|
Markha River (India)
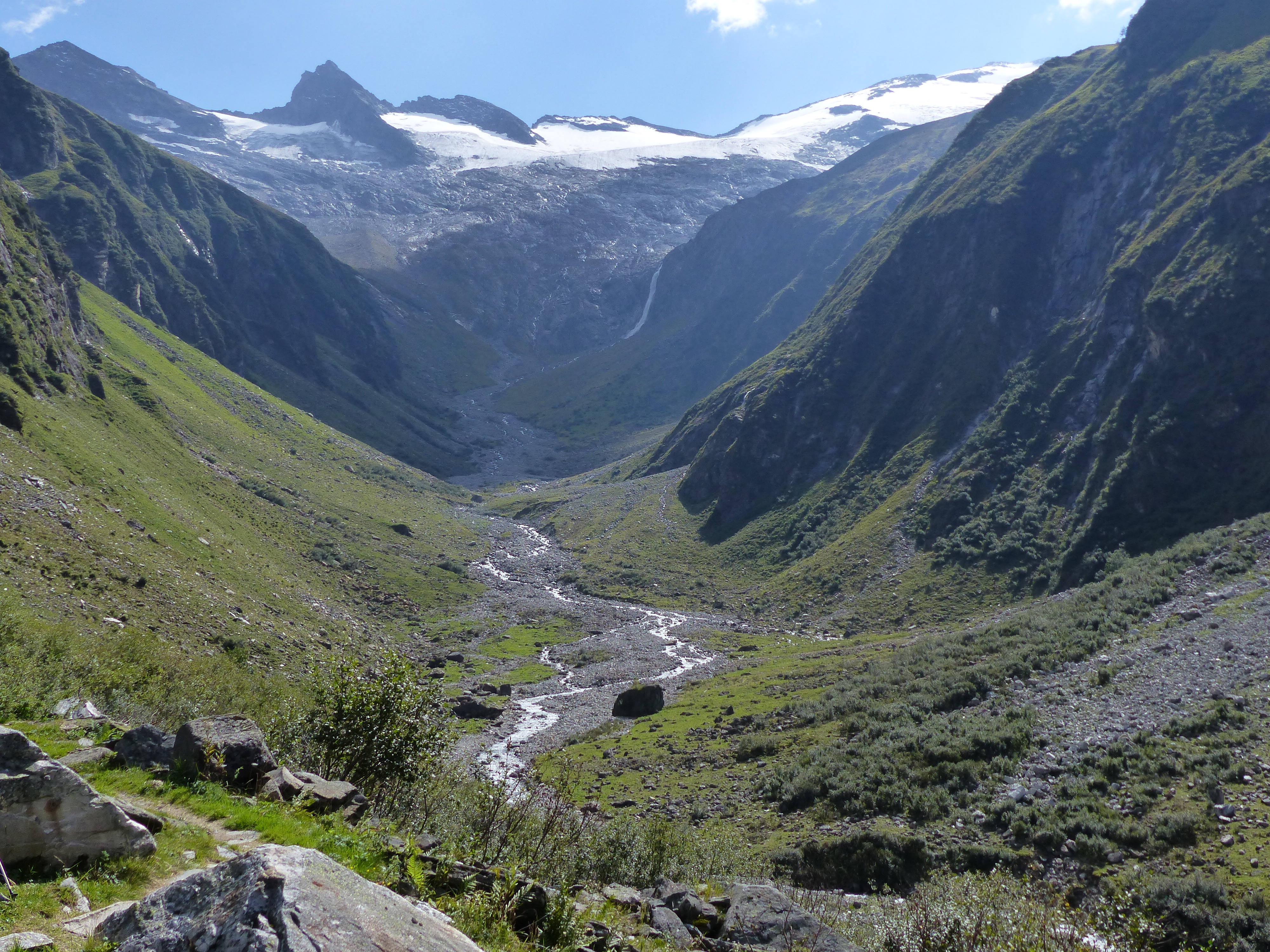
The Markha River is a river in Ladakh, India. It is a tributary of the Zanskar River and starts at the junction of the Langtang Chu and Nimaling Chu. Villages along the river valley include Skiu (Skyu), Markha, Umlung and Hangkar (Hankar). The Markha River lies within the Hemis National Park. The Markha Valley is one of the most popular trekking routes in Ladakh, accessible from Ganda La pass near Spituk in the west, which is usually the beginning point of the trek, and Gongmaru La pass near Hemis, where the trek usually ends. Villages on the route of Markha valley trek are Rumbak, Shingo, Skyu, Sara, Markha and Hankar. Towards the head of the valley you can find the Kang Yatze, a mountain. The Markha River also passes to the south of the Stok range which includes the Stok Kangri mountain. Nomadic families herd their yaks in this valley. Many small monasteries exist, of which Techa gompa is the most important Buddhist monastery A monastery is a building or co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markha Valley1 , a river in Ladakh, India
{{geodis ...
Markha may refer to: * Markha, a former village, incorporated into the city of Yakutsk, Sakha Republic, Russia * Markha, Olyokminsky District, a village in Olyokminsky District, Sakha Republic, Russia * Markha (Vilyuy), a tributary of the Vilyuy in the Sakha Republic, Russia * Markha (Lena), a tributary of the Lena in the Sakha Republic, Russia * Markha River (India) The Markha River is a river in Ladakh, India. It is a tributary of the Zanskar River and starts at the junction of the Langtang Chu and Nimaling Chu. Villages along the river valley include Skiu (Skyu), Markha, Umlung and Hangkar (Hankar). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gongmaru La
Hemis National Park is a high-elevation national park in Ladakh, India. Globally famous for its snow leopards, it is believed to have the highest density of them in any protected area in the world. It is the only national park in India that is north of the Himalayas, the largest notified protected area in India (largest National park) and is the second largest contiguous protected area, after the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve and surrounding protected areas. The park is home to a number of species of endangered mammals, including the snow leopard. Hemis National Park is India's protected area inside the Palearctic realm, outside the Changthang Wildlife Sanctuary northeast of Hemis, and the proposed Tso Lhamo Cold Desert Conservation Area in North Sikkim. The park is bounded on the north by the banks of the Indus River, and includes the catchments of Markha, Sumdah and Rumbak, and parts of the Zanskar Range. History The park was founded in 1981 by protecting the Rumbak and Markh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which may be a chapel, church, or temple, and may also serve as an oratory, or in the case of communities anything from a single building housing only one senior and two or three junior monks or nuns, to vast complexes and estates housing tens or hundreds. A monastery complex typically comprises a number of buildings which include a church, dormitory, cloister, refectory, library, balneary and infirmary, and outlying granges. Depending on the location, the monastic order and the occupation of its inhabitants, the complex may also include a wide range of buildings that facilitate self-sufficiency and service to the community. These may include a hospice, a school, and a range of agricultural and manufacturing buildings such as a barn, a fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Techa Gompa
The Techa is an eastward river on the eastern flank of the southern Ural Mountains noted for its nuclear contamination. It is long, and its basin covers . It begins by the once-secret nuclear processing town of Ozyorsk about northwest of Chelyabinsk and flows east then northeast to the small town of Dalmatovo to flow into the mid-part of the Iset, a tributary of the Tobol. Its basin is close to and north of the Miass, longer than these rivers apart from the Tobol. Water pollution From 1949 to 1956 the Mayak complex dumped an estimated of water into the Techa River, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stok Kangri
Stok Kangri () is the highest mountain in the Stok Range of the Zazkar Mountains a Trans-Himalayan mountain in the Ladakh region of north India. The peak is located in Hemis National Park, 12 km southwest of the trailhead () in the village of Stok and around 15 km southwest of the city of Leh, the capital of Ladakh. Despite its high altitude, Stok Kangri is a popular trekking peak and is often climbed as an initial non-technical foray into high altitude mountaineering. However, the difficulty of Stok Kangri is often underestimated and the need to acclimatise before and during the ascent makes Stok Kangri an enduring challenge. In late July and August, all but the top of the peak may be snow-free. The elevation data was verified by GPS readings from 11 satellites at the Summit during a late July 2007 joint Nepalese-US expedition which encountered snow cover for 85% of the final four-hour, four km, 900 metre climb. Another GPS reading provided a 6136-meter elevat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kang Yatze
Kang Yatze or Kang Yatse (elevation ) is a mountain located at the end of the Markha valley in the Himalayas in the Ladakh region of northwest India. It is located in the Hemis National Park. Location The mountain has two main summits, the lower western peak (Kang Yatze II) is easier (Alpine PD) and more frequently climbed, although lower at about 6270m. The higher eastern peak is the true summit (Kang Yatze I) although less frequently climbed as it is across a technically difficult knife-edge traverse. An alternative is to climb the North East ridge then directly up the steep snow face (Alpine AD+/D-). Approach Route - 6270 meter peak is mainly done from mid-June till September end. There are two approach routes to this peak. One is from Chilling and trekking through the Markha Valley, passing by the villages of Skiu, Markha and Hankar. Another approach starts from the village of Shang Sumdo and steeply climbs up the Markha Gorge passing by the campsite of Chyuskirmo, Larts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Of The Valley
The head of the valley or, less commonly, the valley head, refers to the uppermost part of a valley.Leser (2005), p. 935. Description The head of a valley may take widely differing forms; for example, in highland regions the valley often ends in a broad, evenly sloping hollow. The higher the head of the valley, the more likely it is to resemble the geomorphological shape of a cirque. In glacial valleys or trough valleys, it may be referred to as the trough head or trough end.Leser (2005), p. 978. In mountains with predominantly crystalline rock the heads of the valleys are generally very wet, sometimes boggy and often support lush alpine meadows, whilst those made of limestone are usually dry and covered in talus or gravel. Where there has been ice age glaciation, the valley bottoms are modified by moraines and mountain lakes are common. See also * Structural basin * U-shaped or trough valley * Landform * Valley step A valley step (german: Talstufe or ''Talschwelle'') i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemis
Hemis, also spelled Hamis, is a village in the Leh district of Ladakh, India. It is located in the Kharu tehsil, 40 km southeast of Leh town on the Leh-Manali Highway and under-construction Bilaspur–Leh line. Hemis is well known for the Hemis monastery that was established in 1672 AD by king Sengge Namgyal. The village hosts a colorful festival held in July. It is close to the Hemis National Park, an area that is home to the endangered snow leopard. The national park was created in 1981. Hemis Monastery Hemis Monastery already existed before the 11th century. Nāropā, the pupil of the yogi Tilopa, and teacher of the translator Marpa was connected with this monastery. A translation of Naropa's biography has been found in Hemis monastery. It has been translated by A. Grünwedel (Năro und Tilo, Festschrift Ernst Kuhn, München 1916). In 1887, Nicolas Notovitch wrote a book claiming to be the translation of a document held in Hemis Library that states Jesus had spent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spituk
Spituk or Pitok () is a census town located in the Leh district of Ladakh, India India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so .... References {{Leh district Cities and towns in Leh district ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganda La
Hemis National Park is a high-elevation national park in Ladakh, India. Globally famous for its snow leopards, it is believed to have the highest density of them in any protected area in the world. It is the only national park in India that is north of the Himalayas, the largest notified protected area in India (largest National park) and is the second largest contiguous protected area, after the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve and surrounding protected areas. The park is home to a number of species of endangered mammals, including the snow leopard. Hemis National Park is India's protected area inside the Palearctic realm, outside the Changthang Wildlife Sanctuary northeast of Hemis, and the proposed Tso Lhamo Cold Desert Conservation Area in North Sikkim. The park is bounded on the north by the banks of the Indus River, and includes the catchments of Markha, Sumdah and Rumbak, and parts of the Zanskar Range. History The park was founded in 1981 by protecting the Rumbak and Markh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |