|
Magnesia Litera Winners , a suspension of magn ...
Magnesia may refer to: * Magnesia (hypothetical city), a future colony of Knossos, imagined in Plato's ''Laws'' *Magnesia (regional unit), the southeastern area of Thessaly in central Greece *Ancient Magnesia, a historical region of Greece with borders differing from the modern regional unit *Magnesia ad Sipylum, a city of Lydia, now Manisa in Turkey **Battle of Magnesia, 190 BC, the concluding battle of the Roman–Seleucid War *Magnesia on the Maeander, an ancient Greek city in Anatolia *Magnesia Prefecture, a former prefecture of Greece Chemistry *Magnesium oxide **Periclase or magnesia, a natural mineral of magnesium oxide See also * Magnesian limestone (other) *Magnesium *Milk of magnesia Magnesium hydroxide is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Mg(OH)2. It occurs in nature as the mineral brucite. It is a white solid with low solubility in water (). Magnesium hydroxide is a common component of antacids, such as milk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesia (hypothetical City) , a suspension of magn ...
Magnesia may refer to: * Magnesia (hypothetical city), a future colony of Knossos, imagined in Plato's ''Laws'' *Magnesia (regional unit), the southeastern area of Thessaly in central Greece *Ancient Magnesia, a historical region of Greece with borders differing from the modern regional unit *Magnesia ad Sipylum, a city of Lydia, now Manisa in Turkey **Battle of Magnesia, 190 BC, the concluding battle of the Roman–Seleucid War *Magnesia on the Maeander, an ancient Greek city in Anatolia *Magnesia Prefecture, a former prefecture of Greece Chemistry *Magnesium oxide **Periclase or magnesia, a natural mineral of magnesium oxide See also * Magnesian limestone (other) *Magnesium *Milk of magnesia Magnesium hydroxide is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Mg(OH)2. It occurs in nature as the mineral brucite. It is a white solid with low solubility in water (). Magnesium hydroxide is a common component of antacids, such as milk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laws (dialogue)
The ''Laws'' (Greek: Νόμοι, ''Nómoi''; Latin: ''De Legibus'') is Plato's last and longest dialogue. The conversation depicted in the work's twelve books begins with the question of who is given the credit for establishing a civilization's laws. Its musings on the ethics of government and law have established it as a classic of political philosophy alongside Plato's more widely read ''Republic''. Scholars generally agree that Plato wrote this dialogue as an older man, having failed in his effort to guide the rule of the tyrant Dionysius I of Syracuse, instead having been thrown in prison. These events are alluded to in the ''Seventh Letter''. The text is noteworthy as Plato's only undisputed dialogue not to feature Socrates. Summary Setting Unlike most of Plato's dialogues, Socrates does not appear in the ''Laws'': the dialogue takes place on the island of Crete, and Socrates appears outside of Athens in Plato's writings only twice, in the '' Phaedrus'', where he is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesia (regional Unit)
Magnesia ( el, Μαγνησία, ''Magnisía'', , Ancient Greek: ''Magnēsía'', deriving from the tribe name ''Magnetes'') is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Thessaly. Its capital is the city of Volos. About 70% of the population of Magnesia live in the Greater Volos area, which is the second-largest city in Thessaly and the third busiest commercial port in Greece. According to the most recent census (2011), the population stands at 190,010. The regional unit hosts 2,000,000 tourists annually. Magnesia is represented in the Greek Parliament by six seats. Its main agricultural products are wheat, cotton, tomatoes, grapes, olives, apples and honey. Geography A prominent geographic feature of Magnesia is the Pagasetic Gulf, a bay of the Aegean Sea. The Pelion mountain range closes off the Gulf on the east and south side, leaving only a narrow channel near Trikeri. The highest peak of the wooded Pelion is ''Pourianos Stavros'' or ''Xeforti'', (alti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Magnesia
Anciently, Magnesia ( grc, Μαγνησία) was a region of Ancient Greece, eventually absorbed by ancient Thessaly. Originally inhabited by the Magnetes (Μάγνητες), Magnesia was the long and narrow slip of country between Mounts Ossa and Pelion on the west and the sea on the east, and extending from the mouth of the Peneius on the north to the Pagasaean Gulf on the south. The Magnetes were members of the Amphictyonic League, and were settled in this district in the Homeric times, and mentioned in the ''Iliad''. The Thessalian Magnetes are said to have founded the Asiatic cities of Magnesia ad Sipylum and Magnesia on the Maeander.Aristot. ''ap. Athen.'' 4.173; Conon 29; The towns of Magnesia were: Aesonis, Aphetae, Boebe, Casthanaea, Cercinium, Coracae, Demetrias, Eurymenae, Glaphyrae, Homole or Homolium, Iolcus, Magnesia, Meliboea, Methone, Mylae, Nelia, Olizon, Pagasae, Rhizus, Spalaethra, and Thaumacia Thaumacia or Thaumakie ( grc, Θαυμακία or Θαυ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesia Ad Sipylum
Magnesia Sipylum ( el, Mαγνησία ἡ πρὸς Σιπύλῳ or ; modern Manisa, Turkey) was a city of Lydia, situated about 65 km northeast of Smyrna (now İzmir) on the river Hermus (now Gediz) at the foot of Mount Sipylus. The city should not be confused with its older neighbor, Magnesia on the Maeander, both founded by colonists from the Greek region of Magnesia. The first famous mention of the city is in 190 BC, when Antiochus the Great was defeated in the battle of Magnesia by the Roman consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus. It became a city of importance under Roman rule and, though nearly destroyed by an earthquake in the reign of Tiberius, was restored by that emperor and flourished through the Roman empire. It was an important regional centre through the Byzantine Empire, and during the 13th-century interregnum of the Empire of Nicea. Magnesia housed the Imperial mint, the Imperial treasury, and served as the functional capital of the empire until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
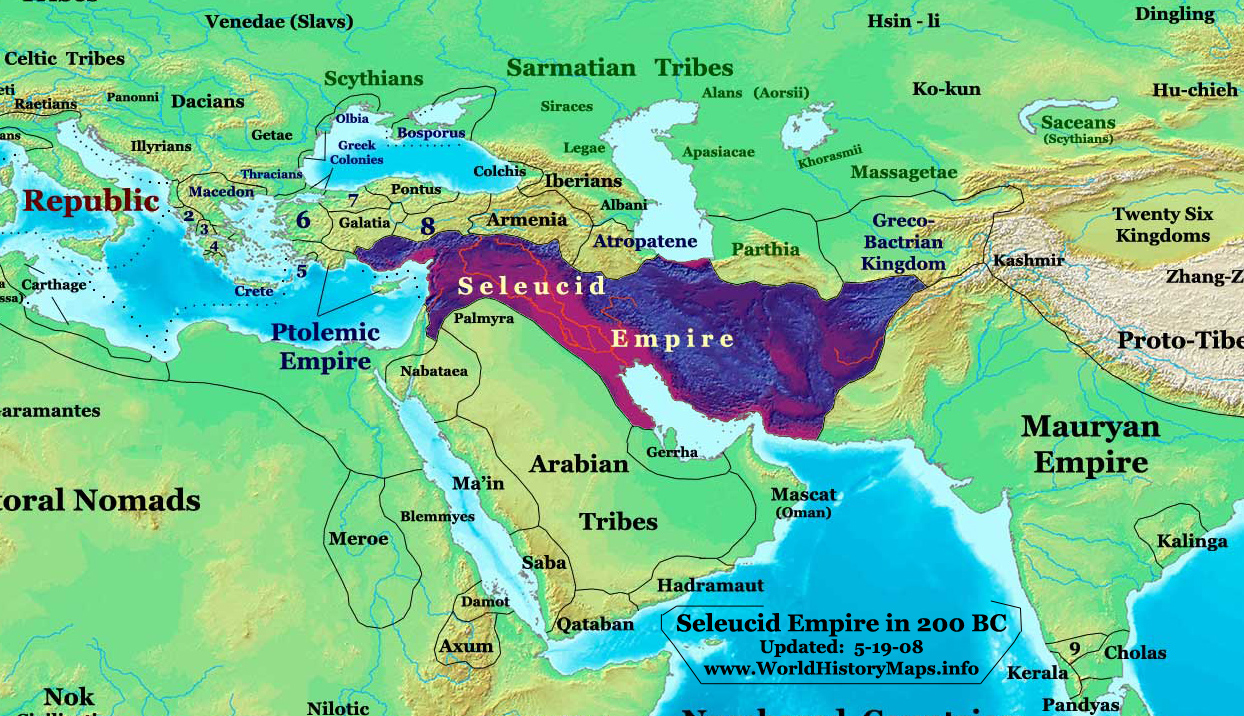
Battle Of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of Pergamon under Eumenes II against a Seleucid army of Antiochus III the Great. The two armies initially camped north-east of Magnesia ad Sipylum in Asia Minor (modern-day Manisa, Turkey), attempting to provoke each other into a battle on favorable terrain for several days. When the battle finally began, Eumenes managed to throw the Seleucid left flank into disarray. While Antiochus' cavalry overpowered his adversaries on the right flank of the battlefield, his army's center collapsed before he could reinforce it. Modern estimates give 10,000 dead for the Seleucids and 5,000 killed for the Romans. The battle resulted in a decisive Roman-Pergamene victory, which led to the Treaty of Apamea that ended Seleucid domination in Asia Minor. Backgrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesia On The Maeander
Magnesia or Magnesia on the Maeander ( grc, Μαγνησία ἡ πρὸς Μαιάνδρῳ or ; la, Magnesia ad Maeandrum) was an ancient Greek city in Ionia, considerable in size, at an important location commercially and strategically in the triangle of Priene, Ephesus and Tralles. The city was named Magnesia, after the Magnetes from Thessaly who settled the area along with some Cretans. It was later called "on the Meander" to distinguish it from the nearby Lydian city Magnesia ad Sipylum. It was earlier the site of Leucophrys mentioned by several ancient writers. The territory around Magnesia was extremely fertile, and produced excellent wine, figs, and cucumbers. It was built on the slope of Mount Thorax, on the banks of the small river Lethacus, a tributary of the Maeander river upstream from Ephesus. It was 15 miles from the city of Miletus. The ruins of the city are located west of the modern village Tekin in the Germencik district of Aydın Province, Turkey. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |