|
Mahood Lake
Mahood Lake is a lake in the South Cariboo region of the Interior of British Columbia in Wells Gray Provincial Park. It is drained by the Mahood River, a tributary of the Clearwater River which has cut a deep canyon into Cambrian rocks and Pleistocene glacial moraines. Mahood Lake is fed by the short Canim River, which drains nearby Canim Lake to the west via Canim Falls and Mahood Falls.Neave, Roland (2015). ''Exploring Wells Gray Park'', 6th edition. Wells Gray Tours, Kamloops, BC. . The lake is 629 metres in elevation, 197 metres deep at its deepest point, approximately 33.5 km² in area, in length (east to west) and a maximum of in width. Mount Mahood is immediately south of the lake and rises to . Discovery and naming There are no written records about First Nations visits to Mahood Lake, but they did use this valley because pictographs can be seen about halfway along the south shore. The Mahood Lake area was the centre of considerable attention between 1872 and 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cariboo
The Cariboo is an intermontane region of British Columbia, Canada, centered on a plateau stretching from Fraser Canyon to the Cariboo Mountains. The name is a reference to the caribou that were once abundant in the region. The Cariboo was the first region of the interior north of the lower Fraser River and its canyon to be settled by non-indigenous people, and played an important part in the early history of the colony and province. The boundaries of the Cariboo proper in its historical sense are debatable, but its original meaning was the region north of the forks of the Quesnel River and the low mountainous basins between the mouth of that river on the Fraser at the city of Quesnel and the northward end of the Cariboo Mountains, an area that is mostly in the Quesnel Highland and focused on several now-famous gold-bearing creeks near the head of the Willow River. The richest of them all, Williams Creek, is the location of Barkerville, which was the capital of the Cariboo Gol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Hunter (Canadian Politician)
Joseph Hunter (May 7, 1839 – April 8, 1935) was a Scottish-born surveyor, civil engineer and political figure in British Columbia. He represented Cariboo from 1871 to 1875 and from 1900 to 1904 and Comox from 1890 to 1898 in the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia. He was born in Aberdeen in 1839 and educated there, concluding his studies at the University of Aberdeen. Hunter came to Victoria, British Columbia in 1864. From 1872, he worked performing surveys for the Canadian Pacific Railway. In 1875, he was employed by the Canadian government to establish a boundary between the province of British Columbia and the state of Alaska on the Stikine River. In 1883, he became chief engineer for the Esquimalt and Nanaimo Railway The Island Rail Corridor, previously the Esquimalt & Nanaimo Railway (E&N Railway), is a railway operation on Vancouver Island and is the only remaining railway on Vancouver Island after the closure of the Englewood Railway in November 2017. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of The Cariboo
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Pacific Survey
The Canadian Pacific Survey or Canadian Pacific Railway Survey comprised many distinct geographical surveys conducted during the 1870s and 1880s, designed to determine the ideal route of the Canadian Pacific Railway. Although much of the survey's activity focused on locating suitable mountain passes through the Canadian Rockies, Selkirk Mountains, Monashee Mountains, Canadian Cascades and Coast Mountains of western Canada, locating the best route across the rugged terrain of the Canadian Shield north of Lake Superior was also a primary goal. The survey played an important role in the exploration of Canada, especially in the mapping of hitherto-uncharted parts of British Columbia. In British Columbia, survey work was overseen by Walter Moberly, a former Colony of British Columbia land official and cabinet member, and involved steamboat support vessels on the Arrow Lakes and Columbia River, and on Kootenay Lake, Shuswap Lake, Seton Lake and others. The survey entailed the first d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
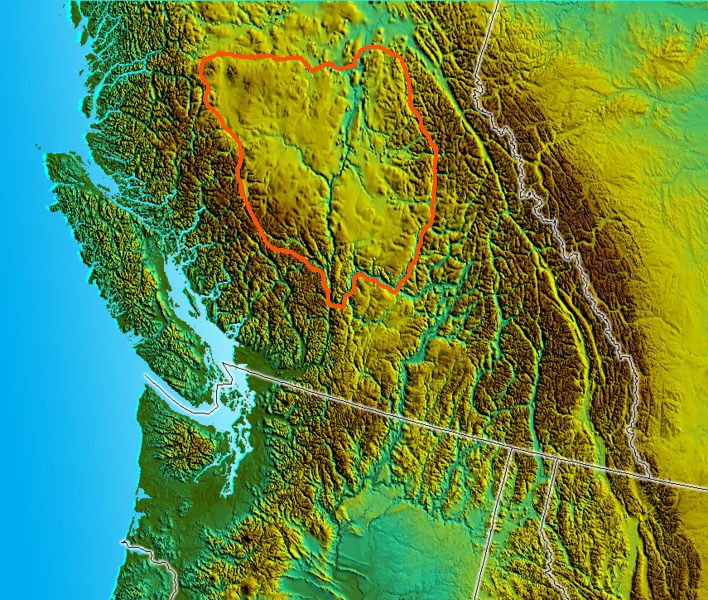
Wells Gray-Clearwater Volcanic Field
The Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, also called the Clearwater Cone Group, is a potentially active monogenetic volcanic field in east-central British Columbia, Canada, located approximately north of Kamloops. It is situated in the Cariboo Mountains of the Columbia Mountains and on the Quesnel and Shuswap Highlands. As a monogenetic volcanic field, it is a place with numerous small basaltic volcanoes and extensive lava flows. Most of the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field is encompassed within a large wilderness park called Wells Gray Provincial Park. This park was established in 1939 to protect Helmcken Falls and the unique features of the Clearwater River drainage basin, including this volcanic field. Five roads enter the park and provide views of some of the field's volcanic features. Short hikes lead to several other volcanic features, but some areas are accessible only by aircraft. Geology Pleistocene epoch Based on radiocarbon and potassium-argon dating, volcan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmcken Falls
Helmcken Falls is a waterfall on the Murtle River within Wells Gray Provincial Park in British Columbia, Canada. The protection of Helmcken Falls was one of the reasons for the creation of Wells Gray Provincial Park in 1939. Helmcken Falls is the fourth highest waterfall in Canada, measured by total straight drop without a break. Higher Canadian waterfalls are Hunlen Falls in Tweedsmuir Provincial Park, Takakkaw Falls in Yoho National Park, and Della Falls in Strathcona Provincial Park, all in British Columbia. There are six other waterfalls on the Murtle River, upstream from Helmcken Falls. The others are The Mushbowl, Dawson Falls, Majerus Falls, Horseshoe Falls, Meadow Falls and McDougall Falls. Only Helmcken, The Mushbowl and Dawson can be reached by road. Majerus, Horseshoe and McDougall Falls are accessed by trails. Meadow Falls is very difficult to view, except by air.Neave, Roland (2015). ''Exploring Wells Gray Park'', 6th edition. Wells Gray Tours, Kamloops, BC. . Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cariboo Highway
Highway 97 is a major highway in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is the longest continuously numbered route in the province, running and is the only route that runs the entire north–south length of the British Columbia, connecting the Canada–United States border near Osoyoos in the south to the British Columbia–Yukon boundary in the north at Watson Lake, Yukon. The highway connects several major cities in BC Interior, including Kelowna, Kamloops, Prince George, and Dawson Creek. Within and near these cities, Highway 97 varies from a two-lane highway to a freeway with as many as six lanes. Some remote sections also remain unpaved and gravelled. The route takes its number from U.S. Route 97, with which it connects at the international border. The highway was initially designated '97' in 1953. Route description The busiest section of Highway 97 is in West Kelowna, carrying almost 70,000 vehicles per day. Some sections in the northern regions of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowhead Highway
The Yellowhead Highway (french: Route Yellowhead) is a major interprovincial highway in Western Canada that runs from Winnipeg to Graham Island off the coast of British Columbia via Saskatoon and Edmonton. It stretches across the four western Canadian provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba and is part of the Trans-Canada Highway system and the larger National Highway System, but should not be confused with the more southerly, originally-designated Trans-Canada Highway. The highway was officially opened in 1970. Beginning in 1990, the green and white Trans-Canada logo was used to designate the roadway. The highway is named for the Yellowhead Pass, the route chosen to cross the Canadian Rockies. The pass and the highway are named after a fur trader and explorer named Pierre Bostonais. He had yellow streaks in his hair, and was nicknamed "Tête Jaune" (Yellowhead). Almost the entire length of the highway is numbered as 16, except for the section in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Fort
Little Fort is a small community on the west bank of North Thompson River in the interior of British Columbia, Canada. It is some north of Kamloops, British Columbia, Kamloops. The community is located at the junction of British Columbia Highway 5, Highway 5 and British Columbia Highway 24, Highway 24 in British Columbia, Canada. The Interlakes Highway, as Highway 24 is also known, runs west to meet British Columbia provincial highway 97, Highway 97 at 93 Mile House, British Columbia, 93 Mile House; it is also known as the Little Fort Highway. The Little Fort Ferry crosses to the east bank of the river. A small fort was established on the East side of the river in the 1840s as a stopping point on the HBC Brigade Trail from the Cariboo to Kamloops. Traces of the trail remain in the Eakin Creek canyon. This settlement was established by Paul Fraser in 1850 and abandoned in 1852. Before 1935, Little Fort post office was known as Mount Ollie. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
100 Mile House
100 Mile House is a district municipality located in the South Cariboo region of central British Columbia, Canada. History 100 Mile House was originally known as Bridge Creek House, named after the creek running through the area. Its origins as a settlement go back to the time when Thomas Miller owned a collection of ramshackle buildings serving the traffic of the gold rush as a resting point for travellers moving between Kamloops and Fort Alexandria, which was north of 100 Mile House farther along the Hudson's Bay Brigade Trail. It acquired its current name during the Cariboo Gold Rush where a roadhouse was constructed in 1862 at the mark up the Old Cariboo Road from Lillooet. In 1930, Lord Martin Cecil left England to come to 100 Mile House and manage the estate owned by his father, the 5th Marquess of Exeter. The estate's train stop on the Pacific Great Eastern (now BC Rail leased and operated by Canadian National) railway is to the west of town and called Exeter. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duncan Hines
Duncan Hines (March 26, 1880 – March 15, 1959) was an Americans, American pioneer of restaurant ratings for travelers. He is best known today for the brand of food products that bears his name. Early life Hines was born in Bowling Green, Kentucky, Bowling Green, Kentucky, the son of a former Confederate soldier. His mother died when he was four, and he was raised by his grandmother. Hines attended Bowling Green Business University, which later merged with what is now Western Kentucky University, and worked in the American West for Wells Fargo and other companies before settling in Chicago. Writing career Hines worked as a Vendor (supply chain), traveling salesman for a Chicago printer, and he had eaten many meals on the road across the United States by 1935 when he was 55. At this time, there was no American interstate highway system and only a few chain restaurants, except in large populated areas. Therefore, travelers depended on local restaurants. Hines and his wife Florenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001. Headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, the railway owns approximately of track in seven provinces of Canada and into the United States, stretching from Montreal to Vancouver, and as far north as Edmonton. Its rail network also serves Minneapolis–St. Paul, Milwaukee, Detroit, Chicago, and Albany, New York, in the United States. The railway was first built between eastern Canada and British Columbia between 1881 and 1885 (connecting with Ottawa Valley and Georgian Bay area lines built earlier), fulfilling a commitment extended to British Columbia when it entered Confederation in 1871; the CPR was Canada's first transcontinental railway. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


