|
Magnetic Sail
A magnetic sail is a proposed method of spacecraft propulsion that uses a static magnetic field to deflect a plasma wind of charged particles radiated by the Sun or a Star thereby transferring momentum to accelerate or decelerate a spacecraft. Most approaches require little to no propellant and thus are a form of Field propulsion. A magnetic sail could also thrust against a planetary ionosphere or magnetosphere. Important use cases are: a modest force from the solar wind sustainable for a long period of time; deceleration in the interstellar medium and the plasma wind of a destination Star following interstellar travel at relativistic speeds achieved by some other means; and efficient deceleration in a planetary ionosphere. Plasma characteristics for the Solar wind, a planetary ionosphere and the interstellar medium and the specifics of the magnetic sail design determine achievable performance; such as, thrust, required power and mass. History of concept Dana Andrews and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Sail Overview
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Magnetism is one aspect of the combined phenomena of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt, and nickel and their alloys. The rare-earth metals neodymium and samarium are less common examples. The prefix ' refers to iron because permanent magnetism was first observed in lodestone, a form of natural iron ore called magnetite, Fe3O4. All substances exhibit some type of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Dipole
In electromagnetism, a magnetic dipole is the limit of either a closed loop of electric current or a pair of poles as the size of the source is reduced to zero while keeping the magnetic moment constant. It is a magnetic analogue of the electric dipole, but the analogy is not perfect. In particular, a true magnetic monopole, the magnetic analogue of an electric charge, has never been observed in nature. However, magnetic monopole quasiparticles have been observed as emergent properties of certain condensed matter systems. Moreover, one form of magnetic dipole moment is associated with a fundamental quantum property—the spin of elementary particles. Because magnetic monopoles do not exist, the magnetic field at a large distance from any static magnetic source looks like the field of a dipole with the same dipole moment. For higher-order sources (e.g. quadrupoles) with no dipole moment, their field decays towards zero with distance faster than a dipole field does. External mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Parameters
Plasma parameters define various characteristics of a plasma, an electrically conductive collection of charged particles that responds ''collectively'' to electromagnetic forces. Plasma typically takes the form of neutral gas-like clouds or charged ion beams, but may also include dust and grains. The behaviour of such particle systems can be studied statistically. Fundamental plasma parameters All quantities are in Gaussian ( cgs) units except energy and temperature which are in electronvolts. The ion mass is expressed in units of the proton mass \mu = m_i/m_p and Z the ion charge in units of the elementary charge e (in the case of a fully ionized atom, Z equals to the respective atomic number). The other physical quantities used are the Boltzmann constant (k), speed of light (c), and the Coulomb logarithm (\ln\Lambda). Frequencies Lengths Velocities Dimensionless * number of particles in a Debye sphere *: \left(\frac\right)n\lambda_D^3 \approx 1.72 \times 10^9\, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma () 1, where \nu_ is the electron gyrofrequency and \nu_ is the electron collision rate. It is often the case that the electrons are magnetized while the ions are not. Magnetized plasmas are ''anisotropic'', meaning that their properties in the direction parallel to the magnetic field are different from those perpendicular to it. While electric fields in plasmas are usually small due to the plasma high conductivity, the electric field associated with a plasma moving with velocity \mathbf in the magnetic field \mathbf is given by the usual Lorentz force, Lorentz formula \mathbf = -\mathbf\times\mathbf, and is not affected by Debye shielding. Mathematical descriptions To completely describe the state of a plasma, all of the particle locations and velocities that describe the electromagnetic field in the plasma region would need to be written down. However, it is generally not practical or necessary to keep track of all the particles in a plasma. Therefore, plasma physicist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
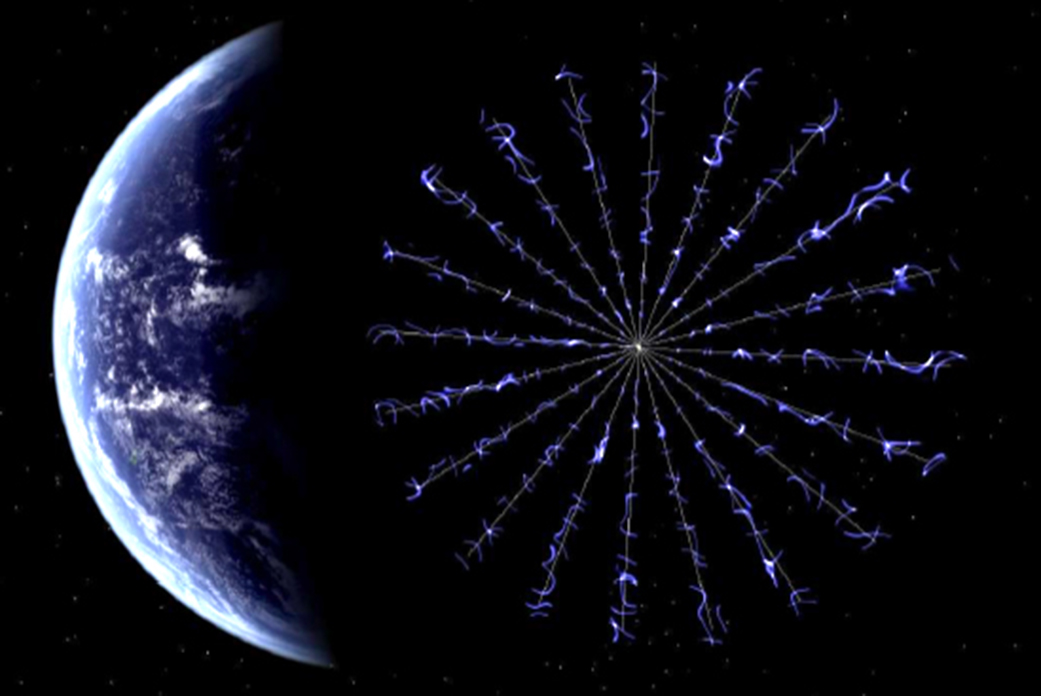
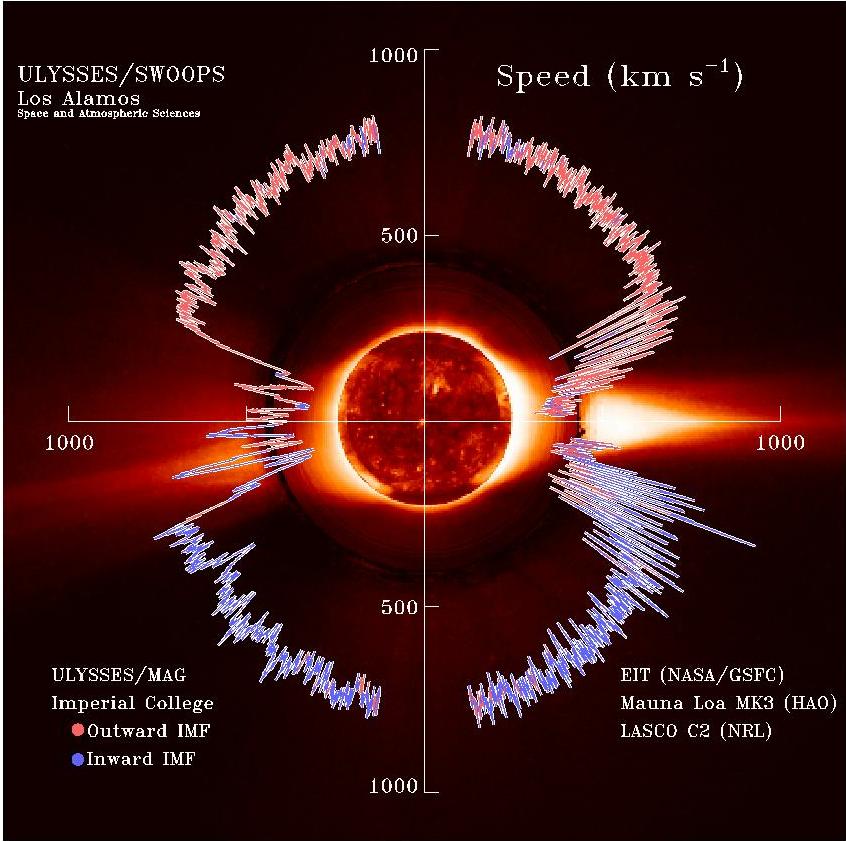
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface. At a distance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Gun
An electron gun (also called electron emitter) is an electrical component in some vacuum tubes that produces a narrow, collimated electron beam that has a precise kinetic energy. The largest use is in cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), used in nearly all television sets, computer displays and oscilloscopes that are not flat-panel displays. They are also used in field-emission displays (FEDs), which are essentially flat-panel displays made out of rows of extremely small cathode-ray tubes. They are also used in microwave linear beam vacuum tubes such as klystrons, inductive output tubes, travelling wave tubes, and gyrotrons, as well as in scientific instruments such as electron microscopes and particle accelerators. Electron guns may be classified by the type of electric field generation (DC or RF), by emission mechanism (thermionic, photocathode, cold emission, plasmas source), by focusing (pure electrostatic or with magnetic fields), or by the number of electrodes. Characteristics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Sail
An electric sail (also known as an electric solar wind sail or an E-sail) is a proposed form of spacecraft propulsion using the dynamic pressure of the solar wind as a source of thrust. It creates a "virtual" sail by using small wires to form an electric field that deflects solar wind protons and extracts their momentum. The idea was first conceptualised by Pekka Janhunen in 2006 at the Finnish Meteorological Institute. Principles of operation and design The electric sail consists of a number of thin, long and conducting tethers which are kept in a high positive potential by an onboard electron gun. The positively charged tethers deflect solar wind protons, thus extracting momentum from them. Simultaneously they attract electrons from the solar wind plasma, producing an electron current. The electron gun compensates for the arriving electric current. One way to deploy the tethers is to rotate the spacecraft, using centrifugal force to keep them stretched. By fine-tuning the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerocapture
Aerocapture is an orbital transfer maneuver in which a spacecraft uses aerodynamic drag force from a single pass through a planetary atmosphere to decelerate and achieve orbit insertion. Aerocapture uses a planet's or moon's atmosphere to accomplish a quick, near-propellantless orbit insertion maneuver to place a spacecraft in its science orbit. The aerocapture maneuver starts as the spacecraft enters the atmosphere of the target body from an interplanetary approach trajectory. The aerodynamic drag generated as the vehicle descends into the atmosphere slows the spacecraft. After the spacecraft slows enough to be captured by the planet, it exits the atmosphere and executes a small propulsive burn at the first apoapsis to raise the periapsis outside the atmosphere. Additional small burns may be required to correct apoapsis and inclination targeting errors before the initial science orbit is established. Compared to conventional propulsive orbit insertion, this nearly fuel-free met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Magnet
A plasma magnet is a proposed spacecraft propulsion device that uses a dipole magnetic field to capture energy from the solar wind. The field acts as a sail, using the captured energy to propel the spacecraft analogously to how the wind propels a sailing vessel. It could accelerate a vessel moving away from the sun and decelerate it when approaching a distant star at the end of an interstellar journey. Thrust vectoring and steering could be achieved by manipulating the dipole tilt for any type of magnetic sail. Solar wind The solar wind is a stream of energetic charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of a star, such as the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between 0.5 and 10 keV. The solar wind travels at velocities greater than 105 m/s. Its dynamic pressure is roughly 2x10−9 N/m2 at 1 AU. A properly designed system allows the spacecraft to accelerate to near the speed of the solar wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotating Magnetic Field
A rotating magnetic field is the resultant magnetic field produced by a system of coils symmetrically placed and supplied with polyphase currents. A rotating magnetic field can be produced by a poly-phase (two or more phases) current or by a single phase current provided that, in the latter case, two field windings are supplied and are so designed that the two resulting magnetic fields generated thereby are out of phase. Rotating magnetic fields are often utilized for electromechanical applications, such as induction motors, electric generators and induction regulators. History In 1824, the French physicist François Arago formulated the existence of rotating magnetic fields using a rotating copper disk and a needle, termed “Arago's rotations.” English experimenters Charles Babbage and John Herschel found they could induce rotation in Arago's copper disk by spinning a horseshoe magnet under it, with English scientist Michael Faraday later attributing the effect to electromagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Magnet (PM)
A plasma magnet is a proposed spacecraft propulsion device that uses a dipole magnetic field to capture energy from the solar wind. The field acts as a sail, using the captured energy to propel the spacecraft analogously to how the wind propels a sailing vessel. It could accelerate a vessel moving away from the sun and decelerate it when approaching a distant star at the end of an interstellar journey. Thrust vectoring and steering could be achieved by manipulating the dipole tilt for any type of magnetic sail. Solar wind The solar wind is a stream of energetic charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of a star, such as the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between 0.5 and 10 keV. The solar wind travels at velocities greater than 105 m/s. Its dynamic pressure is roughly 2x10−9 N/m2 at 1 AU. A properly designed system allows the spacecraft to accelerate to near the speed of the solar wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Institute For Advanced Concepts
The NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts (NIAC) is a NASA program for development of far reaching, long term advanced concepts by "creating breakthroughs, radically better or entirely new aerospace concepts". The program operated under the name NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts from 1998 until 2007 (managed by the Universities Space Research Association on behalf of NASA), and was reestablished in 2011 under the name NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts and continues to the present. The NIAC program funds work on revolutionary aeronautics and space concepts that can dramatically impact how NASA develops and conducts its missions. History The ''NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts'' (NIAC) was a NASA-funded program that was operated by the Universities Space Research Association (USRA) for NASA from 1998 until its closure on 31 August 2007. NIAC was to serve as "an independent open forum, a high-level point of entry to NASA for an external community of innovators, and an external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |