|
Marcus Octavius (aedile 50 BC)
Marcus Octavius ( 53 – 46 BC) was a Roman senator and military commander. He fought for Pompey in the civil war against Julius Caesar. Life Marcus Octavius was son of Gnaeus Octavius, consul in 76 BC. In 53 BC, he accompanied his friend, Appius Claudius Pulcher, governor of Cilicia, to his province, but returned to Rome early in order to run for the office of curule aedile. Elected for the year 50 BC, he and his colleague, Marcus Caelius, asked Cicero, another governor of Cilicia, to send them panthers, to be displayed in the games the aediles had to hold at Rome. During Caesar's civil war, Octavius sided with Pompey against Julius Caesar. At the end of 49 BC, he and Lucius Scribonius Libo were given joint charge of the Liburnian and Achaian squadrons of Pompey's fleet in the Adriatic and Ionian seas. Octavius and Libo defeated Caesar's fleet under Publius Cornelius Dolabella on the Dalmatian coast, and managed to trap fifteen Caesarian cohorts under Gaius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senator
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC). It survived the overthrow of the Roman monarchy in 509 BC; the fall of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC; the division of the Roman Empire in AD 395; and the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476; Justinian's attempted reconquest of the west in the 6th century, and lasted well into the Eastern Roman Empire's history. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, most of the time the Senate was little more than an advisory council to the king, but it also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive magistrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, stretching from the island of Rab in the north to the Bay of Kotor in the south. The Dalmatian Hinterland ranges in width from fifty kilometres in the north, to just a few kilometres in the south; it is mostly covered by the rugged Dinaric Alps. List of islands of Croatia, Seventy-nine islands (and about 500 islets) run parallel to the coast, the largest (in Dalmatia) being Brač, Pag (island), Pag, and Hvar. The largest city is Split, Croatia, Split, followed by Zadar and Šibenik. The name of the region stems from an Illyrians, Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae, who lived in the area in classical antiquity. Later it became a Dalmatia (Roman province), Roman province, and as result a Romance languages, Romance culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa (Roman Province)
Africa Proconsularis was a Roman province on the northern African coast that was established in 146 BC following the defeat of Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisia, the northeast of Algeria, and the coast of western Libya along the Gulf of Sirte. The territory was originally inhabited by Berber people, known in Latin as ''Mauri'' indigenous to all of North Africa west of Egypt; in the 9th century BC, Phoenicians built settlements along the Mediterranean Sea to facilitate shipping, of which Carthage rose to dominance in the 8th century BC until its conquest by the Roman Republic. It was one of the wealthiest provinces in the western part of the Roman Empire, second only to Italy. Apart from the city of Carthage, other large settlements in the province were Hadrumetum (modern Sousse, Tunisia), capital of Byzacena, and Hippo Regius (modern Annaba, Algeria). History Rome's first province in northern Africa was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicilia (Roman Province)
Sicilia (; , Ancient Greek: Σικελία) was the first province acquired by the Roman Republic, encompassing the island of Sicily. The western part of the island was brought under Roman control in 241 BC at the conclusion of the First Punic War with Carthage. A praetor was regularly assigned to the island from c.227 BC. The Kingdom of Syracuse under Hieron II remained an independent ally of Rome until its defeat in 212 BC during the Second Punic War. Thereafter the province included the whole of the island of Sicily, the island of Malta, and the smaller island groups (the Egadi islands, the Lipari islands, Ustica, and Pantelleria). During the Roman Republic, the island was the main source of grain for the city of Rome. Extraction was heavy, provoking armed uprisings known as the First and Second Servile Wars in the second century BC. In the first century, the Roman governor, Verres, was famously prosecuted for his corruption by Cicero. In the civil wars which brought the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corcyra
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The island is part of the Corfu regional unit, and is administered by three municipalities with the islands of Othonoi, Ereikoussa, and Mathraki.https://corfutvnews.gr/diaspasi-deite-tin-tropologia/ The principal city of the island (pop. 32,095) is also named Corfu. Corfu is home to the Ionian University. The island is bound up with the history of Greece from the beginnings of Greek mythology, and is marked by numerous battles and conquests. Ancient Korkyra took part in the Battle of Sybota which was a catalyst for the Peloponnesian War, and, according to Thucydides, the largest naval battle between Greek city states until that time. Thucydides also reports that Korkyra was one of the three great naval powers of fifth century BC Greece, along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidaurum
Epidaurus ( el, Ἐπίδαυρος, la, Epidaurum) or Epidauros was an ancient Greek colony founded sometime in the 6th century BC, renamed to Epidaurum during Roman rule in 228 BC, when it was part of the province of Illyricum (Roman province), Illyricum, later Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia.Wilkes, J. J. The Illyrians, 1992, , page 216, "... hand, the Deraemestae (30) were formed from several smaller groups in the vicinity of the new Roman colony established at Epidaurum (Cavtat near Dubrovnik). ..." It is located at the modern-day Cavtat in Croatia, 15 km (9 mi) south of Dubrovnik. During the civil war between Julius Caesar and Pompey the city was besieged by M. Octavius but saved by the arrival of the consul Publius Vatinius. The city was destroyed by Avars (Carpathians), Avars and Slavic peoples, Slavic invaders in the 7th century. Refugees from Epidaurus fled to the nearby island Laas or Laus (meaning "stone" in Greek), from which ''Ragusa'' (through rhotaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Vatinius
Publius Vatinius was a Roman politician during the last decades of the Republic. He served as a Caesarian-allied plebeian tribune in the year 59 – he was the tribune that proposed the law giving Caesar his Gallic command – and later fought on that side of the civil war. Caesar made him consul in 47 BC; he later fought in Illyricum for the Caesarians and celebrated a triumph for his victories there in 42 BC. Biography Many details about Vatinius' life emerge from Cicero's claims, which "must be taken with a grain of salt and understood as a piece of rhetorical invective, in which an orator would do anything to discredit his opponent, including the use of half-truths and exaggerations". Early political life Vatinius did not appear to have had consular ancestors, making him a ''novus homo''. His first recorded position was a quaestorship in 63 BC, the same year Marcus Tullius Cicero was consul. He was elected last to the quaestorship. Cicero claims he was allotte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulus Gabinius
Aulus Gabinius (by 101 BC – 48 or 47 BC) was a Roman statesman and general. He was an avid supporter of Pompey who likewise supported Gabinius. He was a prominent figure in the latter days of the Roman Republic. Career In 67 BC, when tribune of the plebs, Gabinius brought forward the law (''Lex Gabinia'') which gave Pompey the command in the war against the Pirates of the Mediterranean, with extensive powers that gave him absolute control over the sea and the coasts for 50 miles inland. Through Gabinius' two other measures, loans of money to foreign ambassadors in Rome were made actionable (as a check on the corruption of the Senate) and the Senate was ordered to give audiences to foreign envoys on certain fixed days (February 1-March 1) each year. During the Third Mithridatic War Gabinius served Pompey as a legate. In 65 BC he marched with two legions into Northern Mesopotamia to pressure the Parthian king, Phraates III into a treaty with Pompey. In 61 BC, Gabinius, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
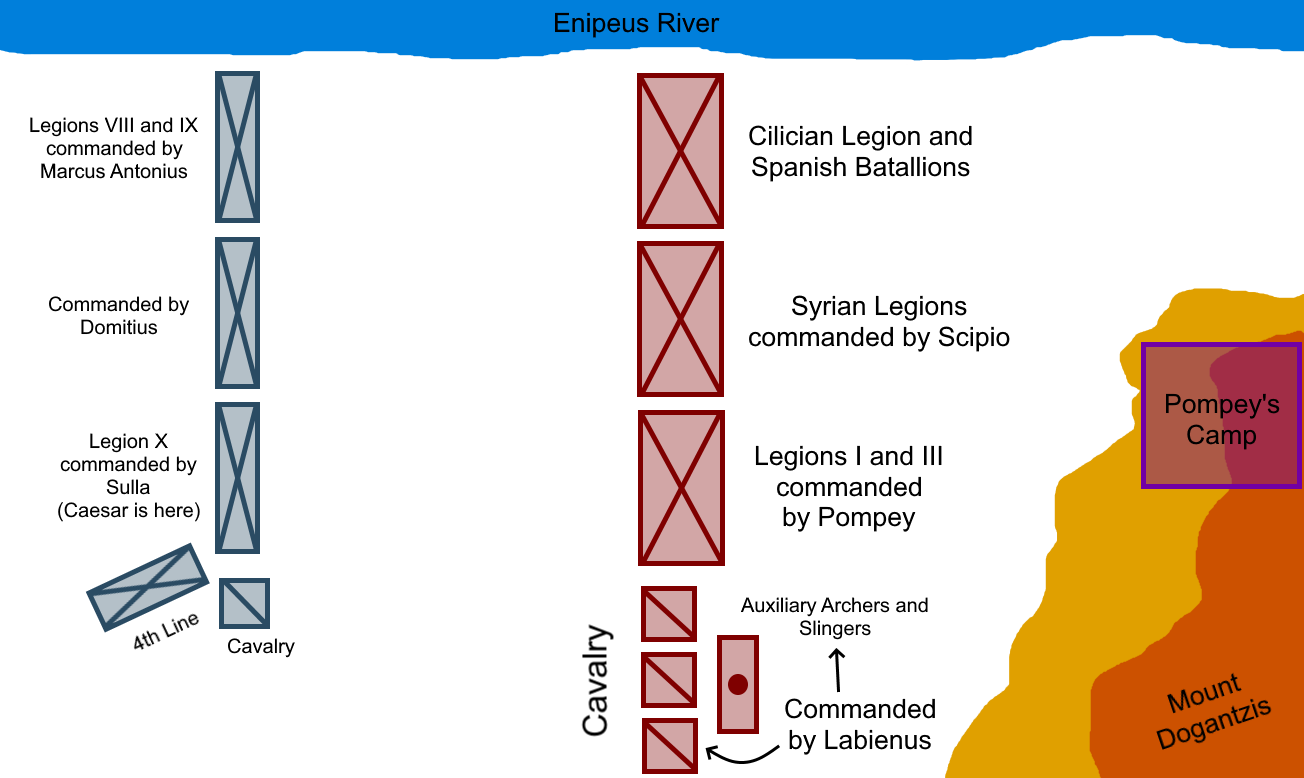
Battle Of Pharsalus
The Battle of Pharsalus was the decisive battle of Caesar's Civil War fought on 9 August 48 BC near Pharsalus in central Greece. Julius Caesar and his allies formed up opposite the army of the Roman Republic under the command of Pompey. Pompey had the backing of a majority of Roman senators and his army significantly outnumbered the veteran Caesarian legions. Pressured by his officers, Pompey reluctantly engaged in battle and suffered an overwhelming defeat, ultimately fleeing the camp and his men, disguised as an ordinary citizen. Eventually making his way to Egypt, he was assassinated upon his arrival at the order of Ptolemy XIII. Prelude Following the start of the Civil War, Caesar had captured Rome, forced Pompey and his allies to withdraw from Italy, and defeated Pompey's legates in Spain. In the campaign season for 48 BC, Caesar crossed the Adriatic and advanced on Dyrrachium. There, he besieged it, but was defeated. Caesar then withdrew east into Thessaly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Salona
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. The art of conducting and resisting sieges is called siege warfare, siegecraft, or poliorcetics. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block the provision of supplies and the reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as " investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, artillery bombardment, mining (also known as sapping), or the us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salona
Salona ( grc, Σάλωνα) was an ancient city and the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia. Salona is located in the modern town of Solin, next to Split, in Croatia. Salona was founded in the 3rd century BC and was mostly destroyed in the invasions of the Avars and Slavs in the seventh century AD. Many Roman characteristics can be seen such as walls; a forum; a theatre; an amphitheatre, public baths and an aqueduct. History Salona grew in the area of the Greek cities of Tragurian and Epetian on the river Jadro in the 3rd century BC. Salona is the largest archaeological park in Croatia and grew to over 60,000 inhabitants. It was the birthplace of Emperor Diocletian. In the first millennium BC the Greeks set up a marketplace.Salona had also been in the territory of the Illyrian Delmatae, before the conquest of the Romans. Salona became the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia because it sided with the future Roman Dictator Gaius Julius Caesar in the civil war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |