|
Mam (Maya Mythology)
Mam 'grandfather' or 'grandson', is a pan-Mayan kinship term as well as a term of respect referring to ancestors and deities. In Classic period inscriptions, the word ''mam'' appears to be used mainly to introduce the name of a grandfather, grandson, or ancestor, often a king. Ethnographically, ''Mam'' refers to several aged Maya deities: *(i) In Kekchi-speaking Belize, 'Mam' is a general designation for the mountain spirits; four Mams were specifically associated with the four corners of the earth (see Bacab).Thompson, Maya History and Religion 1970. * (ii) In the Kekchi-speaking Alta Verapaz of Guatemala, one of the Mams is a greatly feared mountain spirit associated with earthquakes and inundations. An image of this Mam was apparently buried during the Holy Week. *(iii) Among the Huaxtec Mayas (Huastec people), the Mams or Mamlabs are earth deities; there are three or four of them, the most important one (Muxiʼ) being the violent originator of the rainy season. *(iv) Among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacab
Bacab () is the generic Yucatec Maya name for the four prehispanic aged deities of the interior of the earth and its water deposits. The Bacabs have more recent counterparts in the lecherous, drunken old thunder deities of the Gulf Coast regions. The Bacabs are also referred to as ''Pauahtuns''. Yucatec traditions Myth The Bacabs "were four brothers whom God placed, when he created the world, at the four points of it, holding up the sky so that it should not fall. ..They escaped when the world was destroyed by the deluge." Their names were Hobnil, Cantzicnal, Saccimi, and Hosanek. The Bacabs played an important role in the cosmological upheaval associated with Katun 11 Ahau, when Oxlahuntiku 'Thirteen-god' was humbled by Bolontiku 'Nine-god'. According to the Book of Chilam Balam of Chumayel, "then the sky would fall, it would fall down, it would fall down upon the earth, when the four gods, the four Bacabs, were set up, who brought about the destruction of the world." Accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huastec People
The Huastec or Téenek (contraction of ''Te' Inik'', "people from here"; also known as Huaxtec, Wastek or Huastecos) are an indigenous people of Mexico, living in the La Huasteca region including the states of Hidalgo, Veracruz, San Luis Potosí and Tamaulipas concentrated along the route of the Pánuco River and along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico. There are approximately 66,000 Huastec speakers today, of which two-thirds are in San Luis Potosí and one-third in Veracruz, although their population was probably much higher, as much as half a million, when the Spanish arrived in 1529. The ancient Huastec civilization is one of the pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures. Judging from archaeological remains, they are thought to date back to approximately the 10th century BCE, although their most productive period of civilization is usually considered to be the Postclassic era between the fall of Teotihuacan and the rise of the Aztec Empire. The Pre-Columbian Huastecs constructed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximón
Maximón (), also called San Simón, is a Mayan deity and folk saint represented in various forms by the Maya peoples of several towns in the Guatemalan Highlands. Oral tradition of his creation and purpose in these communities is complex, diverse, and born of the ancient Maya traditions centuries ago. Origin The worship of Maximón is believed to have begun at the time of the Spanish conquest of the Maya. The designation of Maximón as a saint is the result of religious syncretism. The modern character of Maximón is thought by analysts to be a blend of several historical, biblical, and Mayan mythological figures. These include Pedro de Alvarado, Judas Iscariot, Saint Peter, and Mam. Maximón's appearance varies greatly by location. While he's popularly depicted as a man in a suit and hat, this isn't a constant. In Santiago Atitlán, he wears colorful garlands and scarves, while in Zunil, he wears sunglasses and a bandana. Mythology Maximón is said to represent both light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itzamna
Itzamna () is, in Maya mythology, an upper god and creator deity thought to reside in the sky. Itzamna is one of the most important gods in the Classic and Postclassic Maya pantheon. Although little is known about him, scattered references are present in early-colonial Spanish reports (''relaciones'') and dictionaries. Twentieth-century Lacandon lore includes tales about a creator god (Nohochakyum or Hachakyum) who may be a late successor to him. In the pre-Spanish period, Itzamna was often depicted in books and in ceramic scenes derived from them. Before the names of the Maya deities were deciphered, Itzamna was known as "god D", and is still sometimes referred to as "god D" by archeologists. Name J. Eric S. Thompson originally interpreted the name Itzamna as "lizard house", ''itzam'' being a Yucatecan word for iguana and ''na'' meaning "house". However, Thompson's translation has gradually been abandoned. While there is no consensus on the exact meaning of the name Itzamna, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
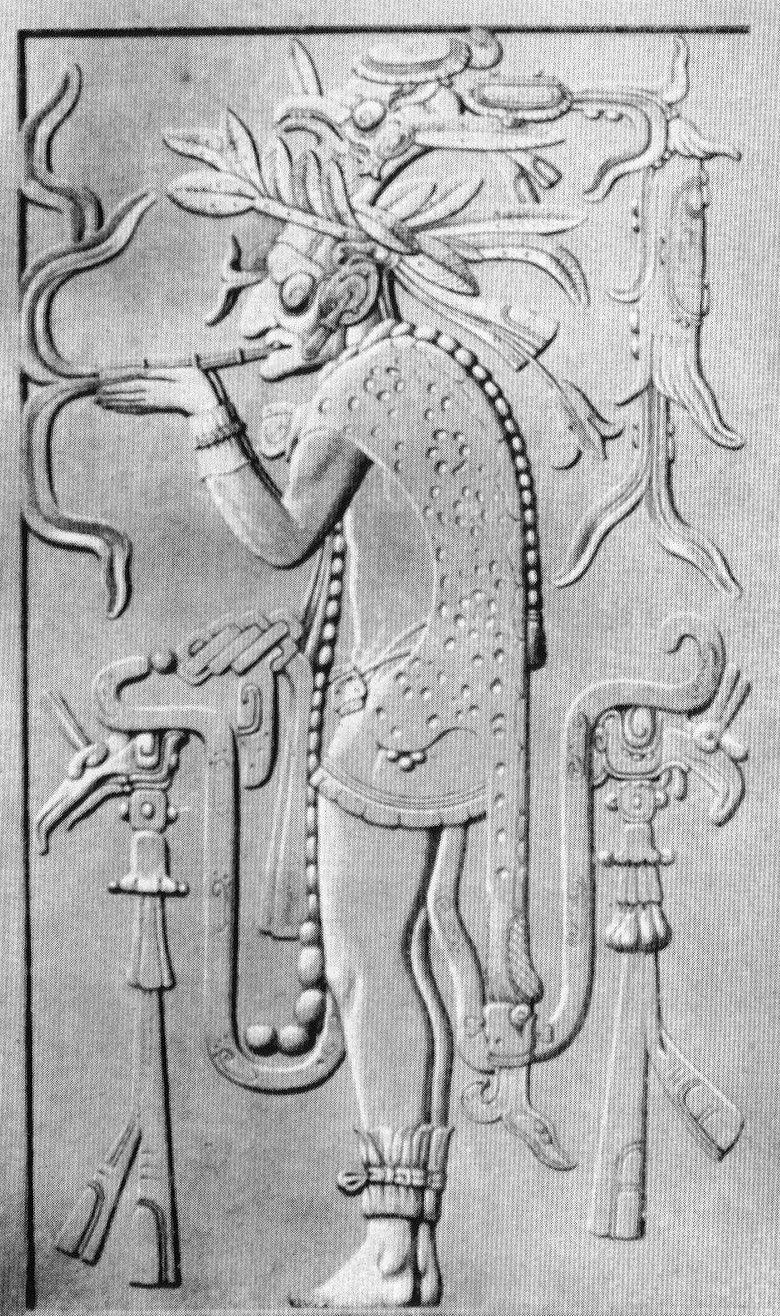
God L
God L of the Schellhas-Zimmermann-Taube classification of codical gods is one of the major pre-Spanish Maya deities, specifically associated with trade. Characterized by high age, he is one of the Mam ('Grandfather') deities. More specifically, he evinces jaguar traits (particularly the ear), a broad feathery hat topped by an owl, and a jaguar mantle or a cape with a pattern somewhat resembling that of an armadillo shell. The best-known monumental representation is on a doorjamb of the inner sanctuary of Palenque's Temple of the Cross. Name The main sign of god L's name glyph in the Dresden Codex consists of the head of an aged man painted black. The reading is unknown, but may conceivably have been Ekʼ Chuah (see below). Functions Attributes and scenes of god L are indicative of at least three main functions. Wealth Recurrent attributes are a bundle of merchandise and a walking-stick. The floating ends of god L's cloth can show footsteps, again pointing to travelling merchants. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huehueteotl
Huehueteotl ( ; ) is an aged Mesoamerican deity figuring in the pantheons of pre-Columbian cultures, particularly in Aztec mythology and others of the Central Mexico region. The spellings Huehuetéotl and Ueueteotl are also used. Although known mostly in the cultures of that region, images and iconography depicting Huehueteotl have been found at other archaeological sites across Mesoamerica, such as in the Gulf region, western Mexico, Protoclassic-era sites in the Guatemalan highlands such as Kaminaljuyú and Late-Postclassic sites on the northern Yucatán Peninsula (Miller and Taube, 1993:189). The name Huehueteotl stems from Nahuatl ''huēhueh'' ("old") and ''teōtl'' ("god"). It seems to connect the Old God to certain Mayan deities called '' Mam'' ("Grandfather"). Huehueteotl is frequently considered to overlap with, or be another aspect of, a central Mexican/Aztec deity associated with fire, Xiuhtecuhtli. In particular the Florentine Codex identifies Huehueteotl as an alte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Deities
This is a list of deities playing a role in the Classic (200–1000 CE), Post-Classic (1000–1539 CE) and Contact Period (1511–1697) of Maya religion. The names are mainly taken from the books of Chilam Balam, Lacandon ethnography, the Madrid Codex, the work of Diego de Landa, and the Popol Vuh. Depending on the source, most names are either Yucatec or Kʼicheʼ. The Classic Period names (belonging to the Classic Maya language) are only rarely known with certainty. Maya mythological beings List Source Key *CHB – Books of Chilam Balam *LAC – Lacandon ethnography *L – de Landa *M — Madrid Codex *PV – the Popol Vuh. A Acan The god of wine and intoxication, identified with the drink Balché. Acat A god of tattoos and tattooing. Alom The god of the sky and wood, a creator deity. Ah-Muzen-Cab God of bees and honey. Awilix The goddess of the moon, queen of the night. B Bacab The old god of the interior of the earth and of thunder, sky-carrier, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |