|
Malamir Knoll
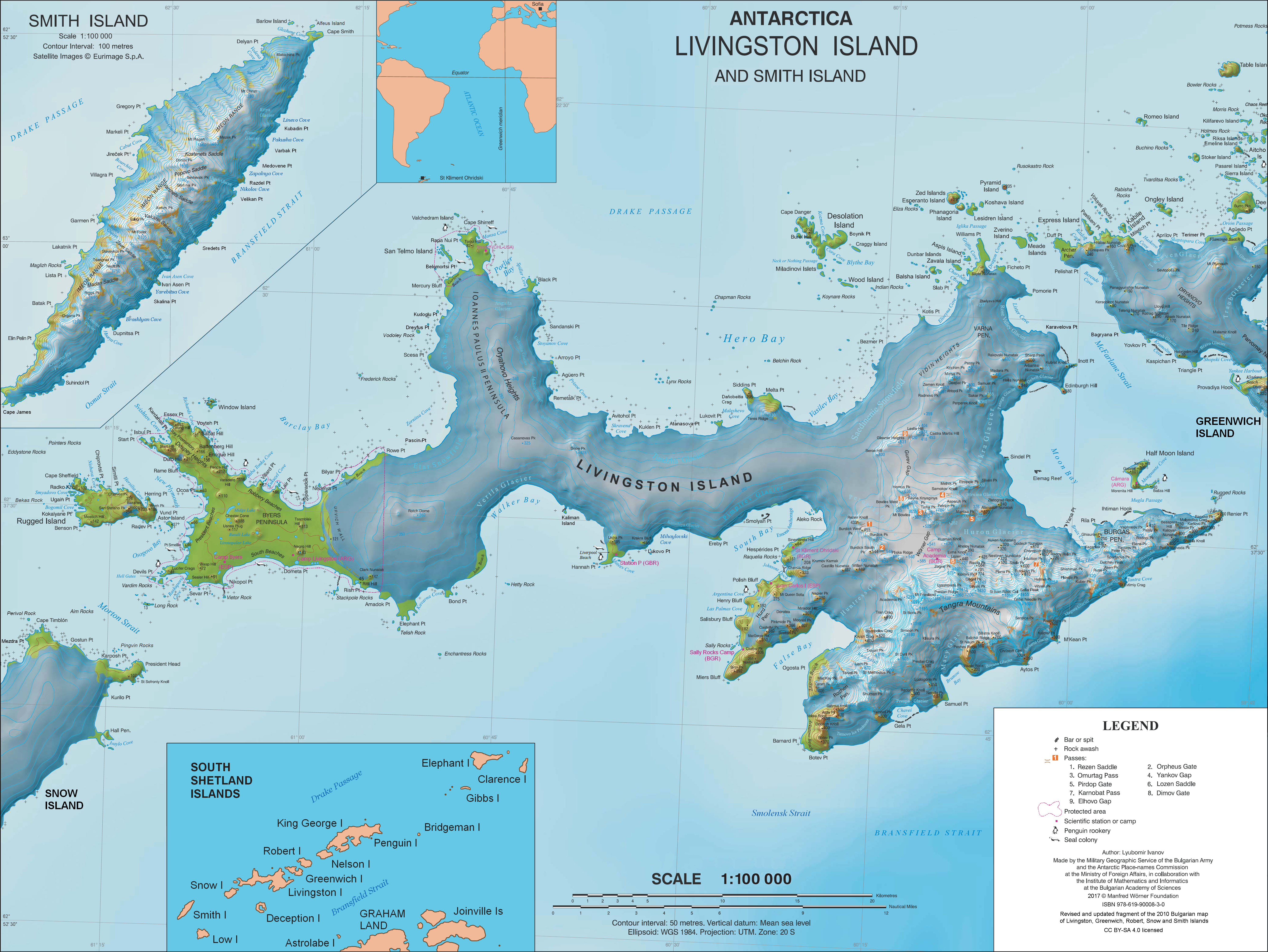
Malamir Knoll (Malamirova Mogila \ma-la-'mi-ro-va mo-'gi-la\) rises to 200 m in the southeast extremity of the Dryanovo Heights, Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It has precipitous and ice-free southwest slopes and was named after the Bulgarian ruler Khan Malamir, 831-836 AD. The knoll is located at , which is 2.37 km east of Tile Ridge, and 2.9 km northeast of Triangle Point, 2.65 km north-northwest of Spit Point and 3.78 km west by south of Labbé Point (Bulgarian topographic survey Tangra 2004/05 and mapping in 2005 and 2009). Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. References Malamir Knoll.SCAR Composite Antarcti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tile Ridge
Tile Ridge (''Rid Tile'' ) is a partly ice-free ridge of elevation 240 m in Dryanovo Heights, Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The ridge is named after the ancient Tile (Tylis), capital town of the Celtic Kingdom in Thrace, 279–213 BC, and ancestor of the present Bulgarian settlement of Tulovo near Stara Zagora City. Location The ridge is located at , which is 2.3 km east-southeast of Lloyd Hill, 2.55 km north of Triangle Point, and 2.37 km west of Malamir Knoll (Bulgarian topographic survey Tangra 2004/05 and mapping in 2009). See also * List of Bulgarian toponyms in Antarctica Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Antarctic Gazetteer
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - , G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangra 2004/05
The Tangra 2004/05 Expedition was commissioned by the Antarctic Place-names Commission at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria, managed by the Manfred Wörner Foundation, and supported by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute, the Institute of Mathematics and Informatics at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Bulgarian Posts, Uruguayan Antarctic Institute, Peregrine Shipping (Australia), and Petrol Ltd, TNT, Mtel, Bulstrad, Polytours, B. Bekyarov and B. Chernev (Bulgaria). Expedition team Dr. Lyubomir Ivanov (team leader), senior research associate, Institute of Mathematics and Informatics at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences; chairman, Antarctic Place-names Commission; author of the 1995 Bulgarian Antarctic ''Toponymic Guidelines'' introducing in particular the present official system for the Romanization of Bulgarian; participant in four Bulgarian Antarctic campaigns, and author of the first Bulgarian Antarctic topographic maps. Doychin Vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labbé Point
Labbé Point is a point projecting into the southwest part of Discovery Bay from Parvomay Neck, Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica with an adjacent ice-free area of .L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. The point forms the northwest side of the entrance to Basullo Cove and the east side of the entrance to ''Vinett Cove'' (). The small ''Basso Island'' () is linked by a mainly submerged spit to the north side of Labbé Point. The features were charted and named by the 1947 Chilean Antarctic Expedition after members of the expedition: Lieutenant Custodio Labbé, navigation officer of the transport ship ''Angamos''; Vinett, the boatswain of the expedition; and Juan Basso, chief storekeeper on the frigate ''Iquique''. Location The point is located at which is southwest of Ash Point, west by north of Ferrer Point, east-southeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spit Point (Greenwich Island)
Spit Point () is a narrow gravel spit forming the south side of the entrance to Yankee Harbor, Greenwich Island, in the South Shetland Islands, situated at the end of Provadiya Hook. The point was known to early sealers in the area and roughly charted on Powell's map of 1822. It was recharted by DI personnel on the ''Discovery II ''Discovery II'', built in 1971, is the second of three Discovery sternwheel riverboats operated by the Riverboat Discovery company. ''Discovery II'' is still in use as a tour vessel on the Chena and Tanana rivers near Fairbanks, Alaska. Hist ...'' in 1935 and given this descriptive name. Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Point
Triangle Point is the low ice-free tipped point forming the northwest side of the entrance to Shopski Cove in the south coast of Parvomay Neck linking the northwest and southeast parts of Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The area was frequented by early 19th century sealers operating from Yankee Harbour. The feature was charted and descriptively named by the Discovery Investigations in 1935. Location The point is located at which is 2.9 km west by north of Spit Point (the north extremity of Provadiya Hook and an entrance point to Yankee Harbour), 7.44 km northwest of Ephraim Bluff, 7.32 km north-northeast of Half Moon Island, 8.27 km east of Inott Point, Livingston Island and 1.4 km southeast of Kaspichan Point Kaspichan Point (Nos Kaspichan \'nos 'ka-spi-chan\) is a point on the southeast side of the entrance to Kramolin Cove on the southwest coast of Greenwich Island, Antarctica. Situated next west of Hebrizelm Hill, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malamir Of Bulgaria
Malamir ( bg, Маламир) was the ruler of Bulgaria in 831–836. Malamir was a son of Omurtag and a grandson of Krum. His name may be of Slavic origin, which would make him the first Bulgar khan to possess a Slavic name; this has led to the speculation that his mother was a Slav, although that cannot be proven. Another theory is that it was an Iranian name, as there is an Iranian city named Malamir. Malamir became ruler of Bulgaria in 831 on the death of his father Omurtag, because his older brother Enravota (Voin) had forfeited his right to the succession by becoming a Christian. It is possible that Malamir was young and inexperienced at the time of his accession, and that affairs of state were managed by his ''kavhan'' (''kaukhanos'') Isbul. About 833, Malamir executed his brother Enravota for refusing to renounce Christianity. After the expiration of the original 30-year peace treaty with the Byzantine Empire in 836, emperor Theophilos ravaged the regions inside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malamir , a knoll in Dryanovo Heights, Greenwich Island
{{Disambig ...
Malamir may refer to: * Malamir of Bulgaria, a Bulgarian ruler (Khan) * Malamir, Iran, a city in Khuzestan Province, Iran * Malamir Knoll Malamir Knoll (Malamirova Mogila \ma-la-'mi-ro-va mo-'gi-la\) rises to 200 m in the southeast extremity of the Dryanovo Heights, Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It has precipitous and ice-free southwest slopes and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led by Asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |