|
Malakasi
Malakasi ( el, Μαλακάσι) is a village and a former municipality in the Trikala regional unit, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Meteora, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 157.534 km2. Population 1,000 (2011). The seat of the municipality was in Panagia. Municipal unit The municipal unit of Malakasi includes the settlements of Korydallos, Malakasi, Panagia, Pefki and Trygona. Geography The village is part of the wider Zagori region, between Epirus and Thessaly. History The village takes its name from the Malakasii, an Albanian tribe or clan that moved to the area from central Albania in the 14th century. The name is of Vlach origin, and it means 'bad encampments'. It was named as such, probably because of the malaria which was the scourge of this area until the post-war period. Ottoman period During the Ottoman period, Epirus and Aetolia-Acarnania were divided into five '' armat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malakasioi
The Malakasi were a historical Albanian tribe in medieval Epirus, Thessaly and later southern Greece. Their name is a reference to their area of origin, Mallakastër in southern Albania. They appear in historical records as one of the Albanian tribes which raided and invaded Thessaly after 1318 and throughout the 14th century were active in the struggles of the Albanian Despotate of Arta against the Despotate of Epirus. Name The primary historical sources for the Malakasi are the ''History'' of John VI Kantakouzenos written in second half of the 14th century and the Chronicle of the Tocco written in the early 15th century. In the ''History'' and the chronicle, the tribe is recorded as ''Malakasaioi''. In Venetian registries of Albanian settlers in southern Greece, they are mentioned as ''Malacassi''. The name most probably refers to their region of origin in the plain of Mallakastër in southern Albania. It is of Aromanian (Vlach) etymology meaning ''bad encampments''. Several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia (, ), and appears thus in Homer's ''Odyssey''. Thessaly became part of the modern Greek state in 1881, after four and a half centuries of Ottoman rule. Since 1987 it has formed one of the country's 13 regions and is further (since the Kallikratis reform of 2011) sub-divided into five regional units and 25 municipalities. The capital of the region is Larissa. Thessaly lies in northern Greece and borders the regions of Macedonia on the north, Epirus on the west, Central Greece on the south, and the Aegean Sea on the east. The Thessaly region also includes the Sporades islands. Name and etymology Thessaly is named after the ''Thessaloi'', an ancient Greek tribe. The meaning of the name of this tribe is unknow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteora (municipality)
Meteora ( el, Μετέωρα, before 2018: ''Kalampaka'') is a municipality in the regional unit of Trikala in the Thessaly region in Greece. Its seat is the town Kalampaka. The municipality Meteora was formed as the municipality Kalampaka at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 8 former municipalities, that became municipal units: * Aspropotamos *Chasia *Kalabaka * Kastania *Kleino *Malakasi Malakasi ( el, Μαλακάσι) is a village and a former municipality in the Trikala regional unit, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Meteora, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal u ... * Tymfaia * Vasiliki In 2018 it was renamed to "Municipality of Meteora". The municipality has an area of 1,658.280 km2. References {{Meteora div Populated places in Trikala (regional unit) 2018 establishments in Greece Municipalities of Thessaly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trikala (regional Unit)
Trikala ( el, Περιφερειακή ενότητα Τρικάλων) is one of the regional units of Greece, forming the northwestern part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Thessaly. Its capital is the town of Trikala. The regional unit includes the town of Kalampaka and the Meteora monastery complex. Geography Trikala borders the regional units of Karditsa (regional unit), Karditsa to the south, Arta (regional unit), Arta to the southwest, Ioannina (regional unit), Ioannina to the west, Grevena (regional unit), Grevena to the north and Larissa (regional unit), Larissa to the east. The southeastern part belongs to the Thessalian Plain. The forested Pindus mountain range dominates the western part. The northern part of Trikala is also mountainous and made up of forests and barren lands, the ranges here are Chasia and Antichasia. Its major river is the Pineios (Thessaly), Pineios, flowing to the south and east. Its climate is mainly of Mediterranean character, with hot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
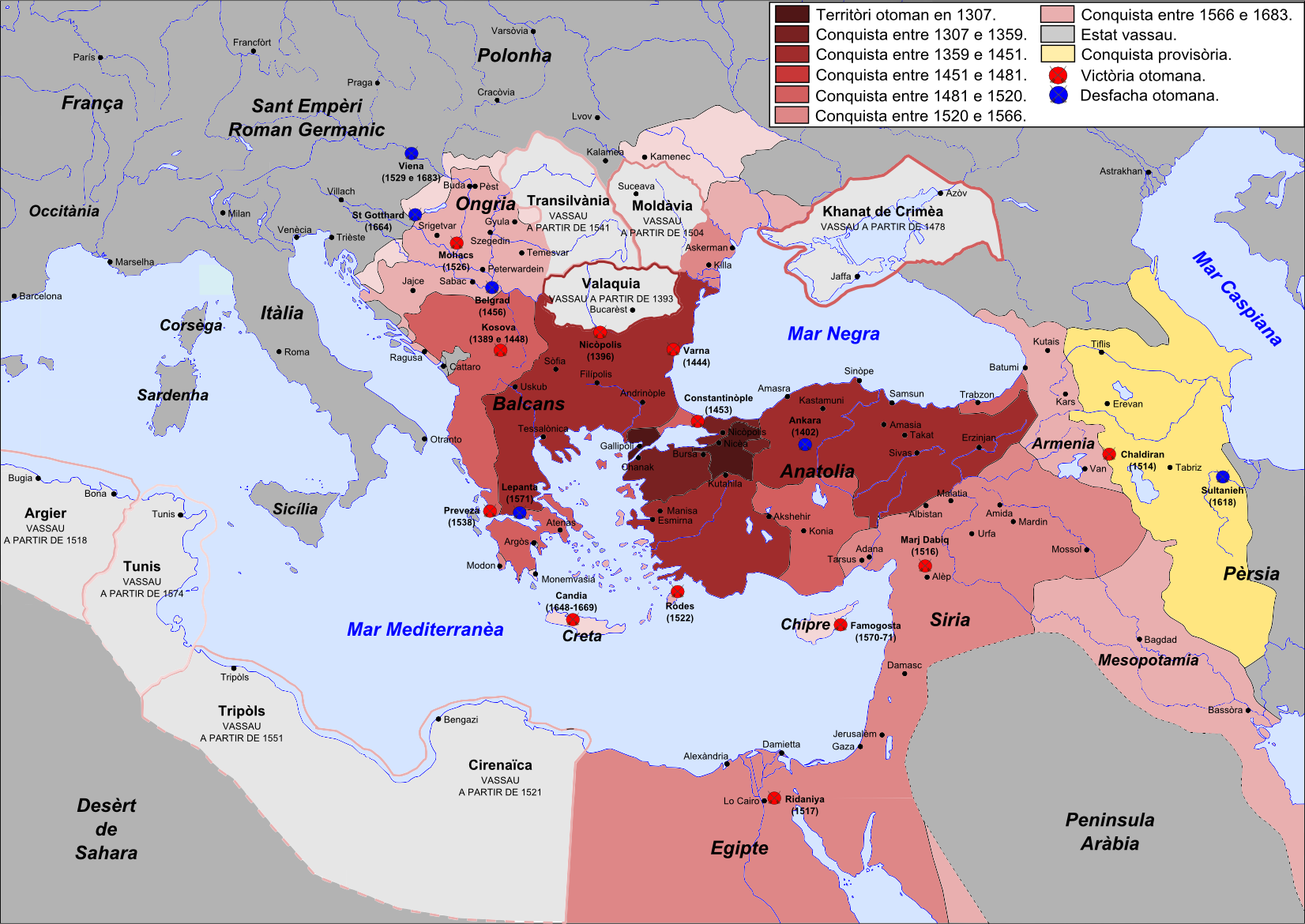
Ottoman Greece
Most of the areas which today are within modern Greece's borders were at some point in the past part of the Ottoman Empire. This period of Ottoman rule in Greece, lasting from the mid-15th century until the successful Greek War of Independence that broke out in 1821 and the proclamation of the First Hellenic Republic in 1822 (preceded by the creation of the autonomous Septinsular Republic in 1800), is known in Greek as ''Tourkokratia'' ( el, Τουρκοκρατία, "Turkish rule"; en, "Turkocracy"). Some regions, however, like the Ionian islands, various temporary Venetian possessions of the Stato da Mar, or Mani peninsula in Peloponnese did not become part of the Ottoman administration, although the latter was under Ottoman suzerainty. The Eastern Roman Empire, the remnant of the ancient Roman Empire which ruled most of the Greek-speaking world for over 1100 years, had been fatally weakened since the sacking of Constantinople by the Latin Crusaders in 1204. The Ottoman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaza
A kaza (, , , plural: , , ; ota, قضا, script=Arab, (; meaning 'borough') * bg, околия (; meaning 'district'); also Кааза * el, υποδιοίκησις () or (, which means 'borough' or 'municipality'); also () * lad, kaza , group=note) is an administrative division historically used in the Ottoman Empire and is currently used in several of its successor states. The term is from Ottoman Turkish and means 'jurisdiction'; it is often translated 'district', 'sub-district' (though this also applies to a ), or 'juridical district'. Ottoman Empire In the Ottoman Empire, a kaza was originally a "geographical area subject to the legal and administrative jurisdiction of a '' kadı''. With the first Tanzimat reforms of 1839, the administrative duties of the ''kadı'' were transferred to a governor ''(kaymakam)'', with the ''kadıs'' acting as judges of Islamic law. In the Tanzimat era, the kaza became an administrative district with the 1864 Provincial Reform Law, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ioannina
Ioannina ( el, Ιωάννινα ' ), often called Yannena ( ' ) within Greece, is the capital and largest city of the Ioannina regional unit and of Epirus, an administrative region in north-western Greece. According to the 2011 census, the city population was 65,574, while the municipality had 112,486 inhabitants.GOV. results of permanent population 2011, p. 10571 (p. 97 of pdf), and in Excel formatTable of permanent population 2011 from the sitHellenic Statistical Authority 24 November 2017. Retrieved 2018-01-09. It lies at an elevation of approximately above sea level, on the western shore of |
Nahiye
A nāḥiyah ( ar, , plural ''nawāḥī'' ), also nahiya or nahia, is a regional or local type of administrative division that usually consists of a number of villages or sometimes smaller towns. In Tajikistan, it is a second-level division while in Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, Jordan, Xinjiang, and the former Ottoman Empire, where it was also called a '' bucak'', it is a third-level or lower division. It can constitute a division of a ''qadaa'', ''mintaqah'' or other such district-type of division and is sometimes translated as " subdistrict". Ottoman Empire The nahiye ( ota, ناحیه) was an administrative territorial entity of the Ottoman Empire, smaller than a . The head was a (governor) who was appointed by the Pasha. The was a subdivision of a Selçuk Akşin Somel. "Kazâ". ''The A to Z of the Ottoman Empire''. Volume 152 of A to Z Guides. Rowman & Littlefield, 2010. p. 151. and corresponded roughly to a city with its surrounding villages. s, in turn, were divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venetiko
Venetiko ( el, Βενέτικο), is a small uninhabited Greek island off the southern coast of the Peloponnese, south of the Cape Akritas. It belongs to the cluster of the Messenian Oinousses. It is administratively part of the municipality of Pylos-Nestor, in Messenia. During the ancient times, it was called Theganoussa ( grc, Θηγανοῦσσά) and it is mentioned by the Pomponius Mela, Pliny the Elder, Pausanias and Ptolemaeus. Pausanias called it an uninhabited island, but it has been inhabited at some period since graves and ruins have been found. It is included in the Natura 2000 Natura 2000 is a network of nature protection areas in the territory of the European Union. It is made up of Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas designated under the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive, respecti .... References Ionian Islands Landforms of Messenia {{Peloponnese-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lidorikion
Lidoriki ( el, Λιδωρίκι, Katharevousa: Λιδωρίκιον) is a village and a former municipality in Phocis, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Dorida, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. In 2011 the population was 3,388. Its area is 409.577 km² covering nearly one-fifth of Phocis. Lidoriki is built on the western slopes of Mount Giona and over the Mornos river valley. It is the centre of the mountains of Dorida. Location Lidoriki is located west of Amfissa, northwest of Itea and east-northeast of Nafpaktos. Lidoriki is located above the Mornos artificial reservoir, formed by the Mornos Dam, completed in 1974. The reservoir supplies most of the drinking water used in Athens. Lidoriki is also connected to Amfissa via the largest tunnel in Greece with 16.5 km length. This is not a street tunnel, but an aquaeduct for the water from the Mornos reservoir. History Lidoriki is attested since the late 9th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzoumerka
Tzoumerka ( el, Τζουμέρκα) is a former municipality in the Ioannina regional unit, Epirus, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality North Tzoumerka, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 71.10 km2. Population 756 (2011). The seat of the municipality was in Chouliarades. During the Axis occupation of Greece (1941-1944) the main base of the EDES The National Republican Greek League ( el, Εθνικός Δημοκρατικός Ελληνικός Σύνδεσμος (ΕΔΕΣ), ''Ethnikós Dimokratikós Ellinikós Sýndesmos'' (EDES)) was one of the major resistance groups formed during t ... resistance organization was found in the Tzoumerka mountain. References Populated places in Ioannina (regional unit) {{Epirus-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_Greece_01.jpg)