|
Mangaia Swiftlet
The Mangaia swiftlet (''Aerodramus manuoi'') is an extinct species of bird in the swift family. It became extinct during prehistoric times. It was endemic to Mangaia in the Cook Islands. It was closely allied with the extant Atiu swiftlet (''Aerodramus sawtelli'') of Atiu, Mangaia's neighbouring island, though it was probably slightly larger.Steadman (2002). It was described from six fossil bones recovered from a Holocene rock shelter deposit on Mangaia. The coracoid and carpometacarpus The carpometacarpus is a bone found in the hands of birds. It results from the fusion of the carpal and metacarpal bone, and is essentially a single fused bone between the wrist and the knuckles. It is a smallish bone in most birds, generally flat ... of the new species are larger and very different qualitatively from those of the Atiu species. This is the first species of ''Aerodramus'' to be described from fossils. References Notes Sources * Mangaia swiftlet Birds of Mangaia Extin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Shelter
A rock shelter (also rockhouse, crepuscular cave, bluff shelter, or abri) is a shallow cave-like opening at the base of a bluff or cliff. In contrast to solutional caves (karst), which are often many miles long, rock shelters are almost always modest in size and extent. Formation Rock shelters form because a rock stratum such as sandstone that is resistant to erosion and weathering has formed a cliff or bluff, but a softer stratum, more subject to erosion and weathering, lies just below the resistant stratum, and thus undercuts the cliff. In arid areas, wind erosion (Aeolian erosion) can be an important factor in rockhouse formation. In most humid areas, the most important factor in rockhouse formation is frost spalling, where the softer, more porous rock underneath is pushed off, tiny pieces at a time, by frost expansion from water frozen in the pores. Erosion from moving water is seldom a significant factor. Many rock shelters are found under waterfalls. File:Rock shelt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Extinctions Since 1500
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Bird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Birds Of Oceania
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of Mangaia
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Birds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodramus
''Aerodramus'' is a genus of small, dark, cave-nesting birds in the Collocaliini tribe of the swift family. Its members are confined to tropical and subtropical regions in southern Asia, Oceania and northeastern Australia. Many of its members were formerly classified in ''Collocalia'', but were first placed in a separate genus by American ornithologist Harry Church Oberholser in 1906. This is a taxonomically difficult group of very similar species. Echolocation, DNA sequencing and parasitic lice have all been used to establish relationships, but some problems, such as the placement of the Papuan swiftlet are not fully resolved. These swiftlets can pose major identification problems where several species occur. What distinguishes ''Aerodramus'' swiftlets from other swifts, and indeed almost all other birds, is their ability to use a simple but effective form of echolocation. This enables them to navigate within the breeding and roosting caves. The nests of ''Aerodramus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
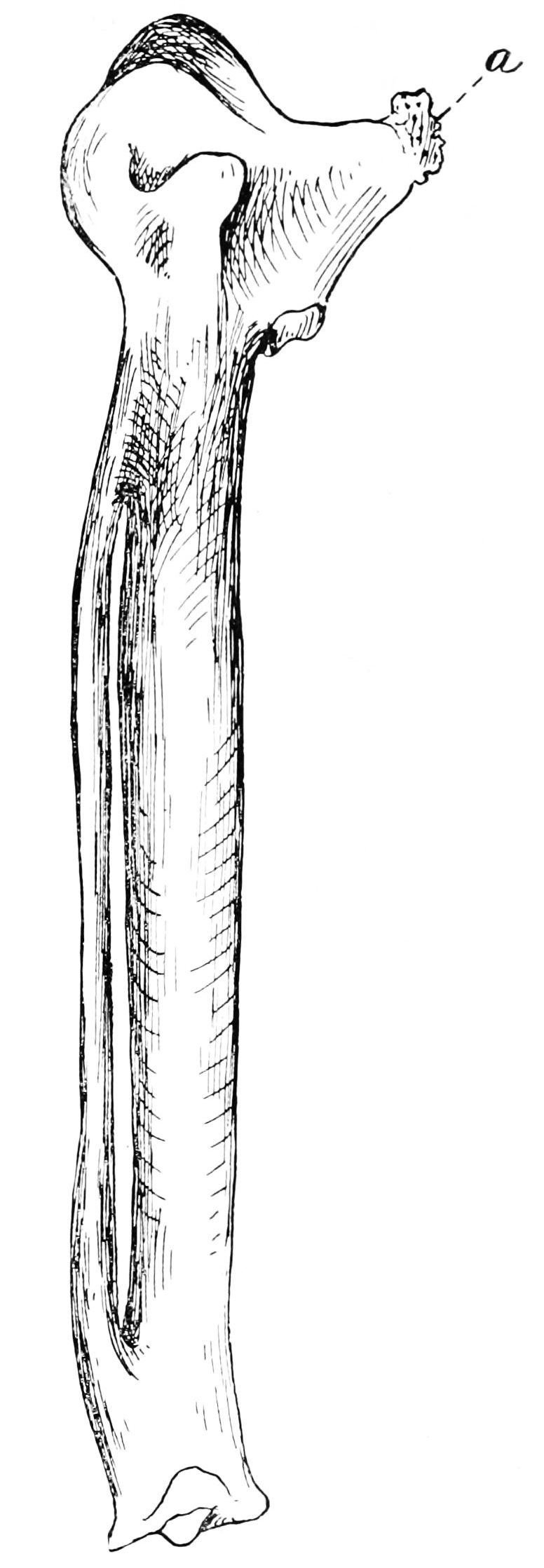
Carpometacarpus
The carpometacarpus is a bone found in the hands of birds. It results from the fusion of the carpal and metacarpal bone, and is essentially a single fused bone between the wrist and the knuckles. It is a smallish bone in most birds, generally flattened and with a large hole in the middle. In flightless birds, however, its shape may be slightly different, or it might be absent entirely. It forms the tip of the wing skeleton in birds. To it, most of the primary remiges attach. The alula, by contrast, is formed by the thumb, which does not completely fuse with the other hand-bones. Likewise, the tipmost primaries attach to the phalanx bones. To non-biologists the carpometacarpus may be best known from buffalo wings. Buffalo wings come in two basic sizes, a large angled one containing three major bones, and a smaller flat one containing only two. The bone missing in the latter is the carpometacarpus. See also * Carpometacarpal joint The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoid
A coracoid (from Greek κόραξ, ''koraks'', raven) is a paired bone which is part of the shoulder assembly in all vertebrates except therian mammals (marsupials and placentals). In therian mammals (including humans), a coracoid process is present as part of the scapula, but this is not homologous with the coracoid bone of most other vertebrates. In other tetrapods it joins the scapula to the front end of the sternum and has a notch on the dorsal surface which, along with a similar notch on the ventral surface of the scapula, forms the socket in which the proximal end of the humerus (upper arm bone) is located. The acrocoracoid process is an expansion adjacent to this contact surface, to which the shoulderward end of the biceps brachii muscle attaches in these animals. In birds (and generally theropods and related animals), the entire unit is rigid and called scapulocoracoid. This plays a major role in bird flight. In dinosaurs the main bones of the pectoral girdle were the sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Steadman
David William Steadman is a paleontologist and ornithologist, and serves as the curator of ornithology at the Florida Museum of Natural History at the University of Florida. His research has concentrated on the evolution, biogeography, conservation, and extinction of tropical birds, particularly in the islands of the Pacific Ocean. He has also authored over 180 scientific publications. He has conducted a number of digs at prehistoric sites and uncovered widescale extinctions caused by humans in the early stages of colonisation. He has conducted several expeditions to the Galápagos Islands, and has described a number of extinct species of birds and more recently was involved in discovering that the Solomon Islands frogmouth is a species (instead of a subspecies of the marbled frogmouth The marbled frogmouth (''Podargus ocellatus'') is a bird in the family Podargidae. The species was first described by Jean René Constant Quoy and Joseph Paul Gaimard in 1830. It is found in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atiu
Atiu, also known as Enuamanu (meaning ''land of the birds''), is an island of the Cook Islands archipelago, lying in the central-southern Pacific Ocean. Part of the Nga-pu-Toru, it is northeast of Rarotonga. The island's population has dropped by two-thirds in the last 50 years. Geography Atiu is a raised volcanic island surrounded by a reef from which rise cliffs of fossilized coral (''makatea''). The makatea cliff forms a ring round the island, creating a virtual plateau. Erosion of the inside of the ring has formed a dip of about into fertile land, which gradually rises again to a central flat-topped hill. The low swampy land consists of taro plantations, marshes and a lake, Tiroto. This fertile area also grows bananas, citrus fruits, pawpaws, breadfruit and coconuts. The island is surrounded by a fringing reef. The ''makatea'' is honeycombed with caves, some of which have been used for burials. History Polynesians are believed to have lived on Atiu since at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atiu Swiftlet
The Atiu swiftlet or Sawtell's Swiftlet (''Aerodramus sawtelli'') is a species of bird in the swift family, endemic to Atiu in the Cook Islands. This small, dark swift measures long. It is sooty-brown above, slightly lighter below. Its natural habitat In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...s are the island's fernlands and mixed horticultural areas over which it feeds, and in makatea limestone caves within which it nests. The species is known on Atiu as kopeka. References External links * * * * Atiu swiftlet Birds of the Cook Islands Atiu swiftlet Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{apodiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)