|
Marie Françoise Bernard
Marie Françoise "Fanny" Bernard (née Martin) (16 September 1819 – 9 October 1901) was the wife of the pioneer in experimental research in physiology, Claude Bernard. She was shocked by his use of vivisection, and created an anti-vivisection society. Background Marie Françoise Martin married Claude Bernard on Wednesday 7 May 1845, and it was her dowry from her father, a physician, that allowed him to pursue his studies under François Magendie at the Collège de France in Paris. They had three children—Jeanne-Henriette, Marie-Claude, and a son who died in infancy. Marie Françoise became opposed to her husband's research methods. Magendie, Claude Bernard and his fellow physiologists—men such as Charles Richet in France and Michael Foster in England—were strongly criticized for the vivisection they carried out on animals, particularly dogs. Anti-vivisectionists infiltrated Magendie's lectures in Paris, where he was dissecting dogs without anaesthetic, allegedly shoutin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vivisection
Vivisection () is surgery conducted for experimental purposes on a living organism, typically animals with a central nervous system, to view living internal structure. The word is, more broadly, used as a pejorative catch-all term for experimentation on live animalsTansey, E.MReview of ''Vivisection in Historical Perspective by Nicholaas A. Rupke, book reviews, National Center for Biotechnology Information, p. 226. by organizations opposed to animal experimentation,Yarri, Donna''The Ethics of Animal Experimentation: A Critical Analysis and Constructive Christian Proposal, Oxford University Press, 2005, p. 163. but the term is rarely used by practising scientists. Human vivisection, such as live organ harvesting, has been perpetrated as a form of torture. Animal vivisection Research requiring vivisection techniques that cannot be met through other means is often subject to an external ethics review in conception and implementation, and in many jurisdictions use of anesthesia is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
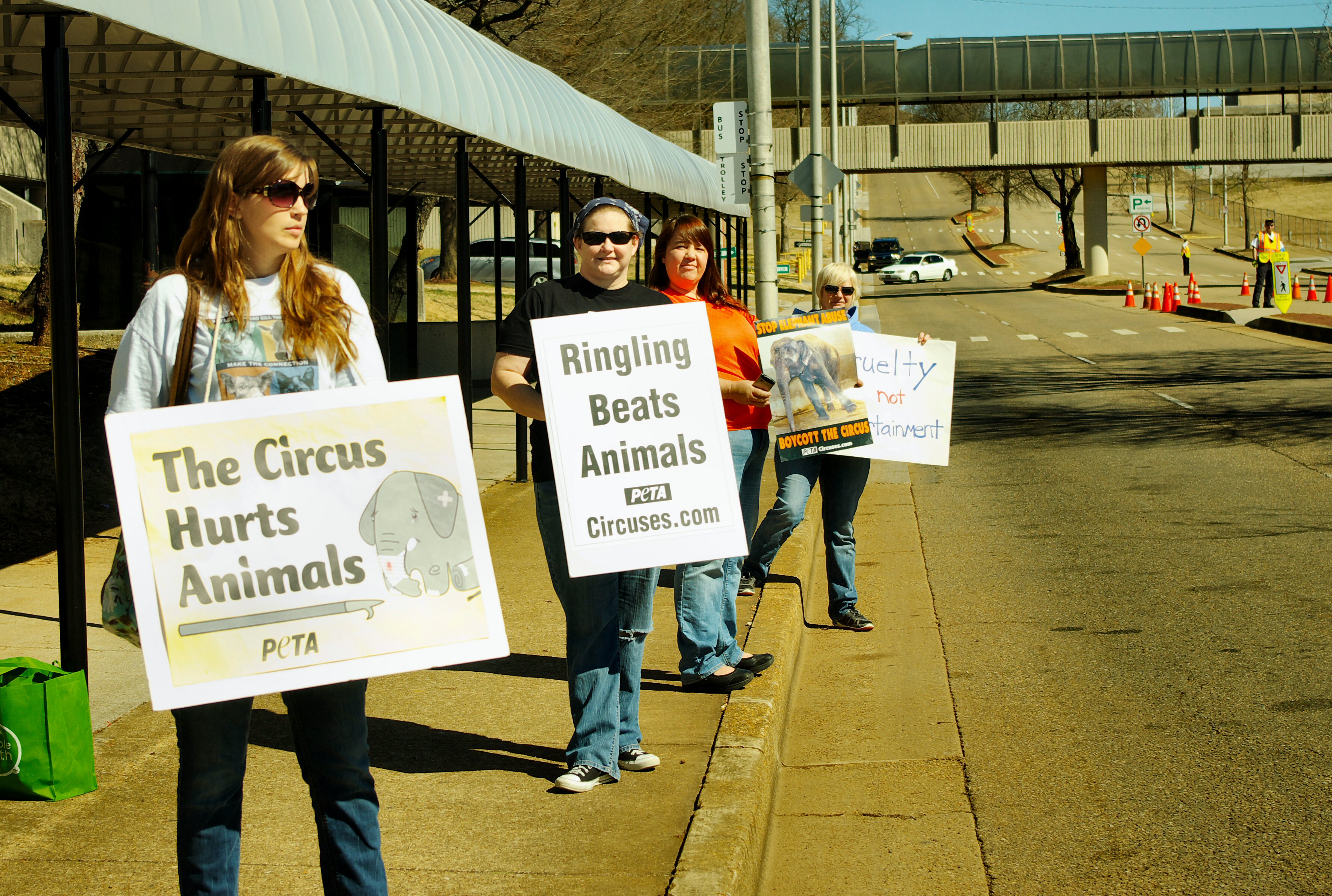
Brown Dog Affair
The Brown Dog affair was a political controversy about vivisection that raged in Britain from 1903 until 1910. It involved the infiltration of University of London medical lectures by Swedish feminists, battles between medical students and the police, police protection for the statue of a dog, a libel trial at the Royal Courts of Justice, and the establishment of a Royal Commission to investigate the use of animals in experiments. The affair became a that divided the country. The controversy was triggered by allegations that, in February 1903, William Bayliss of the Department of Physiology at University College London performed an illegal vivisection, before an audience of 60 medical students, on a brown terrier dog—adequately anaesthetized, according to Bayliss and his team; conscious and struggling, according to the Swedish activists. The procedure was condemned as cruel and unlawful by the National Anti-Vivisection Society. Outraged by the assault on his reputation, Bayl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Women Activists
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Welfare Workers
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Activists
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Testing
Animal testing, also known as animal experimentation, animal research, and ''in vivo'' testing, is the use of non-human animals in experiments that seek to control the variables that affect the behavior or biological system under study. This approach can be contrasted with field studies in which animals are observed in their natural environments or habitats. Experimental research with animals is usually conducted in universities, medical schools, pharmaceutical companies, defense establishments, and commercial facilities that provide animal-testing services to the industry. The focus of animal testing varies on a continuum from pure research, focusing on developing fundamental knowledge of an organism, to applied research, which may focus on answering some questions of great practical importance, such as finding a cure for a disease. Examples of applied research include testing disease treatments, breeding, defense research, and toxicology, including cosmetics testing. In edu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caroline Earle White
Caroline White ( Earle; 1833–1916) was an American philanthropist and anti-vivisection activist. She co-founded the Pennsylvania Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (PSPCA) in 1867, founded its women's branch (WPSPCA) in 1869, and founded the American Anti-Vivisection Society (AAVS) in 1883. White was also an active clubwoman, and was involved in literary societies and women's suffrage, and worked with organizations that helped the poor obtain medical services.Buettinger, Craig"Women and antivivisection in late nineteenth century America" ''Journal of Social History'', Vol. 30, No. 4 (Summer, 1997), pp. 857-872. Background Early life and education Caroline Earle was born in Philadelphia on September 28, 1833, to Quaker parents Thomas Earle (American politician), Thomas Earle and Mary Hussey. Thomas Earle was a successful Philadelphia lawyer who was devoted to the Abolitionism in the United States, abolitionist cause and often represented both free and fugitive Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Kingsford
Anna Kingsford (; 16 September 1846 – 22 February 1888), was an English anti-vivisectionist, vegetarian and women's rights campaigner. She was one of the first English women to obtain a degree in medicine, after Elizabeth Garrett Anderson, and the only medical student at the time to graduate without having experimented on a single animal. She pursued her degree in Paris, graduating in 1880 after six years of study, so that she could continue her animal advocacy from a position of authority. Her final thesis, ''L'Alimentation Végétale de l'Homme'', was on the benefits of vegetarianism, published in English as ''The Perfect Way in Diet'' (1881). She founded the Food Reform Society that year, travelling within the UK to talk about vegetarianism, and to Paris, Geneva, and Lausanne to speak out against animal experimentation. Kingsford was interested in Buddhism and Gnosticism, and became active in the Theosophical movement in England, becoming president of the London Lodge of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frances Power Cobbe
Frances Power Cobbe (4 December 1822 – 5 April 1904) was an Anglo-Irish writer, philosopher, religious thinker, social reformer, anti-vivisection activist and leading women's suffrage campaigner. She founded a number of animal advocacy groups, including the National Anti-Vivisection Society (NAVS) in 1875 and the British Union for the Abolition of Vivisection (BUAV) in 1898, and was a member of the executive council of the London National Society for Women's Suffrage. She was the author of a large number of books and essays, including ''An Essay on Intuitive Morals'' (1855), ''The Pursuits of Women'' (1863), ''Cities of the Past'' (1864), ''Essays New and Old on Ethical and Social Subjects'' (1865), ''Darwinism in Morals, and other Essays'' (1872), ''The Hopes of the Human Race'' (1874), ''The Duties of Women'' (1881), ''The Peak in Darien, with some other Inquiries touching concerns of the Soul and the Body'' (1882), ''The Scientific Spirit of the Age'' (1888) and ''The Mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Rights Movement
The animal rights (AR) movement, sometimes called the animal liberation, animal personhood, or animal advocacy movement, is a social movement that seeks an end to the rigid moral and legal distinction drawn between human and non-human animals, an end to the status of animals as property, and an end to their use in the research, food, clothing, and entertainment industries. Terms and factions All animal liberationists believe that the individual interests of non-human animals deserve recognition and protection, but the movement can be split into two broad camps. Animal rights advocates believe that these basic interests confer moral rights of some kind on the animals, and/or ought to confer legal rights on them;"Animal rights," ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 2007. see, for example, the work of Tom Regan. Utilitarian liberationists, on the other hand, do not believe that animals possess moral rights, but argue, on utilitarian grounds — utilitarianism in its simplest form advoca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Bernard
Claude Bernard (; 12 July 1813 – 10 February 1878) was a French physiologist. Historian I. Bernard Cohen of Harvard University called Bernard "one of the greatest of all men of science". He originated the term ''milieu intérieur'', and the associated concept of homeostasis (the latter term being coined by Walter Cannon). Life and career Bernard was born in 1813 in the village of Saint-Julien near Villefranche-sur-Saône. He received his early education in the Jesuit school of that town, and then proceeded to the college at Lyon, which, however, he soon left to become assistant in a druggist's shop. He is sometimes described as an agnostic and even humorously referred to by his colleagues as a "great priest of atheism". Despite this, after his death Cardinal Ferdinand Donnet claimed Bernard was a fervent Catholic, with a biographical entry in the ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. His leisure hours were devoted to the composition of a vaudeville comedy, and the success it achieved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




