|
Martin Gruber Anastomosis
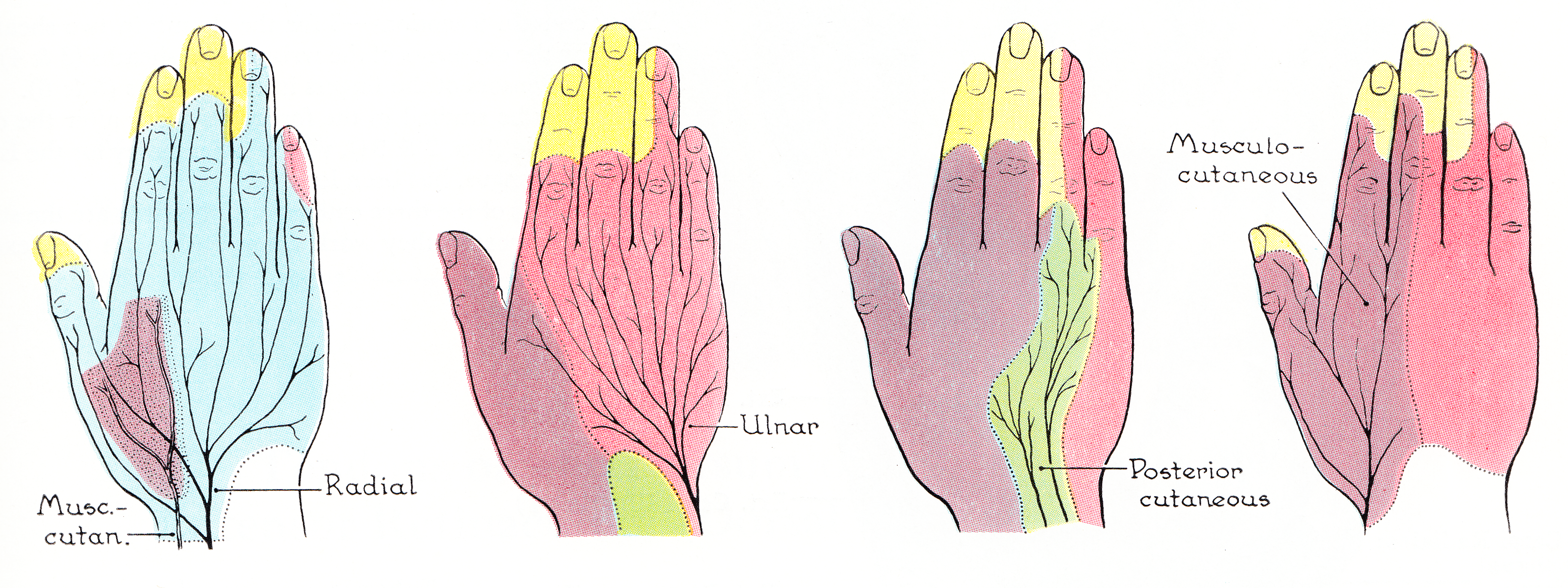
A Martin-Gruber anastomosis (MGA) is a connection from the median nerve to the ulnar nerve in the forearm. An anastomosis occurs when two structures that normally are not connected have a connection. In this case the connection is a nerve. The Martin-Gruber anastomosis is most common anastomosis that occurs between these two nerves. This connection carries motor axons which innervate some of the usually ulnar nerve innervated intrinsic muscles. This inconstant pattern of connection can serve as explanation for a difficult or challenging differential diagnosis. In one study, the MGA was found in 22.9% of cadaver A cadaver or corpse is a dead human body that is used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue to repair a defect in a living human being. Stud ... specimens, while another found the incidence at ~11%. This relatively high incidence demonstrates the necessity for healthcar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Nerve
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus. The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has contributions from ventral roots of C5-C7 (lateral cord) and C8 and T1 (medial cord). The median nerve is the only nerve that passes through the carpal tunnel. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the disability that results from the median nerve being pressed in the carpal tunnel. Structure The median nerve arises from the branches from lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, courses through the anterior part of arm, forearm, and hand, and terminates by supplying the muscles of the hand. Arm After receiving inputs from both the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, the median nerve enters the arm from the axilla at the inferior margin of the teres major muscle. It then passes vertically down and courses lateral to the brachial ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Nerve
In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds. This nerve can cause an electric shock-like sensation by striking the medial epicondyle of the humerus posteriorly, or inferiorly with the elbow flexed. The ulnar nerve is trapped between the bone and the overlying skin at this point. This is commonly referred to as bumping one's "funny bone". This name is thought to be a pun, based on the sound resemblance between the name of the bone of the upper arm, the humerus, and the word "humorous". Alternatively, according to the Oxford English Dictionary, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
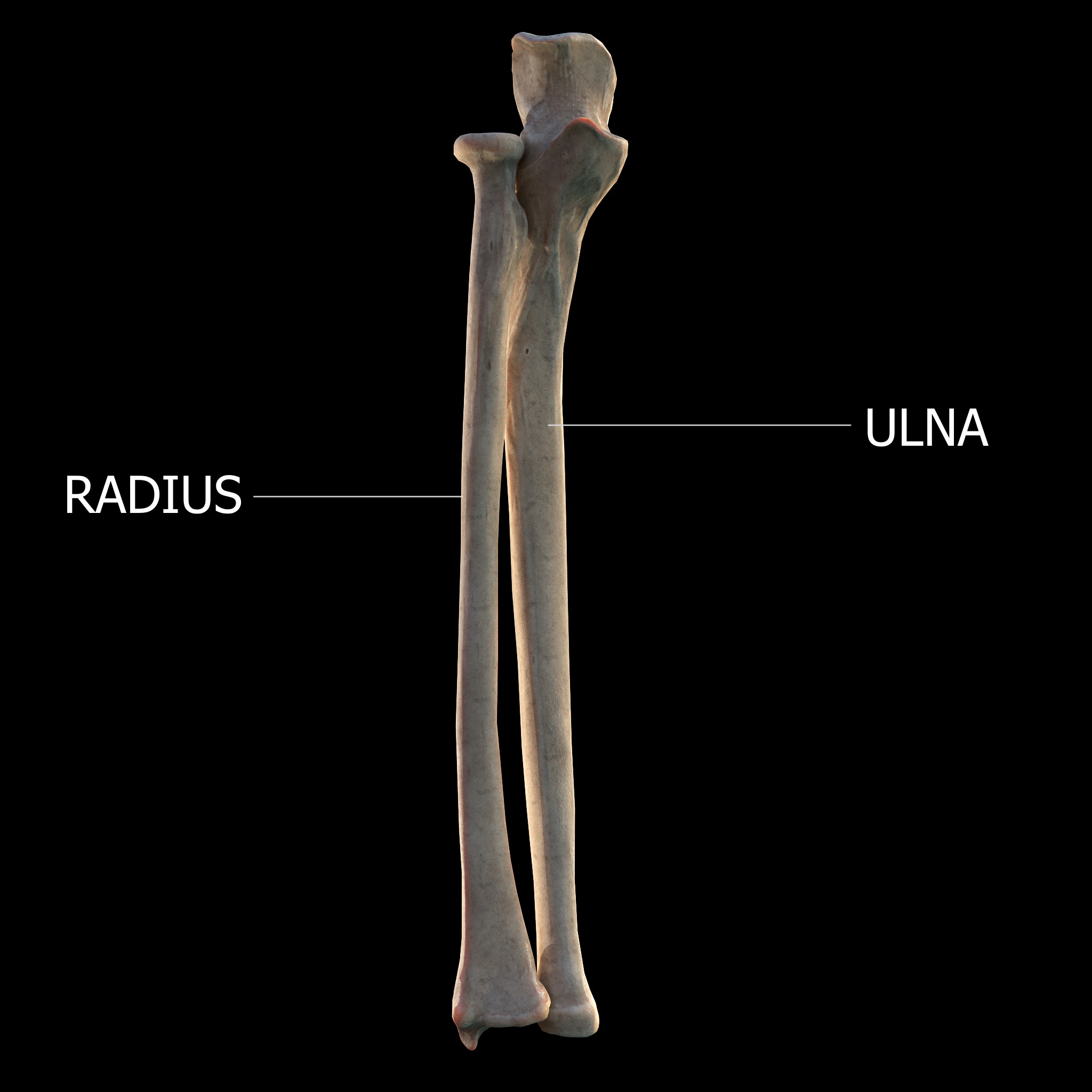
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow (brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (abbreviated DDx) is a method of analysis of a patient's history and physical examination to arrive at the correct diagnosis. It involves distinguishing a particular disease or condition from others that present with similar clinical features. Differential diagnostic procedures are used by clinicians to diagnose the specific disease in a patient, or, at least, to consider any imminently life-threatening conditions. Often, each individual option of a possible disease is called a differential diagnosis (e.g., acute bronchitis could be a differential diagnosis in the evaluation of a cough, even if the final diagnosis is common cold). More generally, a differential diagnostic procedure is a systematic diagnostic method used to identify the presence of a disease entity where multiple alternatives are possible. This method may employ algorithms, akin to the process of elimination, or at least a process of obtaining information that shrinks the "p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadaver
A cadaver or corpse is a dead human body that is used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue to repair a defect in a living human being. Students in medical school study and dissect cadavers as a part of their education. Others who study cadavers include archaeologists and arts students. The term ''cadaver'' is used in courts of law (and, to a lesser extent, also by media outlets such as newspapers) to refer to a dead body, as well as by recovery teams searching for bodies in natural disasters. The word comes from the Latin word ''cadere'' ("to fall"). Related terms include ''cadaverous'' (resembling a cadaver) and ''cadaveric spasm'' (a muscle spasm causing a dead body to twitch or jerk). A cadaver graft (also called “postmortem graft”) is the grafting of tissue from a dead body onto a living human to repair a defect or disfigurement. Cadavers can be observed for their sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerves Of The Upper Limb
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) are f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |