|
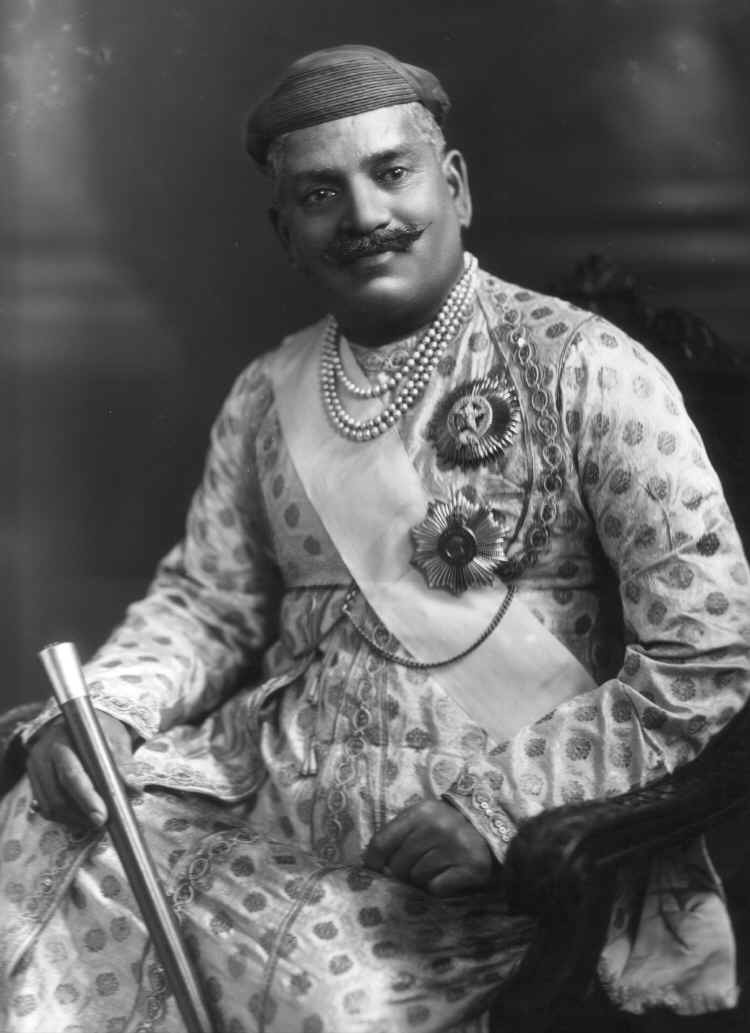
Mahendra Pratap
Raja Mahendra Pratap Singh (1 December 1886 – 29 April 1979) was an Indian freedom fighter, journalist, writer, revolutionary, President in the Provisional Government of India, which served as the Indian Government in exile during World War I from Kabul in 1915, and social reformist in the Republic of India. He also formed the Executive Board of India in Japan in 1940 during the Second World War. He also took part in the Balkan War in the year 1911 along with his fellow students of MAO college. He is popularly known as "Aryan Peshwa". Early life Pratap was born in the ruling Jat family of the state of Mursan in the Hathras District of Uttar Pradesh on 1 December 1886. He was the third son of Raja Ghanshyam Singh. At the age of three, Raja Harnarayan Singh of Hathras adopted him as his son.Bhattacharya, Abinash Chandra (1962). ''Bahirbharate Bharater Muktiprayas'' (in Bengali), Kalikata:Firma K.L.Mukhopadhyaya, pp. 9–24 He was married to Balveer Kaur belonging to the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provisional Government Of India
The Provisional Government of India was a provisional government-in-exile established in Kabul, Afghanistan on December 1, 1915 by the Indian Independence Committee during World War I with support from the Central Powers. Its purpose was to enrol support from the Afghan Emir as well as Tsarist (and later Bolshevik) Russia, China, and Japan for the Indian Movement. Established at the conclusion of the Kabul Mission composed of members of the Berlin Committee, German and Turkish delegates, the provisional government was composed of Mahendra Pratap as President, Maulana Barkatullah as Prime Minister, Deobandi Maulavi Ubaidullah Sindhi as Home Minister, Deobandi Maulavi Bashir as War Minister, and Champakraman Pillai as Foreign Affairs Minister. The provisional government found significant support from the internal administration of the Afghan government, although the Emir refused to declare open support, and ultimately, under British pressure it was forced to withdraw f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformist
Reformism is a political doctrine advocating the reform of an existing system or institution instead of its abolition and replacement. Within the socialist movement, reformism is the view that gradual changes through existing institutions can eventually lead to fundamental changes in a society's political and economic systems. Reformism as a political tendency and hypothesis of social change grew out of opposition to revolutionary socialism, which contends that revolutionary upheaval is a necessary precondition for the structural changes necessary to transform a capitalist system to a qualitatively different socialist system. Responding to a pejorative conception of reformism as non-transformational, non-reformist reform was conceived as a way to prioritize human needs over capitalist needs. As a doctrine, centre-left reformism is distinguished from centre-right or pragmatic reform which instead aims to safeguard and permeate the ''status quo'' by preventing fundamental structural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjab (British India)
Punjab was a province of British India. Most of the Punjab region was annexed by the East India Company in 2 April 1849, and declared a province of British Rule, it was one of the last areas of the Indian subcontinent to fall under British control. In 1858, the Punjab, along with the rest of British India, came under the direct rule of the British Crown. It had an area of 358,354.5 km2. The province comprised four natural geographic regions – ''Indo-Gangetic Plain West'', ''Himalayan'', ''Sub-Himalayan'', and the ''North-West Dry Area'' – along with five administrative divisions – Delhi, Jullundur, Lahore, Multan, and Rawalpindi – and a number of princely states. In 1947, the Partition of India led to the province's division into East Punjab and West Punjab, in the newly independent dominions of India and Pakistan respectively. Etymology The region was originally called Sapta Sindhu,D. R. Bhandarkar, 1989Some Aspects of Ancient Indian Culture: Sir William Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land area. The state capital is Chandigarh, which it shares with the neighboring state of Punjab, and the most populous city is Faridabad, which is a part of the National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region. The city of Gurugram is among India's largest financial and technology hubs. Haryana has 6 Divisions of Haryana, administrative divisions, 22 List of districts of Haryana, districts, 72 sub-divisions, 93 tehsil, revenue tehsils, 50 sub-tehsils, 140 Community development block in India, community development blocks, 154 List of cities in Haryana by population, cities and towns, 7,356 villages, and 6,222 Gram panchayat, villages panchayats. Haryana contains 32 special economic zones (SEZs), mainly located within the industrial corri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely State
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the the Crown, British crown. There were officially 565 princely states when India and Pakistan became independent in 1947, but the great majority had contracted with the viceroy to provide public services and tax collection. Only 21 had actual state governments, and only four were large (Hyderabad State, Mysore State, Kashmir and Jammu (princely state), Jammu and Kashmir State, and Baroda State). They Instrument of accession, acceded to one of the two new independent nations between 1947 and 1949. All the princes were eventually pensioned off. At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent, apart from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jind
Jind is one of the largest and oldest city in Jind district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is administrative headquarter of Jind district. Rani Talab is the main destination for tourists while Pandu-Pindara and Ramrai are the main religious spots, attracting devotees for the holy bath during '' Amavasya''. The fort of Jind was built by Sidhu Jat ruler Maharaja Gajpat Singh in 1776 AD. Etymology Jind was named Jayantapura after the lord of victory Jayant (Indra), whom Pandavas worshipped before the Mahabharata war. According to oral tradition, Pandavas built the Jayanti Devi Temple in honour of Jyanti Devi (the goddess of victory, a feminine representation of Indra). They offered prayers for success and then started a battle against Kaurava. The town was built around the temple and named Jayantapuri (Abode of Jyanti Devi) which was later renamed to Jind. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja Harnarayan Singh
''Raja'' (; from , IAST ') is a royal title used for South Asian monarchs. The title is equivalent to king or princely ruler in South Asia and Southeast Asia. The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested from the Rigveda, where a ' is a ruler, see for example the ', the "Battle of Ten Kings". Raja-ruled Indian states While most of the Indian salute states (those granted a gun salute by the British Crown) were ruled by a Maharaja (or variation; some promoted from an earlier Raja- or equivalent style), even exclusively from 13 guns up, a number had Rajas: ; Hereditary salutes of 11-guns : * the Raja of Pindrawal * the Raja of Morni * the Raja of Rajouri * the Raja of Ali Rajpur * the Raja of Bilaspur * the Raja of Chamba * the Raja of Faridkot * the Raja of Jhabua * the Raja of Mandi * the Raja of Manipur * the Raja of Narsinghgarh * the Raja of Pudukkottai * the Raja of Rajgarh * the Raja of Sangli * the Raja of Sailana * the Raja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghanshyam Singh
Swaminarayan (IAST: ', 3 April 1781 – 1 June 1830), also known as Sahajanand Swami, was a yogi and ascetic, who is believed by followers to be a manifestation of God Krishna, or as the highest manifestation of Purushottam, and around whom the Swaminarayan Sampradaya developed. In 1800, he was initiated into the ''Uddhav'' ''sampradaya'' by his guru, Swami Ramanand, and was given the name Sahajanand Swami. Despite opposition, in 1802 Ramanand handed over the leadership of the Uddhav Sampraday to him before his death. According to the Swaminarayan-tradition, Sahajanand Swami became known as Swaminarayan, and the Uddhav Sampraday as the Swaminarayan Sampradaya, after a gathering in which he taught the Swaminarayan Mantra to his followers. He emphasized "moral, personal, and social betterment," and ''ahimsa'', and is also remembered within the sect for undertaking reforms for women and the poor, and performing non-violent yajñas (fire sacrifices) on a large scale. Dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 after India had become a republic. It was a successor to the United Provinces (UP) during the period of the Dominion of India (1947–1950), which in turn was a successor to the United Provinces (UP) established in 1935, and eventually of the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh established in 1902 during the British Raj. The state is divided into 18 divisions and 75 districts, with the state capital being Lucknow, and Prayagraj serving as the judicial capital. On 9 November 2000, a new state, Uttaranchal (now Uttarakhand), was created from Uttar Pradesh's western Himalayan hill region. The two major rivers of the state, the Ganges and its tributary Yamuna, meet at the Triveni Sangam in Prayagraj, a Hindu pilgrimage site. Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hathras
Hathras is a historical city in Uttar Pradesh, India. It is also the headquarters of Hathras district, formed on 3 May 1997 by merging parts of Aligarh, Mathura and Agra. It is a part of the Aligarh Division. The primary spoken language is a dialect of Hindi, Braj Bhasha, which is closely related to Khariboli, one of, several dialects spoken in the Delhi region. It is known for production of asafoetida (aka hing). Administration Hathras is a district headquarter with three subdivisions - Hathras, Sikandra Rao, and Sadabad. It is a Lok Sabha constituency under the reserved category of Schedule Caste. The district has three assembly constituencies, following three subdivisions. The Hathras district, formerly known as Mahamaya Nagar, was created in 1997 with the incorporation of parts of the Aligarh, Mathura, and Agra districts. Local bodies Hathras has nine local bodies: * Hathras *Sikandra Rao *Sasni * Sadabad *Mursan * Hasayan * Sahpau * Mendu * Purdil Nagar Geograp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mursan
Mursan is a town and a Nagar Panchayat in Hathras district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The primary spoken language is a dialect of Hindi, Braj Bhasha, which is closely related to Khariboli. In past, Raja Mahendra Pratap Singh was the ruler of Mursan. At present, the Chairman of Mursan is Rajnesh Kushwah. Former Chairmen of Mursan: * Lal ji Saraswat * Giriraj Kishor Sharma * Deshraj Singh Demographics India census, Mursan had a population of 11,550. Males constitute 54% of the population and females 46%. Mursan has an average literacy rate of 57%, lower than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy is 66%, and female literacy is 46%. In Mursan, 17% of the population is under 6 years of age. Notable people *Raja Mahendra Pratap Transport * By Roadways, there is a small government but stand in Mursan nearby Mursan Police Station. * By Railways, there is one and only railway station in Mursan Town named as Mursan and station code is MSN MSN (meaning Micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jat People
The Jat people ((), ()) are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in late medieval times, and subsequently into the Delhi Territory, northeastern Rajputana, and the western Gangetic Plain in the 17th and 18th centuries. Quote: "Hiuen Tsang gave the following account of a numerous pastoral-nomadic population in seventh-century Sin-ti (Sind): 'By the side of the river.. f Sind along the flat marshy lowlands for some thousand li, there are several hundreds of thousands very great manyfamilies ..hichgive themselves exclusively to tending cattle and from this derive their livelihood. They have no masters, and whether men or women, have neither rich nor poor.' While they were left unnamed by the Chinese pilgrim, these same people of lower Sind were called Jats' or 'Jats of the wastes' by the Arab geographers. The Jats, as 'dromedary men.' we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |