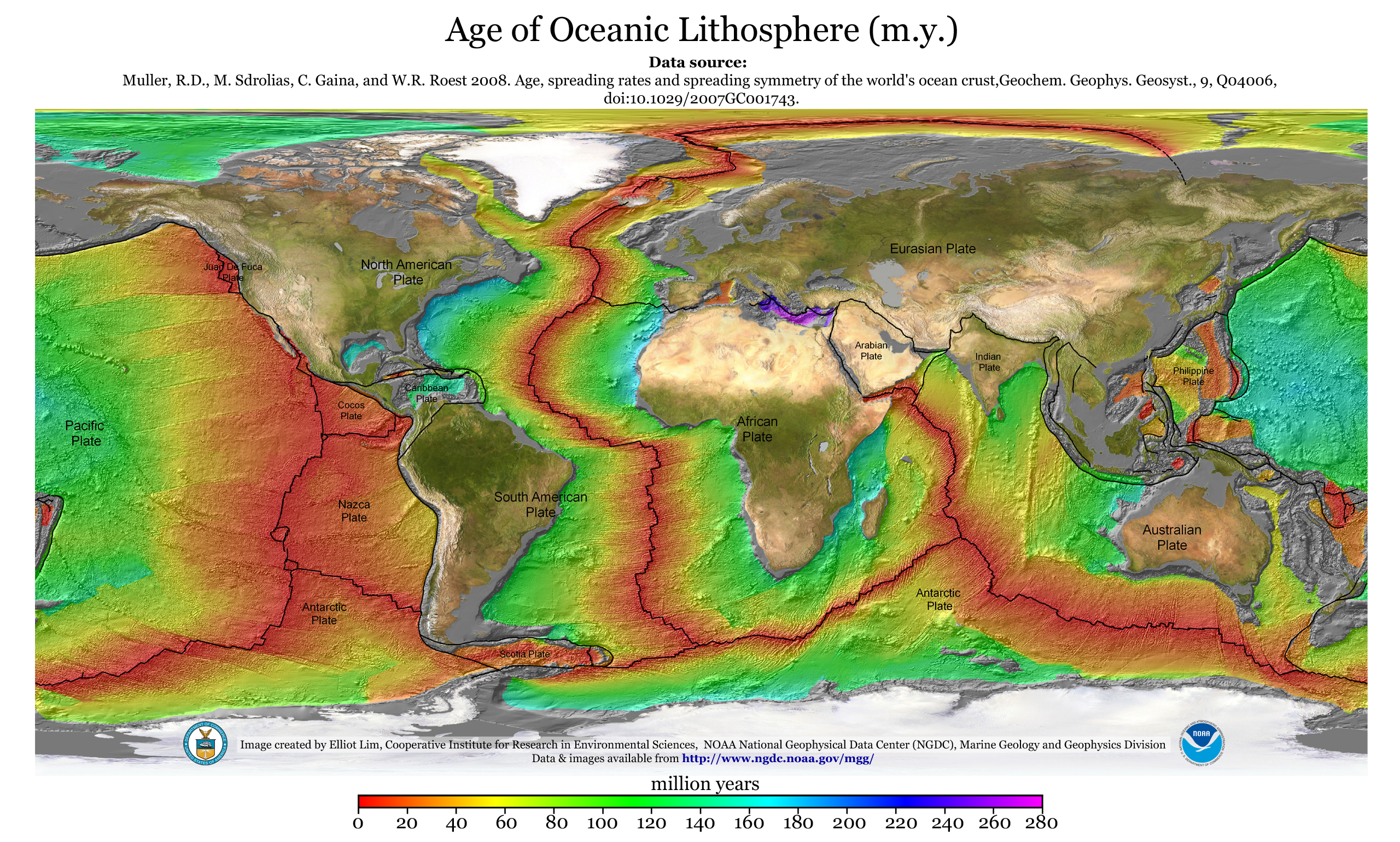
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust overlies the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however, it is denser, having a mean density of about 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. The crust uppermost is the result of the cooling of magma derived from mantle material below the plate. The magma is injected into the spreading center, which consists mainly of a partly solidified crystal mush derived from earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |