|
Mairtine
The Mairtine (Martini, Marthene, Muirtine, Maidirdine, Mhairtine) were an important people of late prehistoric Munster, Ireland who by early historical times appear to have completely vanished from the Irish political landscape. They are notable for their former capital, ''Medón Mairtine'', becoming the chief church of the later Eóganachta, namely Emly. Mairtine mac Sithcheann Geoffrey Keating's ''History of Ireland'' includes the following section, which may refer to the eponymous ancestor: ''"Eochaidh Apthach (Eochu Apthach) son of Fionn, son of Oilill, son of Flann Ruadh, son of Rothlan, son of Mairtine, son of Sithcheann, son of Riaghlan, son of Eoinbhric son of Lughaidh, son of Ioth, son of Breoghan (Breogán), held the sovereignty of Ireland one year; and he was called Eochaidh Apthach because of the number who died in Ireland in his time; for the plague or other disease seized upon the men of Ireland each month, from which many of them died; hence the name Eochaidh Aptha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eóganachta
The Eóganachta or Eoghanachta () were an Irish dynasty centred on Cashel which dominated southern Ireland (namely the Kingdom of Munster) from the 6/7th to the 10th centuries, and following that, in a restricted form, the Kingdom of Desmond, and its offshoot Carbery, to the late 16th century. By tradition the dynasty was founded by Conall Corc but named after his ancestor Éogan, the firstborn son of the semi-mythological 3rd-century king Ailill Aulom. This dynastic clan-name, for it was never in any sense a 'surname,' should more accurately be restricted to those branches of the royal house which descended from Conall Corc, who established Cashel as his royal seat in the late 5th century. High Kingship issue Although the Eóganachta were powerful in Munster, they never provided Ireland with a High King. Serious challenges to the Uí Néill were however presented by Cathal mac Finguine and Feidlimid mac Cremthanin. They were not widely recognized as High Kings or Kings of Tar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
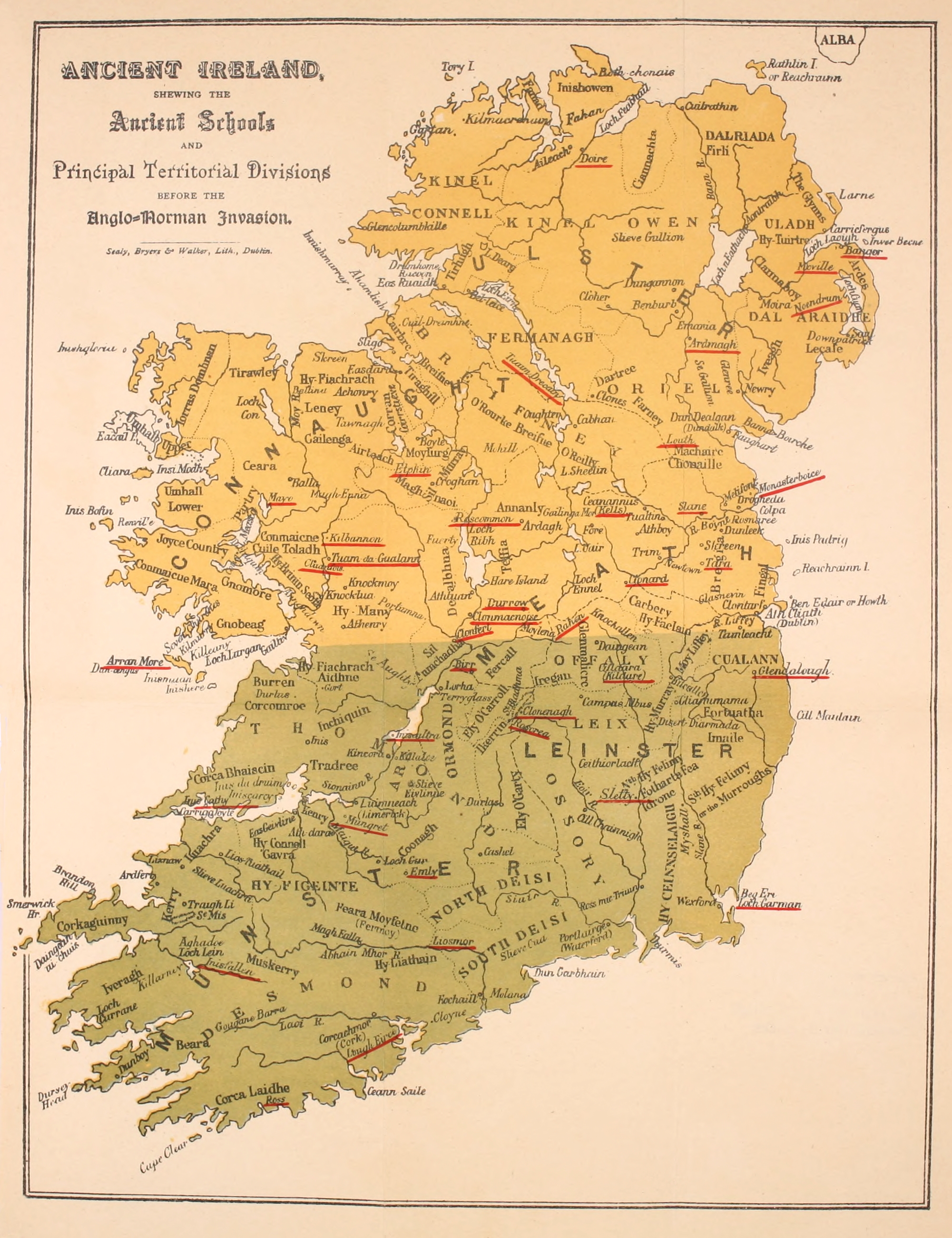
Emly
Emly or Emlybeg () is a village in County Tipperary, Ireland. It is a civil parish in the historical barony of Clanwilliam. It is also an Ecclesiastical parish in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Cashel and Emly. It is situated on the R515 Regional Road which goes west from Tipperary Town to Abbeyfeale, County Limerick. Emly lies 14 km west of Tipperary town and had a population of 302 in the 2016 census. History Ancient times The yew tree references the pre-Christian history of Emly. Emly is one of the oldest centres of Christianity in Ireland and pre-dates the coming to Ireland of the National Apostle, St. Patrick. Up until the early Middle Ages, Emly was the premier diocese in the south of Ireland. St. Ailbe is the patron saint of the Archdiocese of Cashel and Emly. Tradition tells us that he preached Christianity in Munster before the arrival of St. Patrick, and he is also associated with the founding of a monastery at Emly, which remained a Cathedral city unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest on Earth. Geopolitically, Ireland is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Ireland), which covers five-sixths of the island, and Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million living in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domnainn
The Fir Domnann were a people named in Irish legendary history. The name ''Fir Domnann'' is based on the root ''dumno''-, which means both ‘deep’ and ‘the world’. The suffix -''on''- often occurs in Gaulish and British divine names. The tribal name Dumnonii, found in Britain, would therefore mean ‘people of the god of the world’. Old Irish ''fir'' means ‘men’, and so ''Fir Domnann'' had the same meaning as the British tribal name, leading to conjecture that these tribes had a common origin. For example, O'Rahilly's historical model proposed that the Domnann were a P-Celtic, pre-Goidelic people who, along with the Galeóin, invaded the south-east coast of Ireland from Britain. O’Rahilly's theory of P-Celtic preceding Goidelic in Ireland is not widely accepted by experts today, but the idea of some connection between the British and Irish tribes of the same name remains. In early Irish literature the Fir Domnann were located in ''Cóice Laigean'' (Leinster). A pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dáibhí Ó Cróinín
Dáibhí Iarla Ó Cróinín (born 29 August 1954) is an Irish historian and authority on Hiberno-Latin texts, noted for his significant mid-1980s discovery in a manuscript in Padua of the "lost" Irish 84-year Easter table. Ó Cróinín was Professor of History at NUI Galway and Member of the Royal Irish Academy. He specialises in the history of Ireland, Britain and Europe during the Middle Ages and Hiberno-Latin texts. Early life and education Ó Cróinín received a B.A. in Early Irish History from University College Dublin (UCD) in 1975 and an M.Phil. in Medieval Studies from the same in 1977. Academia While wandering around Padua in the mid-1980s Ó Cróinín happened upon an example of the Irish 84-year Easter table in a manuscript there - this Easter table, so central to the Easter controversy, had until that time been presumed lost but Ó Cróinín had found one covering the period AD 438–521. For this he received his Ph.D. from University College Galway in 1985; the Pon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Lecan
The (Great) Book of Lecan (Irish: ''Leabhar (Mór) Leacáin'') (RIA, MS 23 P 2) is a medieval Irish manuscript written between 1397 and 1418 in Castle Forbes, Lecan (Lackan, Leckan; Irish ''Leacán''), in the territory of Tír Fhíacrach, near modern Enniscrone, County Sligo. It is in the possession of the Royal Irish Academy. ''Leabhar Mór Leacáin'' is written in Middle Irish and was created by Ádhamh Ó Cuirnín for Giolla Íosa Mór Mac Fhirbhisigh. The material within was transcribed from the Book of Leinster, latter copies of the Book of Invasions, the dinsenchas, the banshenchas and the Book of Rights. At one stage it was owned by James Ussher. James II of England then deposited it at the Irish College, Paris. In 1787, the Chevalier O'Reilly returned it to Ireland, where it was at one stage in the possession of Charles Vallancey. He passed it on to the Royal Irish Academy. There were originally 30 folios; the first nine were apparently lost in 1724. These contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leth Cuinn
Leath Cuinn (Conn's Half) and Leath Moga (Mugh's half) are legendary ancient divisions of Ireland. Leath Cuinn was the island north of the Esker Riada (east-west drumlin belt from Dublin to Galway Bay). Conn Cétchathach, for whom this division is named, was a retrospective ancestor of the Connachta and Uí Néill dynasties. Ireland's legendary ancient division into Leath Cuinn (Conn's Half) and Leath Moga (Mugh's half) resulted from the battle of Maigh Nuadad in 123 A.D. Conn, defeated by Eoghan Mor (also known as Mug Nuadat), was forced to accede to the division of Ireland into two halves: * The North - taking in Connacht, Ulster and Meath - would be Conn's Half * The South - taking in Munster, Osraighe and Leinster - would be Eoghan's Half. To solidify the arrangement, Conn's daughter, Sadhbh was married to Ailill Aulom, son of Eoghan. The Eoganacht dynasty in Munster claimed, as descendants of Oiloill Olum, the historical right as overkings of Leath Moga (i.e. overlordsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Déis Tuaisceirt
IN, In or in may refer to: Places * India (country code IN) * Indiana, United States (postal code IN) * Ingolstadt, Germany (license plate code IN) * In, Russia, a town in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast Businesses and organizations * Independent Network, a UK-based political association * Indiana Northeastern Railroad (Association of American Railroads reporting mark) * Indian Navy, a part of the India military * Infantry, the branch of a military force that fights on foot * IN Groupe , the producer of French official documents * MAT Macedonian Airlines (IATA designator IN) * Nam Air (IATA designator IN) Science and technology * .in, the internet top-level domain of India * Inch (in), a unit of length * Indium, symbol In, a chemical element * Intelligent Network, a telecommunication network standard * Intra-nasal (insufflation), a method of administrating some medications and vaccines * Integrase, a retroviral enzyme Other uses * ''In'' (album), by the Outsiders, 1967 * In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dál GCais
The Dalcassians ( ga, Dál gCais ) are a Gaelic Irish clan, generally accepted by contemporary scholarship as being a branch of the Déisi Muman, that became very powerful in Ireland during the 10th century. Their genealogies claimed descent from Tál Cas. Their known ancestors are the subject of ''The Expulsion of the Déisi'' tale and one branch of their blood-line went on to rule the petty kingdom of Dyfed in Wales during the 4th century; probably in alliance with the Roman Emperor Magnus Maximus. Brian Bóruma is perhaps the best-known king from the dynasty and was responsible to a significant degree for carving out their fortunes. The family had built a power base on the banks of the River Shannon and Brian's brother Mahon became their first King of Munster, taking the throne from the rival Eóganachta. This influence was greatly extended under Brian who became High King of Ireland, following a series of wars against Hiberno-Norse kingdoms and the Chiefs of other Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munster
Munster ( gle, an Mhumhain or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the south of Ireland. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" ( ga, rí ruirech). Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, the ancient kingdoms were shired into Counties of Ireland#2.1 Pre-Norman sub-divisions, counties for administrative and judicial purposes. In later centuries, local government legislation has seen further sub-division of the historic counties. Munster has no official function for Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local government purposes. For the purposes of the International Organization for Standardization, ISO, the province is listed as one of the provincial sub-divisions of the State (ISO 3166-2:IE) and coded as "IE-M". Geographically, Munster covers a total area of and has a population of 1,364,098, with the most populated city being Cork (city), Cork. Other significant urban centres in the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dubhaltach MacFhirbhisigh
Dubhaltach Mac Fhirbhisigh (), also known as Dubhaltach Óg mac Giolla Íosa Mór mac Dubhaltach Mór Mac Fhirbhisigh, Duald Mac Firbis, Dudly Ferbisie, and Dualdus Firbissius ( fl. 1643 – January 1671) was an Irish scribe, translator, historian and genealogist. He was one of the last traditionally trained Irish Gaelic scholars, and was a member of the Clan MacFhirbhisigh, a leading family of northern Connacht. His best-known work is the ''Leabhar na nGenealach'', which was published in 2004 as ''The Great Book of Irish Genealogies'', by Éamonn de Búrca, more than 300 years after it had been written. Family and education Mac Fhirbhisigh was most likely born at the family castle, in the parish of Lackan, Tireragh, County Sligo, sometime in the first quarter of the 17th century. He was originally known as ''Dubhaltach Og'' ("young Dubhaltach") to distinguish him from his grandfather, ''Dubhaltach Mór'' ("big Dubhaltach"). He was the eldest of four sons born to Giolla Íosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connacht
Connacht ( ; ga, Connachta or ), is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, Conmhaícne, and Delbhna). Between the reigns of Conchobar mac Taidg Mór (died 882) and his descendant, Aedh mac Ruaidri Ó Conchobair (reigned 1228–33), it became a kingdom under the rule of the Uí Briúin Aí dynasty, whose ruling sept adopted the surname Ua Conchobair. At its greatest extent, it incorporated the often independent Kingdom of Breifne, as well as vassalage from the lordships of western Mide and west Leinster. Two of its greatest kings, Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidri Ua Conchobair (c. 1115–1198) greatly expanded the kingdom's dominance, so much so that both became High King of Ireland. The Kingdom of Connacht collapsed in the 1230s because of civil war within the royal dynasty, which enabled widespread Hiber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |