|
Martin Weitzman
Martin Lawrence Weitzman (April 1, 1942 – August 27, 2019) was an economist and a professor of economics at Harvard University. He was among the most influential economists in the world according to Research Papers in Economics (RePEc). His latest research was largely focused on environmental economics, specifically climate change and the economics of catastrophes. Personal A ''New York Times'' obituary details how Weitzman "was born Meyer Levinger on April 1, 1942, on the Lower East Side of Manhattan to Joseph and Helen (Tobias) Levenger. His mother died before he was 1; his father, after returning from military service in World War II, was apparently unable to care for the child, and he was placed in an orphanage. His adoptive parents, Samuel and Fannie (Katzelnick) Weitzman, who were elementary-school teachers, gave him the name Martin Lawrence Weitzman." Weitzman received a B.A. in Mathematics and Physics from Swarthmore College in 1963. He went on to receive an M.S. in S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
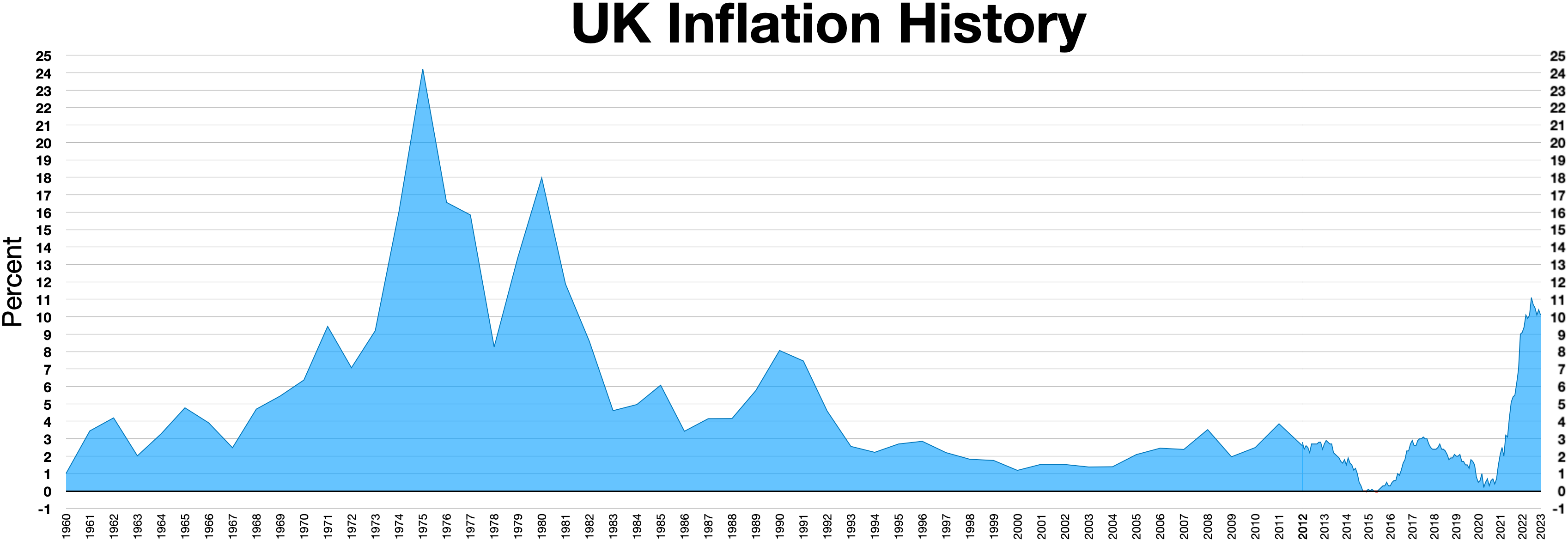
Stagflation
In economics, stagflation or recession-inflation is a situation in which the inflation rate is high or increasing, the economic growth rate slows, and unemployment remains steadily high. It presents a dilemma for economic policy, since actions intended to lower inflation may exacerbate unemployment. The term, a portmanteau of '' stagnation'' and ''inflation'', is generally attributed to Iain Macleod, a British Conservative Party politician who became Chancellor of the Exchequer in 1970. Macleod used the word in a 1965 speech to Parliament during a period of simultaneously high inflation and unemployment in the United Kingdom.Introduction, page 9. Warning the House of Commons of the gravity of the situation, he said: Macleod used the term again on 7 July 1970, and the media began also to use it, for example in ''The Economist'' on 15 August 1970, and ''Newsweek'' on 19 March 1973. John Maynard Keynes did not use the term, but some of his work refers to the conditions that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agency For International Development
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government that is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance. With a budget of over $27 billion, USAID is one of the largest official aid agencies in the world and accounts for more than half of all U.S. foreign assistance—the highest in the world in absolute dollar terms. Congress passed the Foreign Assistance Act on September 4, 1961, which reorganized U.S. foreign assistance programs and mandated the creation of an agency to administer economic aid. USAID was subsequently established by the executive order of President John F. Kennedy, who sought to unite several existing foreign assistance organizations and programs under one agency. USAID became the first U.S. foreign assistance organization whose primary focus was long-term socioeconomic development. USAID's programs are authorized by Congress in the Foreign Assistance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world." Formed in 1944, started on 27 December 1945, at the Bretton Woods Conference primarily by the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes, it came into formal existence in 1945 with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international monetary system. It now plays a central role in the management of balance of payments difficulties and international financial crises. Countries contribute funds to a pool through a quota system from which countries experiencing balance of payments problems can borrow money. , the fund had XDR 477 billion (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Research Institute
SRI International (SRI) is an American nonprofit scientific research institute and organization headquartered in Menlo Park, California. The trustees of Stanford University established SRI in 1946 as a center of innovation to support economic development in the region. The organization was founded as the Stanford Research Institute. SRI formally separated from Stanford University in 1970 and became known as SRI International in 1977. SRI performs client-sponsored research and development for government agencies, commercial businesses, and private foundations. It also licenses its technologies, forms strategic partnerships, sells products, and creates spin-off companies. SRI's headquarters are located near the Stanford University campus. SRI's annual revenue in 2014 was approximately $540 million, which tripled from 1998 under the leadership of Curtis Carlson. In 1998, the organization was on the verge of bankruptcy when Carlson took over as CEO. Over the next sixteen years wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The World Bank
The World Bank Group (WBG) is a family of five international organizations that make leveraged loans to developing countries. It is the largest and best-known development bank in the world and an observer at the United Nations Development Group. The bank is headquartered in Washington, D.C. in the United States. It provided around $98.83 billion in loans and assistance to "developing" and transition countries in the 2021 fiscal year. The bank's stated mission is to achieve the twin goals of ending extreme poverty and building shared prosperity.The World Bank, Press release: "World Bank Group Commitments Rise Sharply in FY14 Amid Organizational Change"July 1 2014, http://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2014/07/01/world-bank-group-commitments-rise-sharply-in-fy14-amid-organizational-change/ref> Total lending as of 2015 for the last 10 years through Development Policy Financing was approximately $117 billion. Its five organizations are the International Bank for Reconstruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John C
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gittins Index
The Gittins index is a measure of the reward that can be achieved through a given stochastic process with certain properties, namely: the process has an ultimate termination state and evolves with an option, at each intermediate state, of terminating. Upon terminating at a given state, the reward achieved is the sum of the probabilistic expected rewards associated with every state from the actual terminating state to the ultimate terminal state, inclusive. The index is a real scalar. Terminology To illustrate the theory we can take two examples from a developing sector, such as from electricity generating technologies: wind power and wave power. If we are presented with the two technologies when they are both proposed as ideas we cannot say which will be better in the long run as we have no data, as yet, to base our judgments on. It would be easy to say that wave power would be too problematic to develop as it seems easier to put up many wind turbines than to make the long floating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics Of Climate Change
The economics of climate change concerns the economic aspects of climate change; this can inform policies that governments might consider in response. A number of factors make this and the politics of climate change a difficult problem: it is a long-term, intergenerational problem; (pb: benefits and costs are distributed unequally both within and across countries; and both the scientific consensus and public opinion on climate change need to be taken into account. Effects of climate change may last a long time, such as sea level rise which will not be reversed for thousands of years. The long time scales and uncertainty associated with global warming have led analysts to develop "scenarios" of future environmental, social and economic changes. These scenarios can help governments understand the potential consequences of their decisions. One of the responses to the uncertainties of global warming is to adopt a strategy of sequential decision making. This strategy recognizes that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |