|
Mahajangasuchidae
Mahajangasuchidae is an extinct family of notosuchian crocodyliforms. It currently contains two genera, '' Mahajangasuchus'' and '' Kaprosuchus'', both of which lived during the Late Cretaceous in Gondwana. It is defined as the most inclusive clade containing ''Mahajangasuchus insignis'' but not ''Notosuchus terrestris'', '' Simosuchus clarki'', '' Araripesuchus gomesii'', ''Baurusuchus pachecoi'', '' Peirosaurus torminni'', '' Goniopholis crassidens'', '' Pholidosaurus schaumbergensis'', or ''Crocodylus niloticus''. Phylogenetically, Mahajangasuchidae is placed just outside pholidosaurids and more derived neosuchians. Defining characters of the family include fused nasals, a jaw articulation below the posterior maxillary tooth row, a deep mandibular symphysis that is oriented anterodorsally, and the formation of a hornlike posterodorsal process from the squamosal and parietal (which is much more pronounced in ''Kaprosuchus''). Phylogeny Cladogram showing the phylogenetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
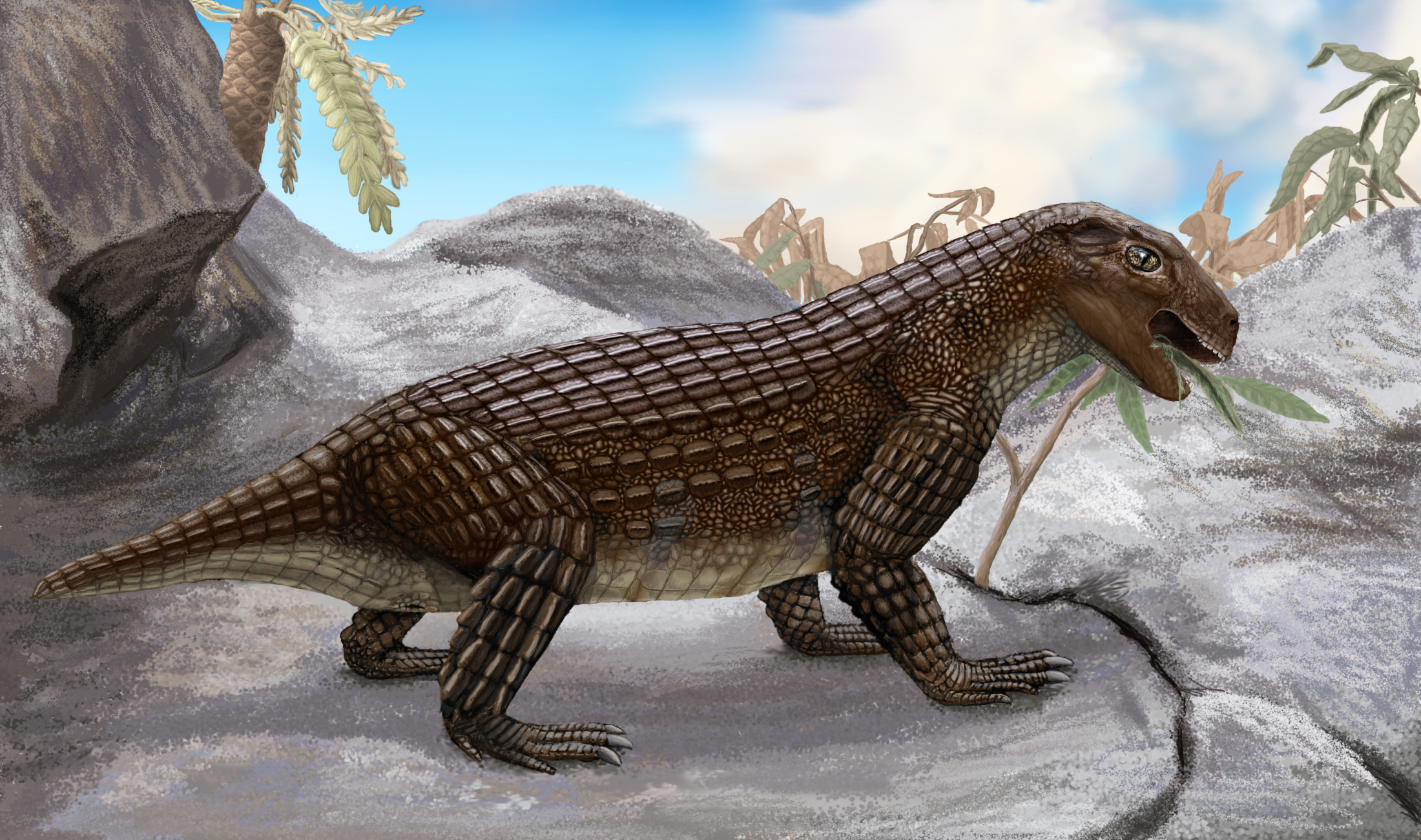
Kaprosuchus 2
''Kaprosuchus'' is an extinct genus of mahajangasuchid crocodyliform. It is known from a single nearly complete skull collected from the Upper Cretaceous Echkar Formation of Niger. The name means "boar crocodile" from the Greek , ''kapros'' ("boar") and , ''soukhos'' ("crocodile") in reference to its unusually large caniniform teeth which resemble those of a boar. It has been nicknamed "BoarCroc" by Paul Sereno and Hans Larsson, who first described the genus in a monograph published in ''ZooKeys'' in 2009 along with other Saharan crocodyliformes such as ''Anatosuchus'' and ''Laganosuchus''. The type species is ''K. saharicus''. Description ''Kaprosuchus'' is known from a nearly complete skull 507 mm in length in which the lower jaw measured 603 mm long. The original description estimated the entire animal to be in length,National Geographic. November 2009. p. 140-141 although newer estimates lowered this to around 4 meters (13.1 ft). It possesses three sets of tusk- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaprosuchus
''Kaprosuchus'' is an extinct genus of mahajangasuchid crocodyliform. It is known from a single nearly complete skull collected from the Upper Cretaceous Echkar Formation of Niger. The name means "boar crocodile" from the Greek , ''kapros'' ("boar") and , ''soukhos'' ("crocodile") in reference to its unusually large caniniform teeth which resemble those of a boar. It has been nicknamed "BoarCroc" by Paul Sereno and Hans Larsson, who first described the genus in a monograph published in ''ZooKeys'' in 2009 along with other Saharan crocodyliformes such as ''Anatosuchus'' and ''Laganosuchus''. The type species is ''K. saharicus''. Description ''Kaprosuchus'' is known from a nearly complete skull 507 mm in length in which the lower jaw measured 603 mm long. The original description estimated the entire animal to be in length,National Geographic. November 2009. p. 140-141 although newer estimates lowered this to around 4 meters (13.1 ft). It possesses three sets of tusk- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notosuchia
Notosuchia is a suborder of primarily Gondwanan mesoeucrocodylian crocodylomorphs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous. Some phylogenies recover Sebecosuchia as a clade within Notosuchia, others as a sister group (see below); if Sebecosuchia is included within Notosuchia its existence is pushed into the Middle Miocene, about 11 million years ago. Fossils have been found from South America, Africa, Asia, and Europe. Notosuchia was a clade of terrestrial crocodilians that evolved a range of feeding behaviours, including herbivory ('' Chimaerasuchus''), omnivory (''Simosuchus''), and terrestrial hypercarnivory (''Baurusuchus''). It included many members with highly derived traits unusual for crocodylomorphs, including mammal-like teeth, flexible bands of shield-like body armor similar to those of armadillos (''Armadillosuchus''), and possibly fleshy cheeks and pig-like snouts (''Notosuchus''). The suborder was first named in 1971 by Zulma Gasparini and has since undergone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahajangasuchus
''Mahajangasuchus'' is an extinct genus of crocodyliform which had blunt, conical teeth. The type species, ''M. insignis'', lived during the Late Cretaceous; its fossils have been found in the Maevarano Formation in northern Madagascar. It was a fairly large predator, measuring up to long. Discovery and naming With the inception of the Mahajanga Basin Project (MBP) in 1993, led by Dr. David Krause, came a significant increase of discoveries and research into the fauna of the Maastrichtian Maevarano Formation in northern Madagascar. This included a variety of crocodylomorphs with the largest specimen being a well preserved disarticulated skeleton discovered in 1995 roughly 1 km south-east of the village of Berivotra. This skeleton, specimen ''UA 8654'', consisted of a complete left and partial right mandible, vertebrae of the cervical, dorsal, saccral and caudal regions, several ribs as well as material of the pectoral, pelvic girdle and limb bones. Osteoderms and isolated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebecia
Sebecia is an extinct clade of mesoeucrocodylian crocodyliforms that includes peirosaurids and sebecids. It was first constructed in 2007 to include ''Hamadasuchus'', Peirosauridae, and ''Sebecus''. It was initially considered to be the sister taxon of the clade Neosuchia, which includes living crocodilians, although some later studies have placed it within Neosuchia as a basal clade. Sebecians were terrestrial crocodyliforms characterized by their deep snouts and ziphodont dentition. They first appeared in the Late Cretaceous, survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, and became extinct in the Miocene epoch. According to paleontologists Hans Larsson and Hans-Dieter Sues, who constructed the clade in 2007, Sebecia also includes genera that were once assigned to Baurusuchidae, namely ''Pabwehshi''. However, other baurusuchids, namely ''Baurusuchus'', were placed outside Sebecia. Therefore, Baurusuchidae was considered polyphyletic and thus not a true clade. Below is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simosuchus
''Simosuchus'' (meaning "pug-nosed crocodile" in Greek, referring to the animal's blunt snout) is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorphs from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. It is named for its unusually short skull. Fully grown individuals were about in length. The type species is ''Simosuchus clarki'', found from the Maevarano Formation in Mahajanga Province, although some fossils have been found in India. The teeth of ''S. clarki'' were shaped like maple leaves, which coupled with its short and deep snout suggests it was not a carnivore like most other crocodylomorphs. In fact, these features have led many palaeontologists to consider it a herbivore. Description ''Simosuchus'' was small, about long based on the skeletons of mature individuals. In contrast to most other crocodyliforms, which have long, low skulls, ''Simosuchus'' has a distinctively short snout. The snout resembles that of a pug, giving the genus its name, which means "pug-nosed crocodile" in Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenomanian
The Cenomanian is, in the ICS' geological timescale, the oldest or earliest age of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or the lowest stage of the Upper Cretaceous Series. An age is a unit of geochronology; it is a unit of time; the stage is a unit in the stratigraphic column deposited during the corresponding age. Both age and stage bear the same name. As a unit of geologic time measure, the Cenomanian Age spans the time between 100.5 and 93.9 million years ago (Mya). In the geologic timescale, it is preceded by the Albian and is followed by the Turonian. The Upper Cenomanian starts around at 95 Mya. The Cenomanian is coeval with the Woodbinian of the regional timescale of the Gulf of Mexico and the early part of the Eaglefordian of the regional timescale of the East Coast of the United States. At the end of the Cenomanian, an anoxic event took place, called the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event or the "Bonarelli event", that is associated with a minor extinction event for marine spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose. Each has two surfaces and four borders. Structure The two nasal bones are joined at the midline internasal suture and make up the bridge of the nose. Surfaces The ''outer surface'' is concavo-convex from above downward, convex from side to side; it is covered by the procerus and nasalis muscles, and perforated about its center by a foramen, for the transmission of a small vein. The ''inner surface'' is concave from side to side, and is traversed from above downward, by a groove for the passage of a branch of the nasociliary nerve. Articulations The nasal articulates with four bones: two of the cranium, the frontal and ethmoid, and two of the face, the opposite nasal and the maxilla. Other animals In primitive bony fish and tetrapod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal, inferior n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamosal
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone. In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including some living reptiles and amphibians. Anatomy and function In animals with a quadratojugal bone, it is typically found connected to the jugal (cheek) bone from the front and ... bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral component of the dermal roof and is typically thin compared to other skull bones. The squamosal bone lies Anatomical terms of location, ventral to the temporal series and otic notch, and is bordered anteriorly by the Postorbital bone, postorbital. Posteriorly, the squamosal articulates with the quadrate bone, quadrate and Pterygoid bone, pterygoid bones. The squamosal is bordered anteroventrally by the jugal and ventrally by the quadratojugal. Function in reptiles In reptiles, the Quadrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neosuchia
Neosuchia is a clade within Mesoeucrocodylia that includes all modern extant crocodilians and their closest fossil relatives. It is defined as the most inclusive clade containing all crocodylomorphs more closely related to ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile Crocodile) than to ''Notosuchus terrestris''. Members of Neosuchia generally share a crocodilian-like bodyform adapted to freshwater aquatic life, as opposed to the terrestrial habits of more basal crocodylomorph groups. The earliest neosuchian is suggested to be the Early Jurassic ''Calsoyasuchus'', which lived during the Sinemurian and Pliensbachian stages in North America. It is often identified as a member of Goniopholididae, though this is disputed, and the taxon may lie outside Neosuchia, which places the earliest records of the group in the Middle Jurassic. Characteristics A tooth notch between the maxilla and premaxilla is a basal characteristic of the Neosuchia, although it is lost in some more derived forms, most nota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |